- New respiratory virus dashboard for Europe: Residents of about 50 European countries can now follow respiratory virus trends for their nations on a new dashboard developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The dashboard compiles data from patient visits to healthcare facilities, laboratory testing, and genetic sequencing of coronavirus variants, according to a press release by the ECDC. Viewers can find summary trends for influenza-like illness as well as specific trends for COVID-19, flu, and RSV. This dashboard is a great step forward for standardizing surveillance data across countries.
- Medicaid unwinding update from KFF: This week, the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) published an update to its Medicaid Enrollment and Unwinding Tracker, which follows the Americans who lost their health insurance following the end of a Medicaid rule tied to the federal public health emergency for COVID-19. At least 10 million people have lost Medicaid coverage as of November 1, KFF reports, though the researchers acknowledge that this number is likely an undercount due to limited data. While disenrollment rates vary by state, overall, 71% of people who lost Medicaid coverage did so for “procedural reasons,” i.e. paperwork issues, according to KFF’s analysis.
- New Long COVID prevalence estimates: In a new paper, published this week in PLOS ONE, researchers at Dartmouth and University College London estimate Long COVID prevalence in the U.S. based on six months of data from the U.S. Census and CDC’s Household Pulse Survey. (Longtime readers may remember that this survey is one of my personal favorite sources for Long COVID data.) About 14% of respondents surveyed between June and December 2022 reported that they had experienced Long COVID at some point, half of them during the time they were surveyed, the researchers found. Americans with less education and lower incomes were more likely to report Long COVID symptoms, and the condition was correlated with physical and mental difficulties such as trouble dressing and bathing.
- Vaccine confidence falling in the U.S.: A new study from the Annenberg Public Policy Center at the University of Pennsylvania finds that vaccine confidence is declining for a variety of diseases, not just COVID-19. The researchers compared results from similar surveys conducted in October 2023 and in April 2021, both of which included about 1,600 people selected for a nationally representative sample. Confidence rates in COVID-19 vaccines dropped from 75% to 63%, while confidence rates that all vaccines approved in the U.S. are generally safe fell from 77% to 71%. At the same time, the researchers found that more survey respondents believed incorrect statements, such as that ivermectin was an effective treatment for COVID-19.
- Reasons for masking in Japan: One more study that caught my attention this week, on a more positive note: a researcher at Osaka University examined Japanese use of masks for COVID-19. Among participants in the researcher’s online surveys, the majority reported still wearing masks in June 2023, even though COVID-19 guidelines in Japan became less strict earlier this year. Social norms in Japan contribute to this behavior, the survey found, as respondents reported that they continued to mask both to avoid infection and to appear “normal” in public spaces. The study provides data behind well-known social norms in Japan, while offering some hope to those of us “lone maskers” in places where the norms are quite different.
Tag: masks
-
Sources and updates, November 5
-
COVID source shout-out: Advocating for masks in healthcare
A reader recently sent me this petition to the Illinois state legislature, which asks lawmakers to request that the state health department reconsider its position on masks in healthcare settings. This petition is one of many advocacy efforts that have pushed for healthcare organizations to continue prioritizing COVID-19 safety.
In Illinois: the state health department ended its mask requirement in healthcare settings on May 11, timed with the end of the public health emergency. This petition, authored by patients, doctors, and researchers in Illinois, requests that legislators tell the health department that this choice was a mistake. Illinois residents can sign onto it here.
For readers outside Illinois who’d like to get involved with these efforts, Mandate Masks US, the COVID Advocacy Initiative, and COVID Safe Campus have compiled a toolkit to advocate for masks in healthcare with political and healthcare organizations. The People’s CDC offers some resources in this area as well. While the advocacy groups’ Week of Action on this issue may have passed (it took place in mid-May), there are still many ways to help push for safer healthcare settings.
-
Clean air has value beyond COVID-19, the wildfire smoke shows us
I left some free masks outside my apartment for my neighbors this week. That orange tint on the photo is from the poor air quality in NYC. This week, much of the eastern U.S. was inundated with wildfire smoke that traveled south from Canada. While fires have been blazing across the country for several weeks, some recent particularly-intense wildfires in Quebec led to smoke so full of pollutants, it set poor air quality records in the U.S.
Americans living in California and other Western states have grown accustomed to wildfire smoke over the last few years; you might remember the orange skies over West Coast cities in fall 2020. But for people on the East Coast (myself included), this week’s smoke was a rude reminder that climate disasters have no borders or boundaries.
