This past Tuesday, April 6, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention put out a press release that I found heartening, yet confusing.
“Nearly 80 percent of teachers, school staff, and childcare workers receive at least one shot of COVID-19 vaccine,” the release proclaims. These vaccinations include “more than 2 million” people in these professions who received doses through the federal retail pharmacy program and “5-6 million” vaccinated through state programs, all of whom received shots before the end of March.
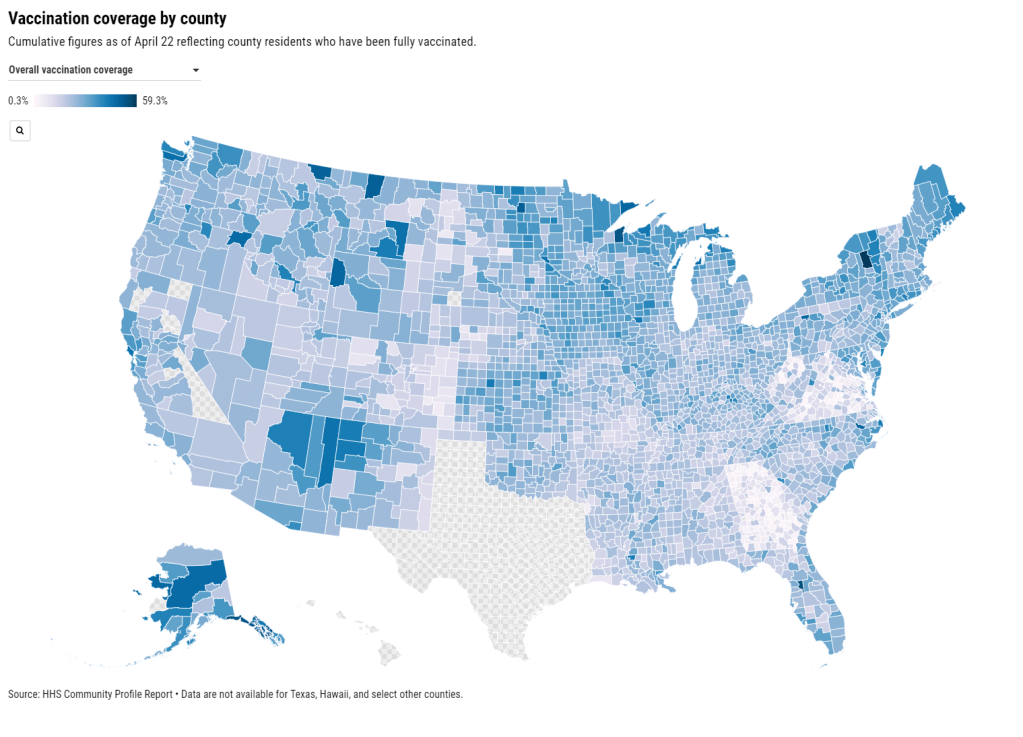
This CDC release is exciting because occupational data—or, figures tying vaccination counts to the jobs of those who got vaccinated—have been few and far between. As I wrote last month, state and local health departments have been unprepared to track this type of data; even getting states to report the race and ethnicity of their vaccinated residents has been a struggle.
While you may need to be a teacher or fit another essential worker category in order to get vaccinated in your state, your provider may require you to show some proof of eligibility without recording that eligibility status anywhere. Meanwhile, school districts and local public health departments might be wary of surveying their local teachers to see who’s been vaccinated. Madeline Will explains the issue in EdWeek:
Yet many vaccination sites do not collect or report occupation data, and many districts are not tracking vaccination rates themselves. Some district leaders say they’re wary of asking employees if they’ve gotten vaccinated because they don’t want to run afoul of any privacy laws, although the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission has said that employers can ask whether employees have gotten a COVID-19 vaccine.
This brings us to the question: how did the CDC get its 80% figure? The agency’s press release is frustratingly unspecific; it’s all of 282 words long, with just one paragraph devoted to what a data journalist like myself would call the methodology, or the explanation of where the data come from.
