This week, I have a new feature out in MIT Technology Review. It’s an investigation into the usage rates and public opinion of exposure notification apps—those Bluetooth-enabled systems that promised to function as a method of digital contact tracing. You can read the story here; and for the CDD this week, I wanted to provide kind-of an extended methodology behind the piece.
The inspiration for this feature came from my conversation with Jenny Wanger, which was published in the CDD back in March. Wanger is the Director of Programs at Linux Foundation of Public Health, a software development network that has worked on exposure notification systems. We discussed the privacy-first design of this technology, as well as how difficult it has been to evaluate how well the apps are working.
That conversation got me thinking: someone should actually try to collect comprehensive data on how many Americans are using exposure notifications. The federal government doesn’t provide any data on this topic, and most of the states that have exposure notification systems available don’t publicly report data, either. But, I thought, there might be other ways to gather some estimates.
When I talked to Lindsay Muscato, an editor at Technology Review’s Pandemic Technology Project (and a longtime CDD reader!), a few weeks later, she agreed that such an investigation would be valuable. The Pandemic Technology Project has done a lot of reporting on exposure notification apps, but hadn’t yet pursued the kind of novel data collection project I was envisioning.
The project started with a hypothesis: that exposure notification systems are underutilized in the U.S. due to a lack of trust in governments and in new technology.
Initially, I planned to use app reviews from the Google Play and Apple stores as the main data source for the story. The two online stores provide download estimates, which I intended to use as a proxy for app usage rates—along with ratings and reviews that I could use as a proxy for public opinion. (Shout-out to machine learning engineer Venelin Valkov, who has put together a great tutorial on scraping and analyzing app store reviews with Python.)
But an interview early in the reporting process caused me to change my data collection plans. I talked to two exposure notification experts at the New Jersey public health agency, who told me that the app download count I saw on the state’s COVID-19 dashboard was actually a significant underrepresentation of the state residents who had exposure notifications enabled on their smartphones.
This data disconnect was due to something called Exposure Notification Express, or ENX. ENX is an upgrade to the digital contact tracing system, released by Apple and Google last September, that made it easier for states to develop new apps. The upgrade also built exposure notifications directly into the iPhone operating system, allowing millions of people to opt into the notifications without downloading a new app.
In short, I couldn’t use app downloads as a proxy for usage rates. I also couldn’t use Apple app store reviews, because the majority of iPhone users were using ENX rather than downloading a new app. Many state apps are listed on the Google Play store but not on the Apple store, for this reason.
I still used Google Play reviews for the public opinion piece of my story. But to determine usage rates, I developed a new plan: reach out to every state public health agency with an exposure notification system and ask for their opt-in numbers. This involved a lot of calling and emailing, including multiple rounds of follow-up for some states.
The vast majority of state public health agencies to whom I reached out did actually get back to me. (Which I appreciate, considering how busy these agencies are!) The only one that didn’t respond was South Dakota; I assumed this state likely had a low number of residents opted into exposure notifications because South Dakota shares an app with two other low-activation states, North Dakota and Wyoming.
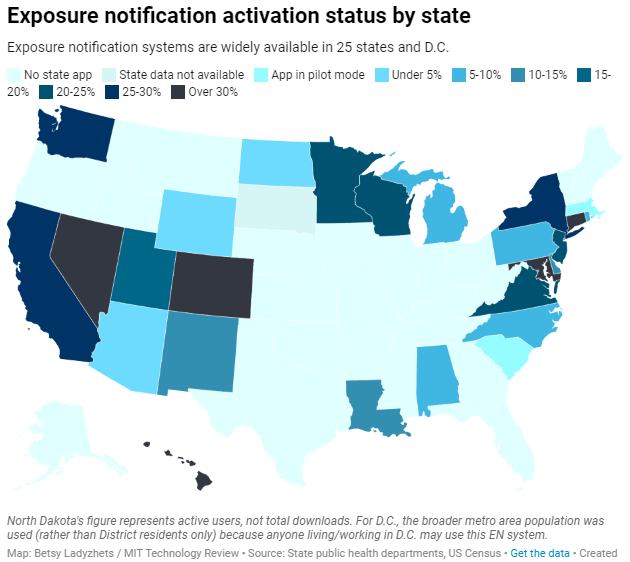
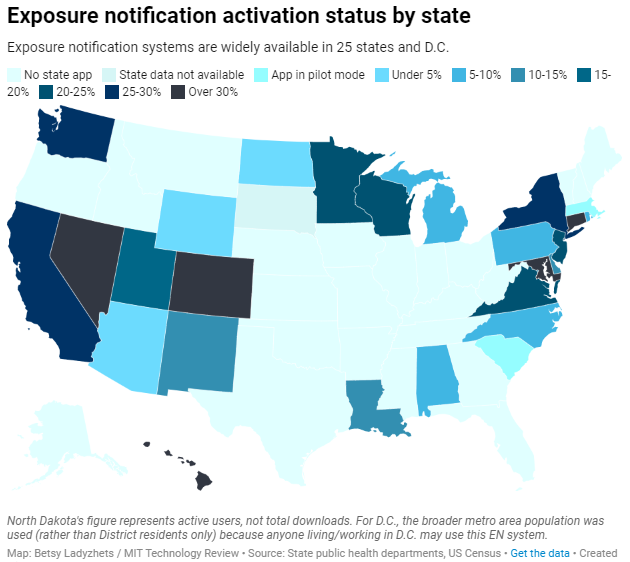
Based on my compilation of state data, 13 states have over 15% of their populations opted into exposure notifications as of early May—passing a benchmark that modeling studies suggest can have an impact on a community’s case numbers.