The smoke also reminded us how important clean air is for our health. The same public health measures that help reduce COVID-19 risk can also reduce the impacts of wildfire smoke. High-quality masks filter out both the pollution in smoke and coronavirus particles at the individual level; ventilation improvements do this at the collective level. And these health measures help with other respiratory viruses, other types of pollution, chronic conditions like asthma… the list goes on.
For COVID-cautious folks like me who still wear masks in public spaces, the smoke situation this week demonstrated that yes, many people are willing to put a mask on if they understand why it’s needed—and if the masks are widely available. In New York City this week, I saw more people wearing masks than I have since the height of the Omicron wave in winter 2021-2022. Public officials encouraged masking and even gave out masks in large numbers.
In addition to broader mask use, more people have become interested in cleaning the air in their homes and in public spaces. Air filter sales spiked on Amazon this week, CNN reported, as did Google searches for these items. My Twitter feed has been full of recommendations for air-cleaning devices and instructions for building DIY filters.
This is all great to see, but I hope it’s not just a one-week trend. If we invest in cleaner air now—both individually and collectively—we’ll be more prepared for the next round of wildfire smoke. (While the worst has likely passed for now, we’re likely to see more events like this in the future.) And we’ll be more protected against COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases.
With that in mind, here are some suggestions that apply to both COVID-19 and air pollution:
- Stock up on high-quality masks, i.e. N95s and KN95s. This STAT article has some helpful information about which masks work well for COVID-19 protection as compared to air pollution. Notably, for COVID-19 protection, it’s more important to mask inside, while for air pollution protection, it’s more important to mask outside.
- Buy or make air filters for your home. Air filters can dramatically improve air quality in an indoor space, and you don’t have to spend hundreds of dollars to get one. Corsi-Rosenthal boxes can be easily constructed with less than $100 of materials.
- Monitor your local air quality. This can include buying a monitor to measure CO2 or pollutants, or following air quality data through public sources. I’ve personally started checking AirNow.gov, a site run by the U.S. government, and IQAir, a crowdsourced air quality tracking site. Checking local air quality data can inform your behavioral choices, similar to checking local COVID-19 statistics.
- Get involved with mask distribution. This week has shown many people are willing to put on a mask, if they understand why it’s needed and can access one. You can help share information and resources, whether that’s getting involved with a mask distribution group in your area or simply donating individually to friends and neighbors. (For example, I left some free masks outside my apartment building this week.)
- Advocate for clean air in public spaces. Public buildings can do a lot to improve their air, such as updating HVAC systems and adding air filters to high-traffic spaces. There are already many groups advocating for this, such as parents organizing for ventilation upgrades at their kids’ schools; I hope the recent wildfire smoke adds new motivation to those efforts.
Do you have other suggestions or resources that you’d like to share with other COVID-19 Data Dispatch readers? Email me, and I’ll send your suggestions in a future newsletter issue.
More about air quality
-
Sources and updates, May 21
- New funding from CDC’s forecasting center: The CDC’s Center for Forecasting and Analytics (CFA) announced a new funding opportunity for state and local health agencies to develop new disease modeling tools. CFA is a relatively new center itself; it launched last year with the goal of modernizing the U.S.’s disease forecasting capacities (see my FiveThirtyEight article about the center for more details). This funding opportunity will, I expect, enable the CFA’s growing staff to work directly with health agencies on advancing analytical methods. I look forward to seeing the results of those projects.
- Experts argue to keep masks in healthcare: A new commentary article, published this week in the Annals of Internal Medicine, argues in favor of keeping mask requirements in healthcare settings. The experts (from the National Institutes of Health and George Washington University) point to real-world experience, suggesting transmission between patients and healthcare workers is less likely when everyone is wearing a mask, preferably one of high quality. This article coincides with an advocacy campaign to keep masks in healthcare, including virtual and in-person actions across the U.S.
- CDC releases provisional drug overdose data for 2022: The CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics has released overdose data for 2022, reporting that nearly 110,000 Americans died of overdoses for the second year in a row. Overdoses have leveled off from 2021, but the 2022 data still represent a sharp increase from pre-pandemic trends. Some states in the South and West Coast (such as Texas, Oklahoma, Wyoming, Washington) saw the sharpest increases from 2021 to 2022, according to the CDC. These data are all preliminary and will be updated later in the year.
