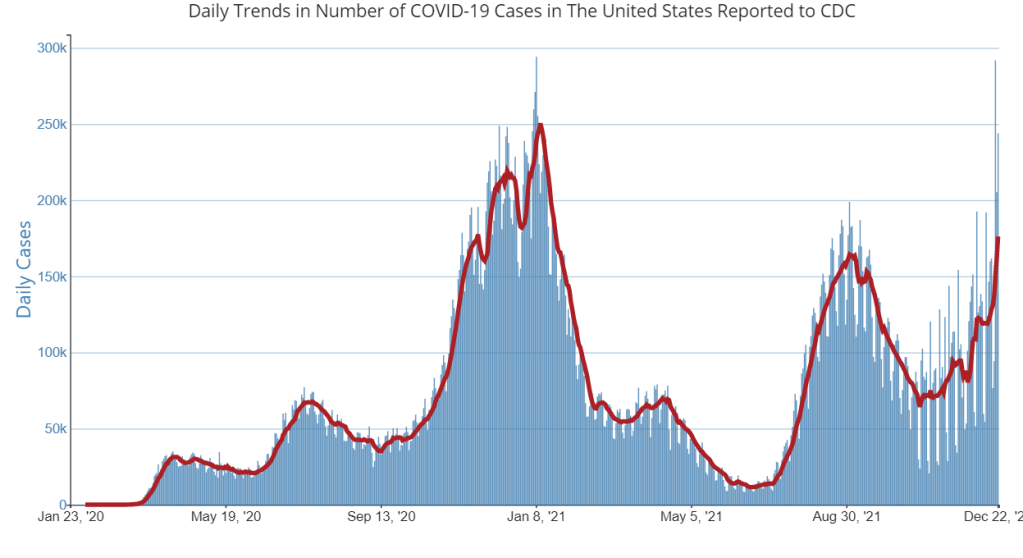
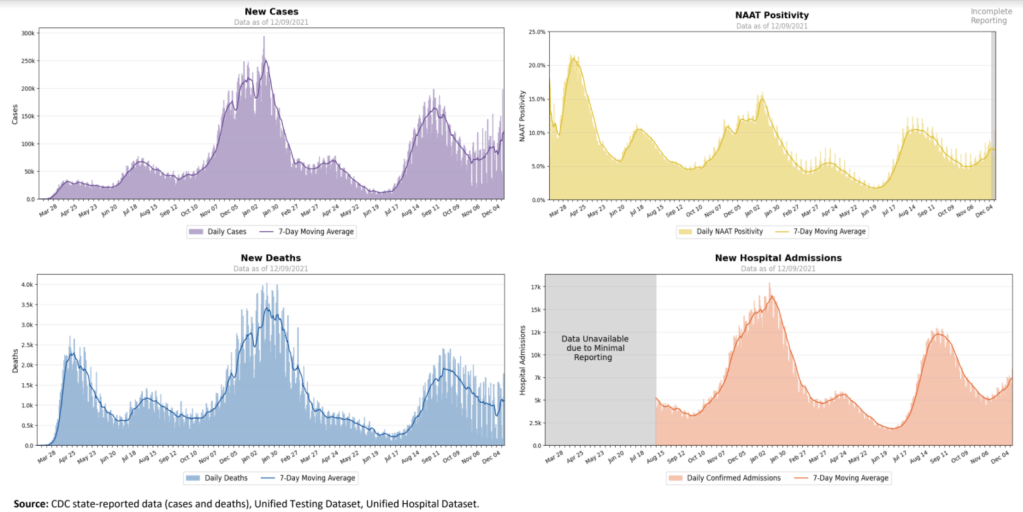
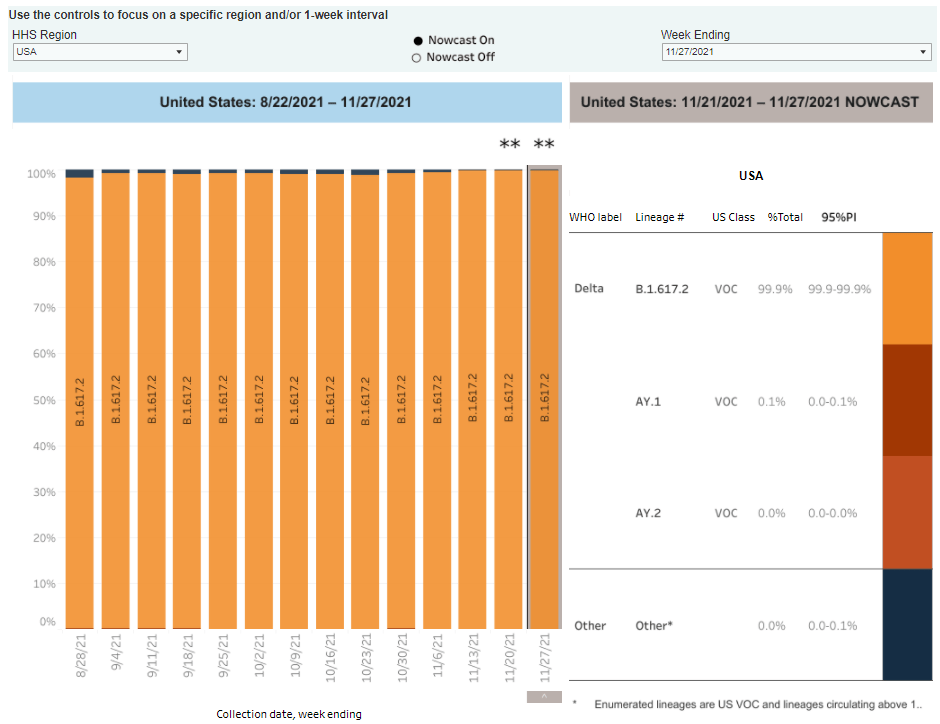
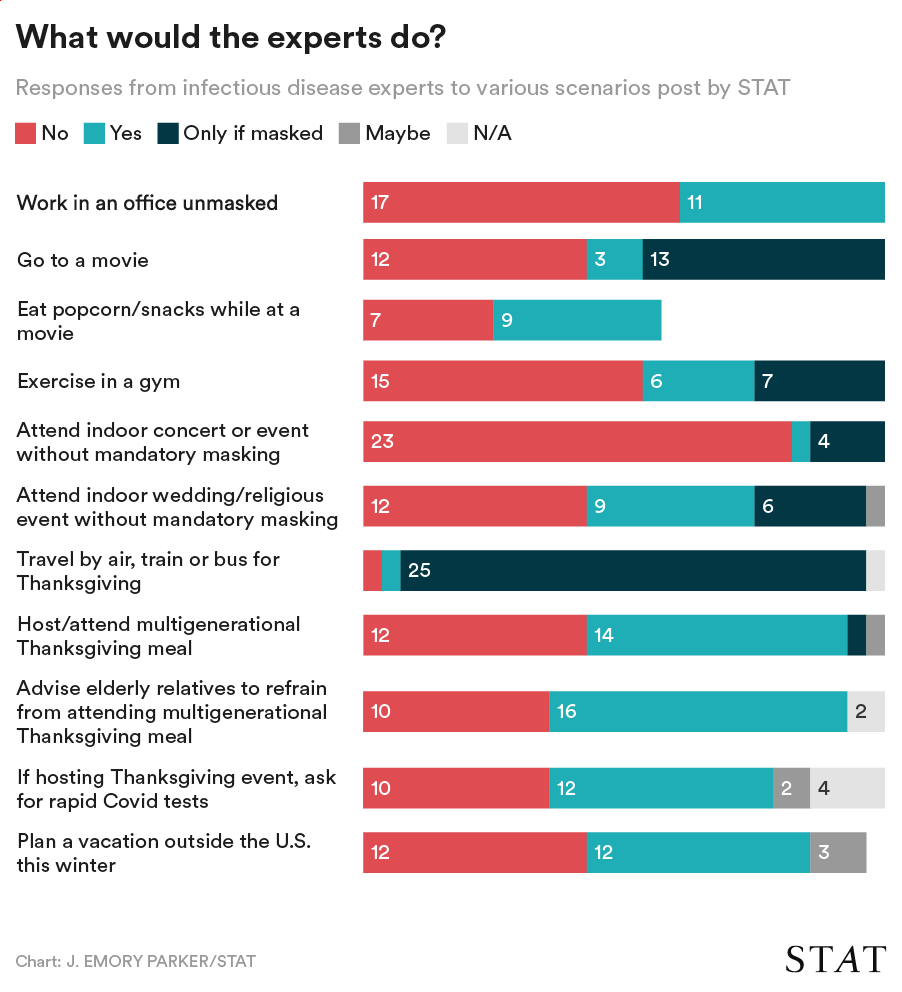
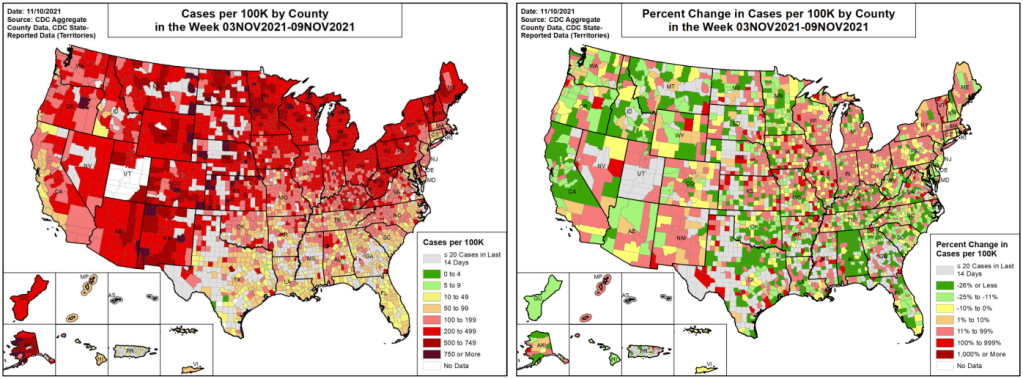
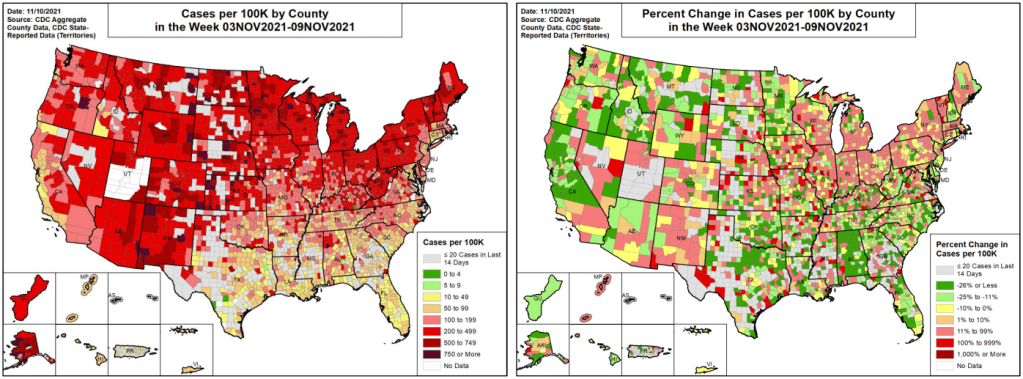
In the past week (January 1 through 7), the U.S. reported about 4.1 million new cases, according to the CDC*. This amounts to:
- An average of 586,000 new cases each day
- 1,251 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- One in 80 Americans testing positive for COVID-19
- 86% more new cases than last week (December 25-31)
Last week, America also saw:
- 115,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals (35 for every 100,000 people)
- 8,700 new COVID-19 deaths (2.7 for every 100,000 people)
- 95% of new cases are Omicron-caused (as of January 1)
- An average of one million vaccinations per day (including booster shots; per Bloomberg)
*Here at the COVID-19 Data Dispatch, we’re back to our regular schedule of national updates based on Friday data, as the CDC has resumed weekly reports following its holiday hiatus.
