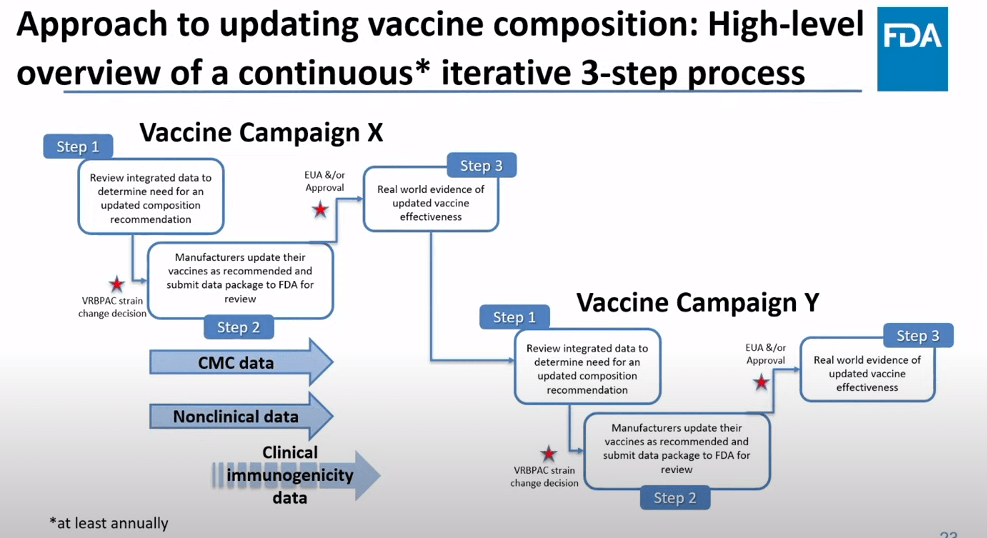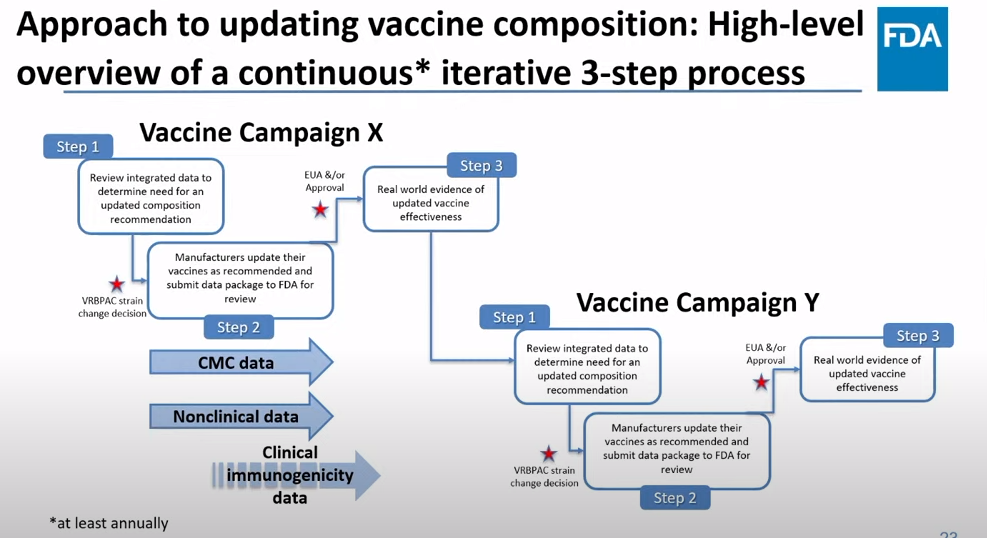
On Thursday, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (or VRBPAC) met to discuss the future of COVID-19 vaccines. While the committee readily agreed that our current, Omicron-specific shots are working well and should be used more broadly, it had a hard time answering other questions about future vaccine regimens—largely due to a lack of good data.