(I used the U.S. Census 2019 Population Estimates to calculate these opt-in rates. I chose to base these rates on overall population numbers, not numbers of adults or smartphone users, because that 15% benchmark I mentioned refers to the overall population.)
This is a smaller number than the engineers who developed this technology may have hoped for. But it does mean these 13 states—representing about one-third of the U.S. population in total—are seeing some degree of case mitigation thanks to exposure notifications. Not bad, for an all-new technology.
I was also impressed by the five states that reported over 30% of their populations had opted into the notifications: Hawaii, Connecticut, Maryland, Colorado, and Nevada. Hawaii had the highest rate by far at about 46%.
For anyone who would like to build on my work, I’m happy to share the underlying data that I collected from state public health agencies. It’s important to note, however, that the comparisons I’m making here are imperfect. Here’s a paragraph from the story that I’d like to highlight:
Comparing states isn’t perfect, though, because there are no federal standards guiding how states collect or report the data—and some may make very different choices to others. For example, while DC reports an “exposure notification opt-in” number on its Reopening Metrics page, this number is actually higher than its residential population. A representative of DC Health explained that the opt-in number includes tourists and people who work in DC, even if they reside elsewhere. For our purposes, we looked at DC’s activation rate as a share of the surrounding metropolitan area’s population (including parts of nearby Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia).
So, did my research support my hypothesis, that exposure notification systems are underutilized in the U.S. due to a lack of trust? Somewhat. I definitely found that the technology has failed to live up to its potential, and the app reviews that I read indicated that many Americans did not trust the technology—or simply failed to understand its role in COVID-19 prevention.
At the same time, however, I found that some states have seen significant shares of their populations opting into the new technology. Plus, the app reviews showed that a lot of people not only trusted the technology—they bought in enough to advocate for it. The majority of states actually had more five-star ratings than any other category, and a lot of those reviewers tried to combat the mistrust they saw elsewhere in the comment section with explanations and endorsements. This is a job that should’ve been done by public health agencies themselves, of course, but the positive reviews may indicate a promising future for this technology.
In the story’s conclusion, I argue that exposure notification technology is still in its trial run here in the U.S. State public health agencies had limited budgets, limited resources, and limited capacity for trust-building. As a result, they focused simply on getting as many people to opt into the technology as possible—rather than any kind of comprehensive data collection or analysis.
“The ultimate goal [of exposure notifications] is for more folks to know they’ve been exposed,” says Hanna Sherrill, an Eagleton Science and Politics Fellow at Rutgers University who worked with the New Jersey public health agency on its exposure notifications system. “Hopefully some of them will take the advice to quarantine, and then they will stop the spread from there. Even if there’s one or two people who do that, that’s a good thing from our perspective.”
Other state public health staffers who responded to Technology Review’s data requests echoed her sentiment—and their attitudes suggest that digital contact tracing in the US may still be in its trial run. We have 26 different prototypes, tested in 26 different communities, and we’re still trying to understand the results.
“In the US, the existing apps and tools have never hit the level of adoption necessary for them to be useful,” Sabeti says. But such success may not be out of reach for future public health crises.
I’m hopeful that, with more investment into this technology, public health agencies can build on the prototypes and develop community trust—before we see another pandemic.
I plan to keep reporting on this topic (including investigation into Google and Apple’s role in the technology, which a couple of readers have pointed out was lacking in the Technology Review piece). If you have further questions or story ideas, don’t hesitate to reach out.
More on contact tracing
- We need better contact tracing dataThe majority of states do not collect or report detailed information on how their residents became infected with COVID-19. This type of information would come from contact tracing, in which public health workers call up COVID-19 patients to ask about their activities and close contacts. Contact tracing has been notoriously lacking in the U.S. due to limited resources and cultural pushback.