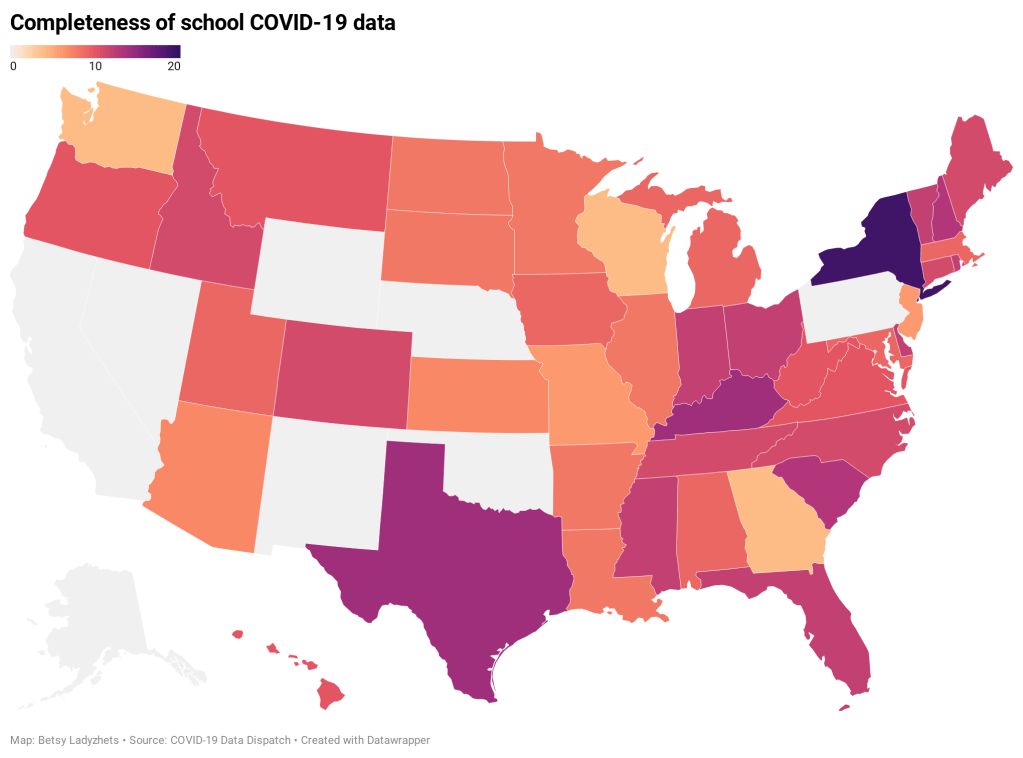
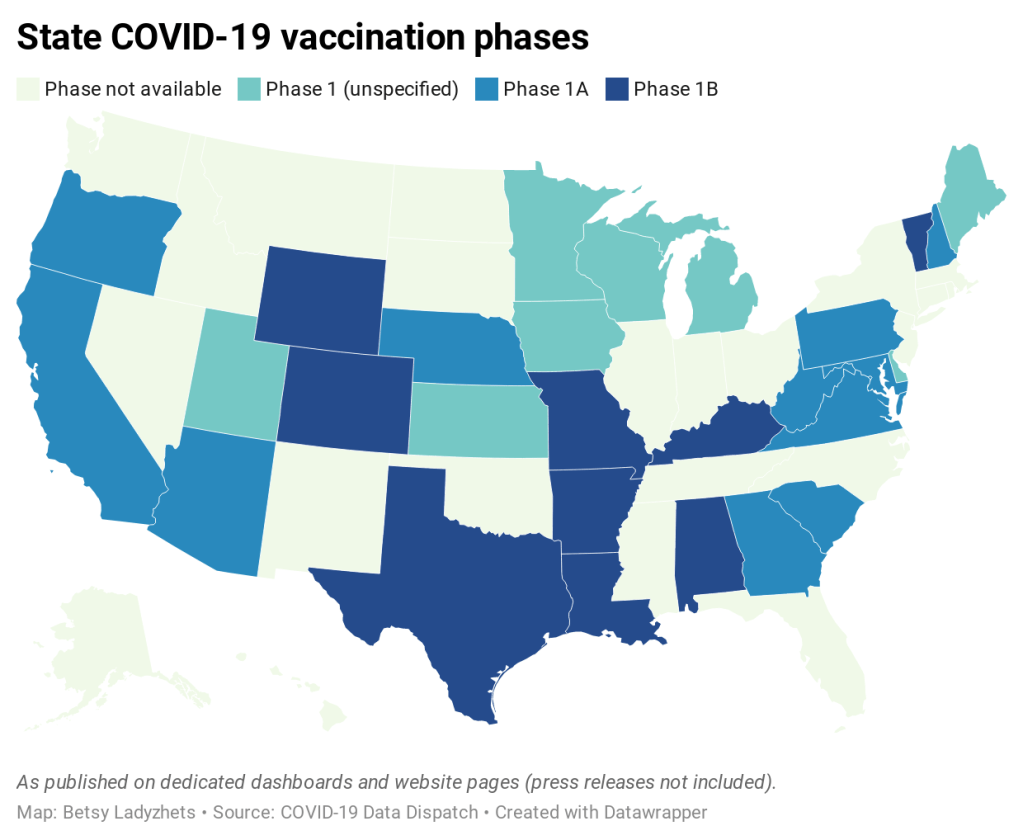
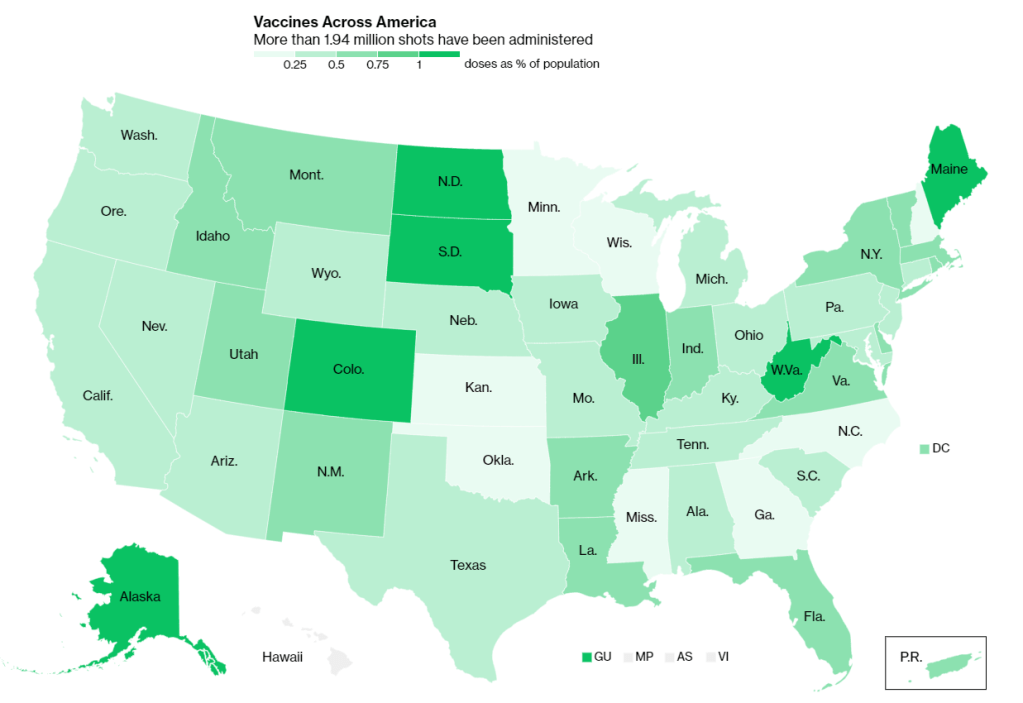
Earlier this week, I got a frantic email from my grandma. She wanted my help in finding a vaccination appointment. She’d talked to her primary care provider and looked at her state public health agency’s website, but wasn’t sure how to actually secure her own spot in line. She lives in California, which is still officially in Phase 1A (vaccinating healthcare workers and long-term care facility residents), but is allowing some providers to start vaccinating seniors and essential workers based on “available supply.”