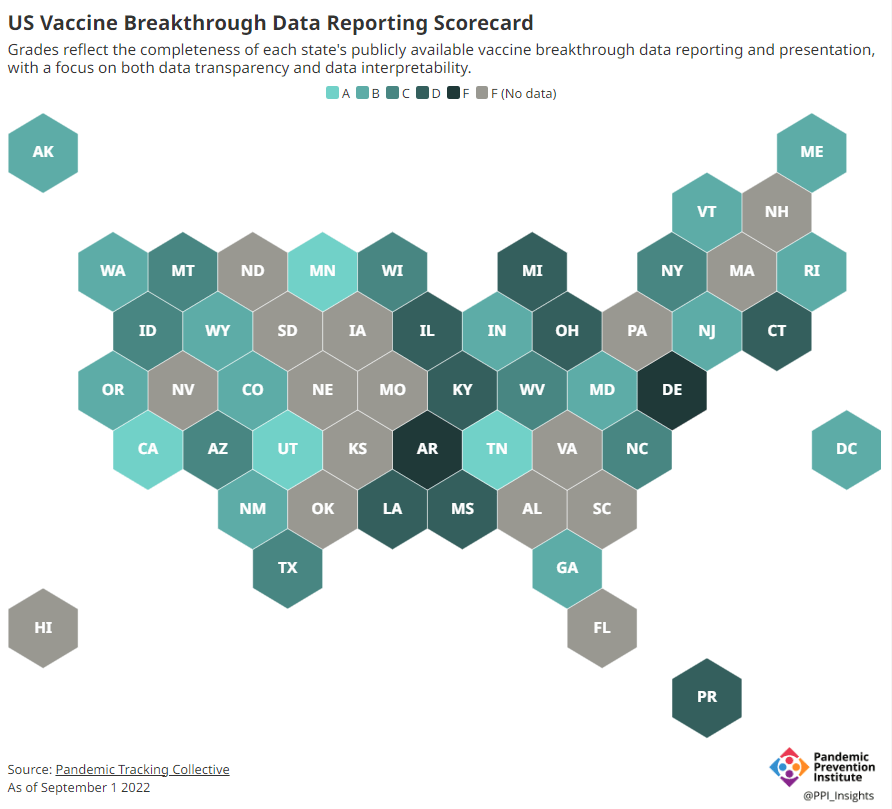
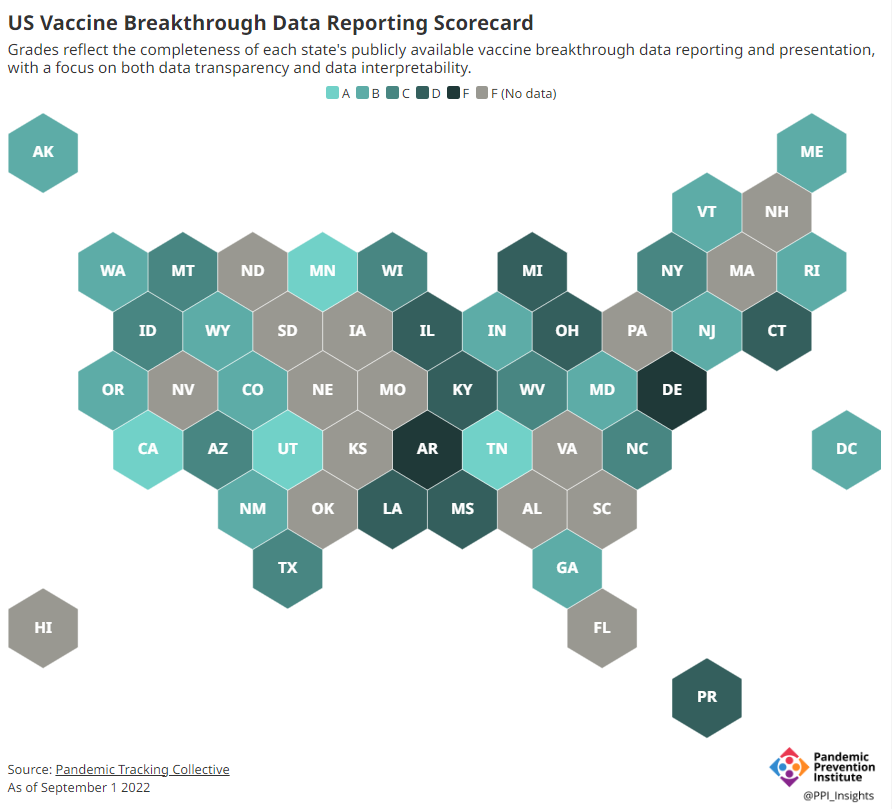
Now, the lack of good U.S. data on vaccine effectiveness is not a new problem. I personally have been writing about this since fall 2021, to the point that I feel like a broken record for bringing it up again. To summarize: the U.S. has a fractured health system in which every state tracks vaccinations differently, with a lot of local public health departments and private companies in the mix, too. As a result, it’s challenging for researchers to determine exactly who is getting COVID-19 after vaccination and how the virus is impacting them.