- Pediatric COVID-19 boosters could save school days: A new modeling study, published this week in JAMA Network Open, suggests that the U.S. could have seen about 10,000 fewer kids hospitalized with COVID-19 and 5.5 million fewer school days lost during the 2022-2023 respiratory virus season, if kids received booster shots in large numbers. The researchers arrived at these estimates through a model that simulated COVID-19 booster vaccination rates at similar levels to annual flu vaccination in kids. Future booster campaigns should focus on children in addition to older adults, the authors argue.
- RSV vaccine for infants moves ahead: Speaking of pediatric vaccinations: the FDA’s vaccine advisory committee met last week to discuss a new vaccine candidate from Pfizer, which would protect infants from RSV. Unlike most pediatric vaccines, this shot would be delivered to pregnant parents in order to protect their babies at birth. While the FDA’s advisors endorsed the vaccine for its effectiveness, some committee members expressed concerns over safety. Helen Branswell at STAT has more details.
-
COVID source shout-out: Mandate Masks NY
Political leaders in New York State recently ended a policy requiring masks in healthcare settings. This is obviously a big issue for high-risk New Yorkers, many of whom have spoken out on social media about wanting to attend important doctors’ appointments without risking COVID-19.
In response to the change, local advocacy organization Mandate Masks NY has compiled a list of hospitals and healthcare centers in New York that are still maintaining mask requirements independently of the state policy. You can find the list here; and the organization has compiled several other lists of businesses requiring masks, available on their website.
As a former COVID Tracking Project volunteer, I’m always glad to see volunteer efforts producing important databases that wouldn’t otherwise be available. Also: it looks like the Mandate Masks NY Twitter account was suspended this weekend—if you know anything about that, please reach out!
-
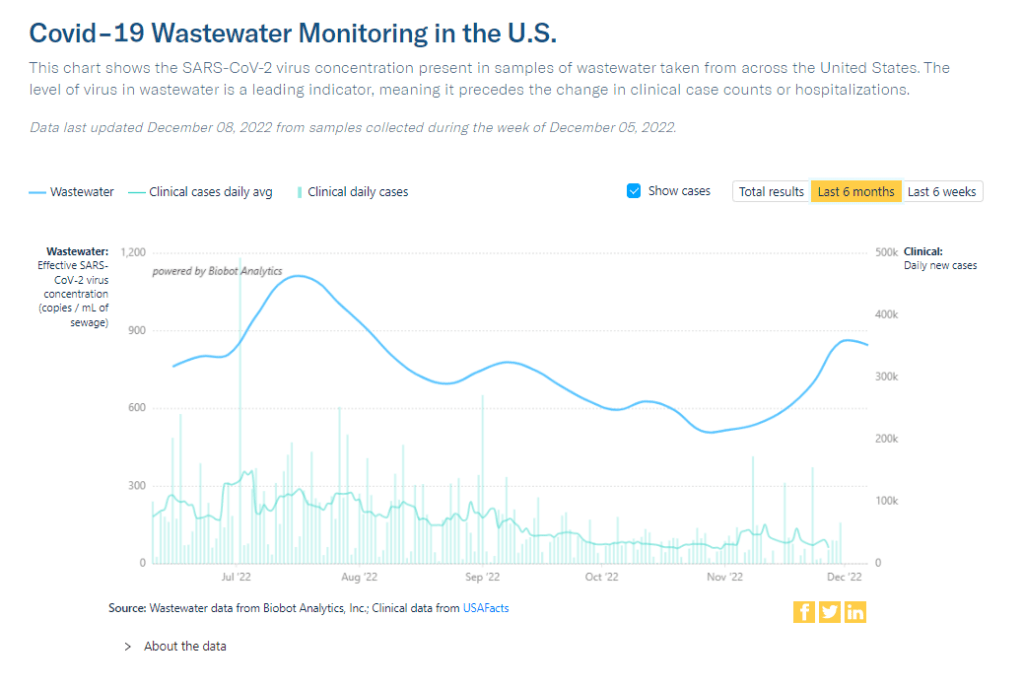
Answering reader questions about data interpretation, good masking

As this chart from Biobot shows, trends in wastewater and case data often look a bit different. But how do you compare wastewater numbers to true infection numbers? This week, I’m sharing answers to three questions from readers that came in recently, through emails and the COVID-19 Data Dispatch Google form. The questions discuss interpreting wastewater and case data, and an interesting masking conundrum.
Q1: Comparing wastewater trends to case trends
I would love to know if there is any data on what levels of COVID in wastewater equals what risk level—are there any guidelines that could be used to turn masking policies on or off, for example? We know going up is bad and that the data is noisy but, if there’s any information on what concentrations in sewage corresponds to what level of cases I would love to know.