Omicron continues to drive record cases across the U.S., as we move from tense holiday gatherings to extremely fractured schools and workplaces. This week, the CDC reported 4.1 million new cases—almost double last week’s number, and about 2.5 times the case peak reported during last winter’s surge.
Put another way: 4.1 million cases amounts to about one in eighty Americans testing positive for COVID-19 in the past week. And that number doesn’t include the vast majority of rapid, at-home tests that continue to be in high demand across the country.
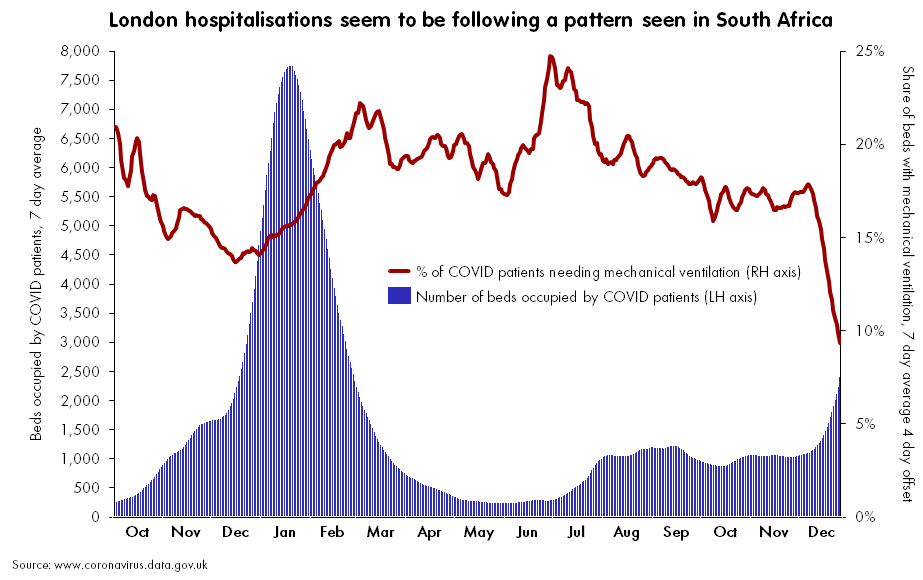
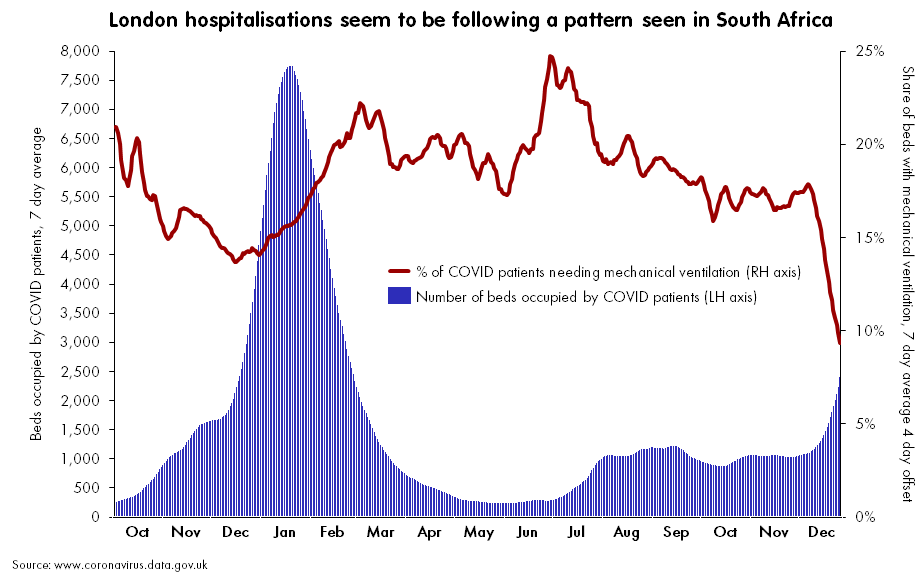
At the same time, hospitalizations are increasing rapidly, with over 100,000 current COVID-19 patients now reported by the CDC. We appear to be on track to pass last year’s peak, 124,000 COVID-19 patients in beds nationwide.