This lack of detailed vaccine effectiveness data was a problem in fall 2021, when federal officials decided on an initial round of booster shots. And it’s still a problem in winter 2023, as the same officials attempt to plot out a future in which COVID-19 is another disease that we deal with on an annual basis.
But this week’s VRBPAC meeting revealed some other areas of data that are also lacking as we try to answer questions about future vaccines. Here’s my summary of five primary data gaps that came up at the meeting, and some suggestions for potential solutions.
Detailed vaccine effectiveness data
The biggest data gap, of course, is our lack of answers to the question: Who is getting sick with COVID-19 after vaccination? And related questions: How sick did they get? Which variants did they get sick with? What preexisting conditions or comorbidities did they have?
Our lack of standardized medical data in the U.S. makes it tough to answer these questions at the population level. Analyzing variants is particularly tricky, given that variant surveillance in the U.S. tends to be entirely anonymized—with no connections between the genomic sequencing of random PCR tests and the health outcomes (or vaccination statuses) of those patients. And analyzing preexisting conditions can be crucial as officials try to decide which groups of people need extra boosters, but these conditions often are not collected in standard databases or linked to COVID-19 records.
As a result, U.S. officials tend to rely on other countries with more comprehensive, standardized data systems for information on how well the vaccines work. We also have to rely on the pharmaceutical companies producing these vaccines, which often don’t openly share their data—they tend to present clinical trial results in press releases, over peer-reviewed studies. Companies also tend to do trials that align better with their own financial interests, rather than looking at the full scope of vaccine effectiveness.
Even in this week’s VRBPAC meeting, scientists from Moderna presented results from a clinical trial—conducted in the U.K.—that tested the company’s bivalent boosters against the original (non-Omicron) boosters.
Better tracking of variants
The primary reason why our COVID-19 vaccines require updates in the first place is the coronavirus’ continued evolution. Every new lineage of Omicron that rises to prevalence is either a bit better at spreading quickly, a bit better at evading immunity from prior infection or vaccination, or both. To successfully tweak our vaccines in the future, scientists will need to know which variants are out there and how dangerous they are.
Right now, variant tracking largely relies on PCR testing, as researchers randomly select some swab samples to sequence. But with fewer and fewer people getting PCR tests, the sample pool is dwindling. As a result, to stay ahead of new variants, the U.S. needs to diversify its surveillance options. That will likely include more variant sequencing from wastewater (as a population-level COVID-19 sample), more sequencing at hospitals and healthcare centers, and more travel surveillance focused on international variant patterns.
Variant surveillance will also need to inform how suited U.S.-developed COVID-19 vaccines are for the rest of the world. Right now, the pharmaceutical companies that have produced the most effective vaccines (i.e. Pfizer and Moderna) are American—so American regulators are essentially dictating vaccine policy for the world, even though their priority is the U.S. FDA official Jerry Weir said as much at the meeting. U.S. hegemony over COVID-19 vaccines will continue to be a complex, fraught topic going forward.
Tracking different types of immunity
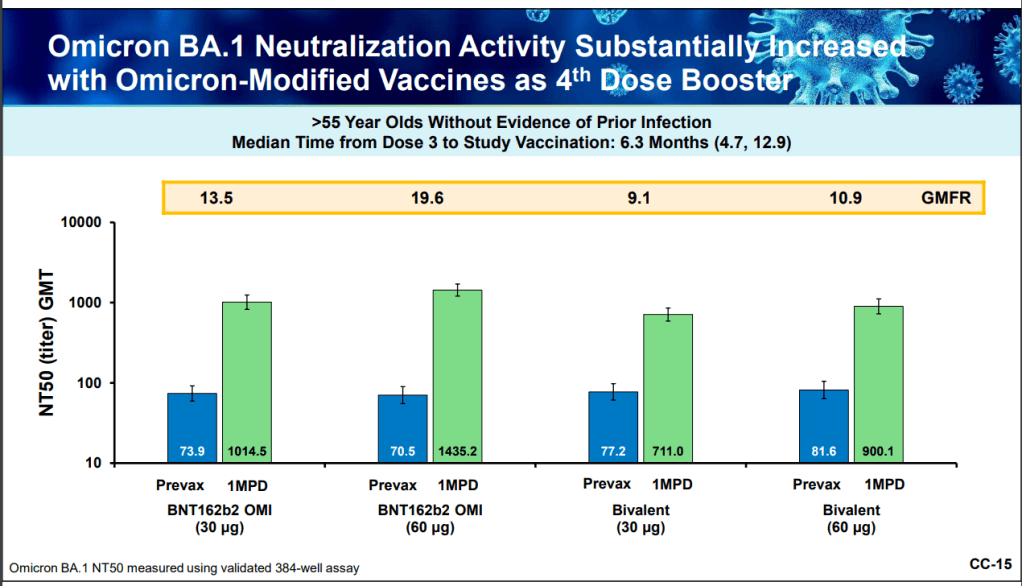
At the VRBPAC meeting, Moderna, Pfizer, and Novavax all presented data on how well their vaccines work against currently-dominant coronavirus variants. While they included some clinical data (case rates, hospitalization rates), the presentations mostly focused on one metric: antibody titers. To calculate if a vaccine works against a certain variant, the easiest strategy is measuring the antibodies produced after a vaccinated blood sample is exposed to that variant.