Here’s that explanation:
CDC, in collaboration with the Administration for Children and Families, the Department of Education, and our non-federal partners, conducted surveys of Pre-K-12 teachers, school staff, and childcare workers at the end of March. CDC received almost 13,000 responses from education staff and nearly 40,000 responses from childcare workers. The responses closely matched available national race/ethnicity and demographic data on this specific workforce.
Let’s unpack this. The CDC worked with two other federal agencies to conduct a survey of this high-priority occupation group, including 13,000 school staff and 40,000 childcare workers. The agency then extrapolated the results of this 53,000-person survey to estimate that 80% of Americans in these occupations have been vaccinated overall. While the CDC doesn’t provide any detail on how workers were chosen for the survey, the press release notes that responses match demographic data for this workforce, indicating that agency researchers did collect race, ethnicity, and other demographic information for those they surveyed.
So, here’s my big question: is the CDC planning to release more detailed results from this survey? And if not… why?
As we’ve noted in past CDD issues, teacher vaccination can go a long way towards inspiring confidence in school reopening programs, in school staff and parents alike. And that confidence is needed right now: February results of the Department of Education’s school COVID-19 survey, released last week, demonstrate that even though the majority of U.S. schools are now offering in-person instruction, only about one-third of students are learning in the classroom full-time. (More on those findings via AP’s Collin Binkley.)
If the CDC released results of this vaccination survey for individual states and demographic groups, local public health and school district leadership may be able to see how their populations compare and respond accordingly. If, say, Texas is vaccinating fewer teachers than New York, Governor Greg Abbott can make a speech telling his state to step it up.
And those states where a higher share of teachers have been vaccinated can use the information to inform school opening plans. The CDC’s press release doesn’t specify what share of that 80% vaccinated represents partially versus fully vaccinated school and childcare workers (which would also be useful data!), but even a workforce that was partially vaccinated at the end of March may be ready for in-person work by the end of April.
All this is to say: show your work, CDC! Give us more detailed data!
It’s also important to note, though, that while teachers are in the spotlight, they aren’t the only occupation for whom vaccination data should be a priority. Many staff in long-term care facilities have been unwilling to get vaccinated even though it would be a highly protective measure for the seniors they care for, Liz Essley Whyte wrote in late March at The Center for Public Integrity.
The federal program that partnered with pharmacy chains to get LTC residents and staff vaccinated is now winding down, Whyte reports, even though some states still have a lot of LTC workers left who need shots. In seven states and D.C., less than a third of staff are vaccinated.
Whyte writes:
Low vaccination rates among staff at these facilities mean that workers continue to have greater risk of contracting COVID-19 themselves or passing the virus to their patients, including residents who can’t be inoculated for medical reasons. Low staff uptake can also complicate nursing homes’ attempt to reopen their doors to visitors like Caldwell, who are striving for some sense of normalcy.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services are hoping to improve data on this issue. This agency proposed a new rule this week that would require nursing homes to tell the CDC how many of their health care workers are vaccinated against COVID-19, POLITICO reported on Friday. This rule would enable the CMS to identify specific facilities that are faring poorly and take appropriate action. And, if such data are made public, it would be easier for both reporters and families of nursing home residents to push for more LTC worker vaccinations.
Still, privacy concerns continue to be a barrier for more detailed vaccination data of all types. Some of the big pharmacy chains that are administering huge shares of shots are requiring vaccine recipients to share their emails or phone numbers when they register for an appointment—then saving that data to use for future marketing. Getting patient contact information is an easy way to ensure people actually show up for their appointments, but when it’s a private company collecting your phone number instead of your public health department, it’s understandable that people might be a bit concerned about giving any information away.
More detailed data standards, along with communication between governments and vaccine providers, could have saved the U.S. from the patchwork of vaccination data we’re now facing. But instead, here we are. Asking the CDC to please send out a longer press release. Maybe with a state-by-state data table included.