My uncle did help my grandma get an appointment—one month from now and an hour’s drive away. Despite living in Berkeley, near several research universities, she’ll be heading to Palo Alto for her shots. I told her to keep a close eye on her county public health department’s website in case something becomes available there (which would be my advice to anyone else in this position), but I couldn’t guarantee that she’d be able to find an appointment any closer than the one she has now.
And she’s not alone: a lot of grandmas are having trouble getting vaccination appointments. In fact, recent survey data from the Kaiser Family Foundation suggests that the majority of American seniors “do not have enough information about when and where they will be able to get the vaccine.” Black, Hispanic, and low income adults also report not having enough information about vaccinations, according to KFF. The minority communities that continue to be heavily impacted by the pandemic are supposed to be first in line for vaccines, but barriers to information and technology—particularly to vaccine registration portals—are leaving them behind once again.
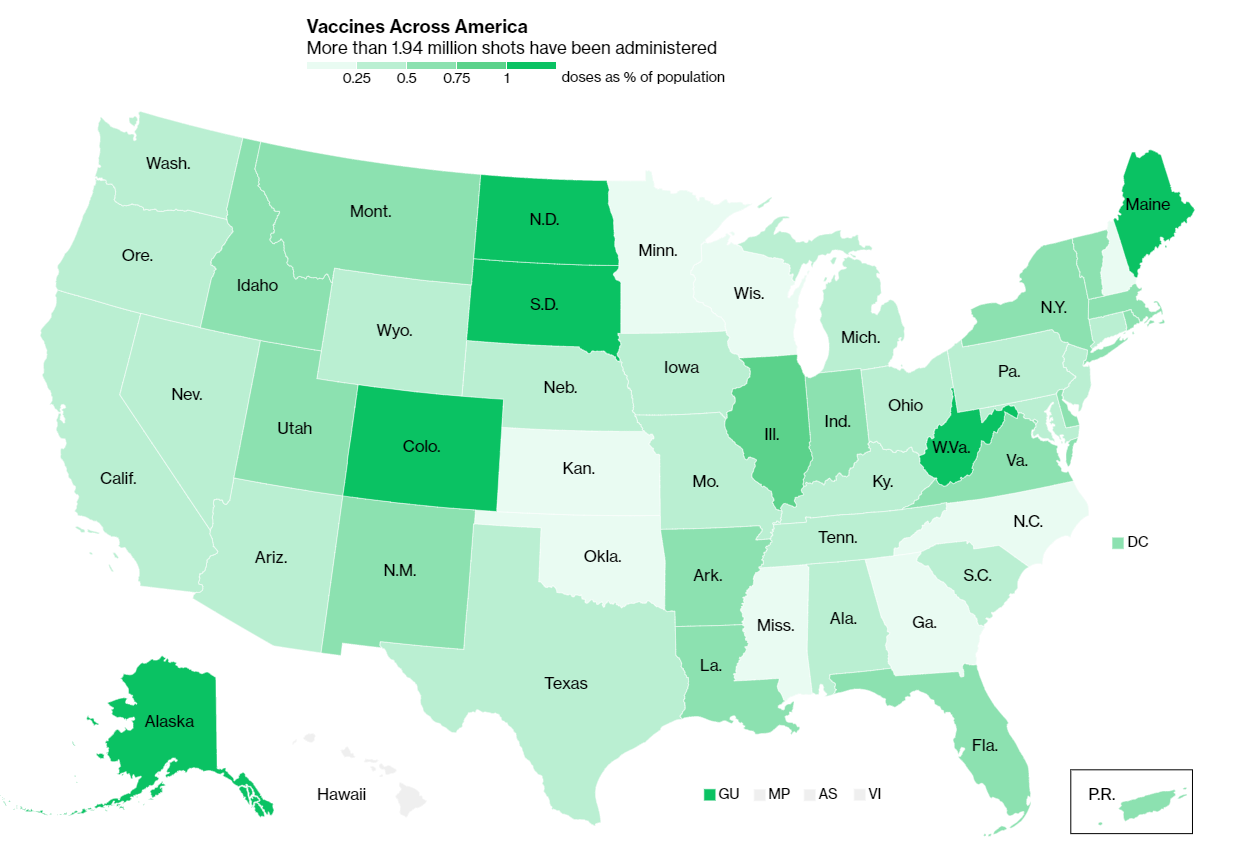
It would be easy to say the problem here is a lack of vaccine doses. But that’s not exactly it. The federal government is distributing millions of doses each week, and many of those doses are making it into arms: according to Bloomberg’s vaccine tracker, an average of 1.1 million shots were reported each day this past week. By sheer numbers, we are already on track to meet President Biden’s 100 million vaccinations in 100 days goal.
Our current problem is, in fact, a logistics one. It’s a build up of infrastructure failures, with all the weight falling on those underfunded local public health departments I mentioned in the previous section. Right now, these public health workers are trying to set up vaccination appointments, while also dealing with constantly-changing information from their state on how many doses they will get, while also stretching out a depleted budget, while also probably short on