I’ve seen a lot of discussion in recent days about hospitalizations “with” COVID-19 versus hospitalizations “for” COVID-19. As Omicron is less severe and more transmissible than other variants, the argument goes, aren’t a lot of those 100,000 COVID-19 patients people who have mild or asymptomatic cases, but tested positive for COVID-19 upon going to the hospital for a different condition?
While it’s true that some COVID-19 patients in hospitals are “incidental,” meaning their cases were caught during routine hospital screening, these cases can still have a major impact on the hospital system. Healthcare workers need to separate these patients from non-COVID patients, take extra care with their PPE, and utilize other resources. Plus, a lot of patients that, at first, appear to “incidentally” have COVID-19 may see the disease worsen their chronic conditions, such as diabetes or COPD.
To better understand the strain on hospitals right now, I recommend reading Ed Yong’s latest feature in The Atlantic—which gets into the “with” versus “for” issue, hospital staffing challenges, and other problems.
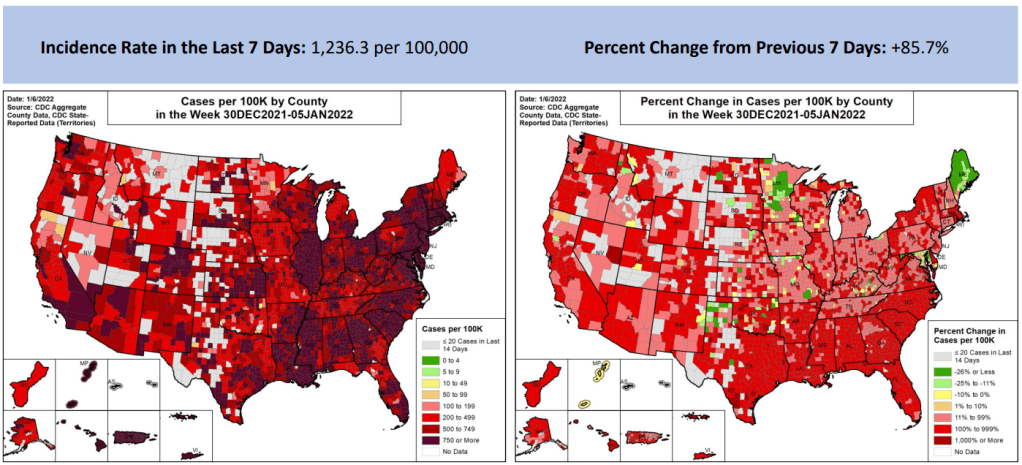
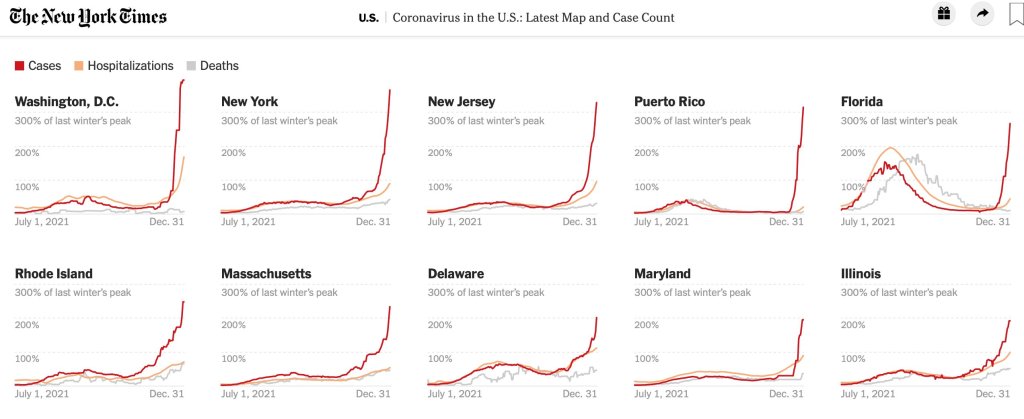
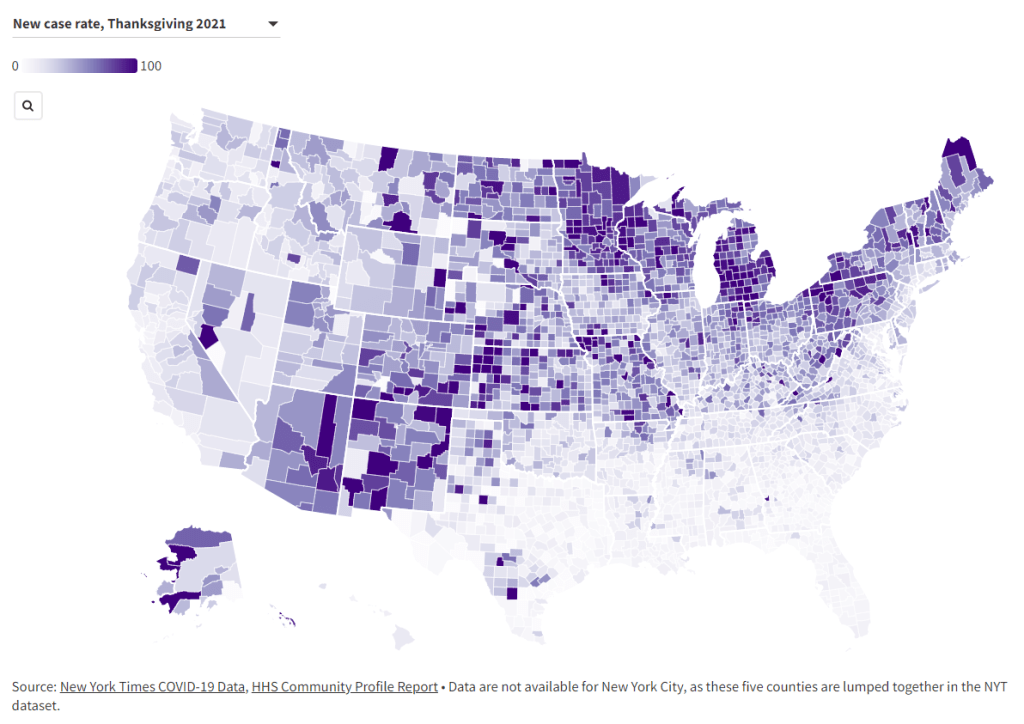
When it comes to hotspots: the Northeast continues to see the highest case rates. New Jersey and New York are leading the pack, both with over 2,400 new cases for every 100,000 residents reported in the last week according to the latest Community Profile Report. (Reminder: the CDC threshold for “high transmission” is 100 new cases per 100,000, so New York and New Jersey are at 24 times the rate of this benchmark.)
Rhode Island, Puerto Rico, D.C., Delaware, Massachusetts, and Florida also have incredibly high case rates, over 1,800 per 100,000 in the last week. Meanwhile, cases are rising rapidly in a number of other Southern and Western states: Texas, the Carolinas, Utah, Arkansas, California, Oregon, and Mississippi have all reported more than 150% case increases in the past week.
If you are able to work from home and avoid public spaces as much as possible, now is the time to do so. January is going to be rough.