While this is the easiest strategy, it’s far from the only way to examine how well a vaccine works. Members of the VRBPAC committee frequently asked the pharmaceutical companies for those other metrics: T cells, B cells, and more ways of measuring the immune system’s response to COVID-19. But the companies had little response to these questions. Even FDA and NIH officials at the meeting admitted that they still didn’t have a good understanding of how, exactly, our current vaccines impact our immune systems, beyond generating antibodies.
To better evaluate future vaccines, scientists will need to get better at measuring other aspects of our immune responses. That includes future mRNA vaccines as well as next-generation vaccines in the works right now, such as nasal vaccines (recently authorized in China and India) and vaccines designed to protect against all variants (currently in development at Duke University and other institutions).
I also think it’s worth noting that, as Katelyn Jetelina writes in her coverage of the VRBPAC meeting at Your Local Epidemiologist, the FDA could require pharmaceutical companies to study the immune system more holistically when they submit further vaccine updates for authorization. “The FDA could require sponsors to do detailed investigations, e.g. assessing lymph nodes, bone marrow, and breakthroughs,” she writes. “This would help us understand immunity better, so we can make better recommendations. It’s not clear why they aren’t pushing for this.”
Improving vaccine safety tracking
Two years after the first COVID-19 vaccines were authorized, we now know that the vaccines are overwhelmingly safe and effective. Most people have mild side effects following their shots, like sore arms and fatigue, but the benefits of getting vaccinated far outweigh the risks. However, some discussion at the VRBPAC meeting indicated that federal agencies could do a better job of tracking rare (yet important) serious side effects.
For example, a safety presentation from the Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center suggested that there might be a small increase in stroke risk for older adults who get vaccinated. The risk has only appeared in one vaccine safety database so far and appears to be minimal, per the FDA, but it’s still worth closer examination.
In addition, as Helen Branswell and Matthew Herper discuss in the STAT News liveblog, the VRBPAC meeting didn’t present much new data about vaccine safety risks for children, such as myocarditis among boys and young men. Plus, we have limited data so far on whether vaccination may contribute to autoimmune conditions or Long COVID-like symptoms, a problem that has shown up in some studies and anecdotal reports.
If public health officials are going to continue encouraging Americans to get COVID-19 shots once a year (or more), they will need to thoroughly address concerns about these potential side effects. This is particularly true for young children, a group that’s been vaccinated at fairly low numbers so far.
Navigating COVID-19’s interactions with other vaccines
At the VRBPAC meeting, FDA officials suggested a potential future in which most Americans get one COVID-19 vaccine per year, on a similar timeline to the annual flu shot. Variant strains might be selected in the spring or summer, with vaccines developed and produced in time for a fall vaccination campaign. Some at-risk groups (older adults, people with compromised immune systems, etc.) might get two doses each year.
To make this possible, the VRBPAC committee members suggested that we’ll need to track how COVID-19 vaccines intersect with other vaccines. For example, if an older adult receives their flu shot and COVID-19 shot in the same doctor’s visit, does that dampen how well one or the other vaccine works? Does it increase the risks of severe side effects? We don’t know, at this point.
Another major area of future study will be how COVID-19 vaccines may fit into regular, childhood immunization schedules for young kids. Similarly to the COVID-19 plus flu question, scientists will need to track any potential interactions between COVID-19 shots and other regular shots—along with answering questions about how many shots are needed, timing between shots, and more.
One day, I’m sure, we will have a regular COVID-19 vaccination schedule in the U.S. that runs parallel to our flu vaccination schedule. But it will take time, discussions, and a lot more data to get there.