personnel because half of their staff quit or got COVID-19 in 2020, while also dealing with backlash from their communities, while also fielding endless calls from confused grandmas… and all of this while still testing, contact tracing, and communicating basic pandemic safety measures. Whew. I got tired just writing that sentence.
Some dimensions of this problem, such as the funding and lack of community trust, are years in the making. But there’s one piece the federal government may be able to solve soon, and it’s a data issue. The federal government is not giving states—and by extension, local public health agencies—enough lead time to coordinate their vaccine distribution. ProPublica reporters Caroline Chen, Isaac Arnsdorf and Ryan Gabrielson explained the situation in a detailed feature this week: unpredictable shipments at the national level mean that vaccine providers are unable to use up all of their shots in some weeks and cancelling appointments in others. The whole piece is worth reading, but I want to highlight the one quotation near the end:
Starting Wednesday, it will be up to the Biden administration to provide clear visibility for states, according to a member of the president-elect’s COVID-19 team, who asked not to be identified because he wasn’t authorized to speak on behalf of the new administration.
“The government can point at the manufacturer, but it’s like asking the [Defense Department], ‘How many planes do you have?’ and them saying, ‘I don’t know, ask Boeing,’” the person said.
Reporters at POLITICO similarly found that public health workers simply don’t trust the dose allocation system. While the Biden administration may want to ramp up vaccine production in order to vaccinate more Americans, this goal may be more easily achieved by ensuring vaccines are properly tracked. At every part of the vaccination pipeline, stakeholders should know how many doses they’re getting and when. Shipments should be predictable, and appointments should be easily managed, freeing up public health workers’ time to take on the important task of actually vaccinating people.
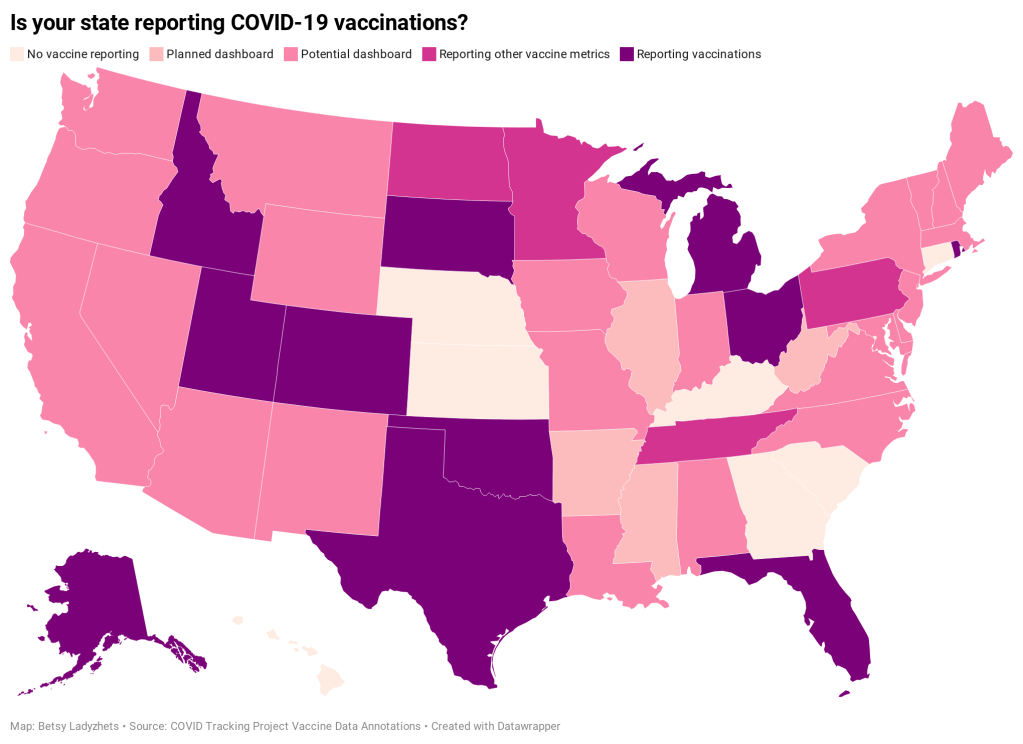
And there are still holes in our data on who’s getting vaccinated, too. Only 23 states are reporting vaccinations by race and ethnicity; this is an improvement from last week, but still a far cry from comprehensive data collection. Another ProPublica investigation, meanwhile, found that many states aren’t requiring providers to report vaccine doses that go wasted, making it difficult to see a comprehensive picture of the shots that get spoiled or thrown in the trash.
It also bears mentioning that Pfizer will now be shipping out fewer vaccine vials to account for the “surprise 6th dose” that providers are often able to get out of each vial—since Pfizer charges by the dose. It is unclear whether this reduction in dose availability will affect the rollout.
One piece of good news, on the vaccination data front: the CDC vaccination tracker stepped up its reporting to include weekend updates, as of yesterday. But the agency still isn’t reporting demographic data, comprehensive data on long-term care facilities, or even a time series of doses administered per day. Vaccination tracking has a long way to go.
Related posts
- Sources and updates, November 12Sources and updates for the week of November 12 include new vaccination data, a rapid test receiving FDA approval, treatment guidelines, and more.
- How is the CDC tracking the latest round of COVID-19 vaccines?Following the end of the federal public health emergency in May, the CDC has lost its authority to collect vaccination data from all state and local health agencies that keep immunization records. As a result, the CDC is no longer providing comprehensive vaccination numbers on its COVID-19 dashboards. But we still have some information about this year’s vaccination campaign, thanks to continued CDC efforts as well as reporting by other health agencies and research organizations.
- Sources and updates, October 8Sources and updates for the week of October 8 include new papers about booster shot uptake, at-home tests, and Long COVID symptoms.
- COVID source shout-out: Novavax’s booster is now availableThis week, the FDA authorized Novavax’s updated COVID-19 vaccine. Here’s why some people are excited to get Novavax’s vaccine this fall, as opposed to Pfizer’s or Moderna’s.