I would love to be able to point you to specific guidelines about matching wastewater levels to cases, but unfortunately this isn’t really available right now. And if it were available, you would likely need to tailor the analysis pretty closely to where you live.
An ongoing challenge with using wastewater surveillance data, as I wrote about for FiveThirtyEight and MuckRock in the spring, is that this type of environmental information is categorically pretty different from traditional case data. When a public health agency provides case numbers, they are adding up results from tests done in hospitals, doctors’ offices, and other healthcare settings. Each test result generally represents one person and can be interpreted with that framework.
But with wastewater data, figuring out exactly what your test results represent can be more complicated. The data generally include people sick with COVID-19 who shed the coronavirus in their waste, but different people might shed different amounts of virus depending on what stage of illness they’re at, the severity of their symptoms, and possibly other factors that scientists are still working to figure out. Environmental factors like a big rainstorm or runoff from nearby agriculture could also interfere with the data. Population shifts, like college students returning to their campus after a break, can cause noise, too.
As a result, public health experts who interpret wastewater data generally need a lot of data—like, a year or more of testing’s worth of data—from a specific location in order to analyze how wastewater trends correlate with case trends. And the data has to be consistent; if your wastewater collection team switches their sample processing methods halfway through the year, that might interrupt the analysis.
A few institutions have figured out the wastewater-to-cases correlation for their communities. For examples, see the section on San Diego in this story and this paper by researchers in Gainesville, Florida. But for most research groups and health departments, it’s still a work in progress.
All of that said, I don’t think this complexity should stop individuals or organizations from using wastewater data to recommend turning mask policies (or other policies) on or off. This surveillance might be less precise, but a sustained increase in coronavirus concentrations in the sewer is still certainly cause for concern and can be used to inform public health guidance.
Q2: Estimating case underreporting
How do you estimate how undercounted COVID testing is? Asking because I work for Whentotest.org—our COVID Risk Quiz assumes that COVID testing is undercounted by 7x, but I believe I’ve seen you estimate that it could be undercounted by as much as 20x. Wondering how you get to that number—we want to keep our Quiz as up to date as possible, and that number is a moving target.
It is definitely a moving target, since COVID-19 testing (especially the lab-based PCR testing that generally contributes to official case numbers) can go up or down depending on people’s access to tests, perceptions of how much transmission is going on, and so many other factors.
That said, I would personally put undercounting in the 10 times to 20 times range for this fall, likely with different levels of undercounting for different locations. I have two sources for the 20 times number: the first is an estimate from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation made in September, suggesting that 4% to 5% of infections in the U.S. were reported at that time. (If 5% of infections are reported, case counts are 20 times higher than reported cases.)
My second source is a paper from epidemiologist Denis Nash and his team at the City University of New York, released as a preprint earlier this fall. The researchers surveyed a representative sample of 3,000 U.S. adults, finding that about 17% of the respondents had Omicron during a two-week period in the summer BA.5 surge. Extrapolating from the survey findings, the researchers estimated that about 44 million people across the country had COVID-19 in this timeframe—compared to 1.8 million reported cases. This estimate suggests reported cases were undercounted by a factor of 24.
Unfortunately, I have to use months-old estimates here because the U.S. does not have a regular data source comparing cases to true infections. The Census and CDC’s Household Pulse Survey comes close to this, as it includes questions about whether survey respondents have recently received a COVID-19 diagnosis; but it doesn’t ask about rapid tests, recent exposure, or other factors needed to determine the true infection rate, so the numbers here are also underestimates.
Personally, I keep a close eye out for survey studies like those done by Nash and his team at CUNY and use those results to inform how I interpret national case data. I’ll make sure to flag any future studies like this for readers.
Q3: Nose-only masking
I follow some masking subs on Reddit and folks periodically suggest to others or refer to hacking masks that only cover their nose (KN95, N95s, etc.) for dental appointments or unavoidable indoor eating scenarios. Assuming they’re successful in creating a proper seal for these “half masks,” would there actually be any scientific backing this is helpful in minimizing risk?
I wasn’t sure how to answer this question, so I shared it on Twitter, tagging a couple of masking and ventilation experts I know.
Overall, the consensus that emerged from my replies is that it could be helpful to wear a mask over one’s nose for short periods of time, but it’s hard to say for sure due to a lack of rigorous research in this area. Behavior also plays a big role in how effective such a mask might be in alleviating risk.
One expert, Devabhaktuni Srikrishna, pointed out that having a sealed filter over one’s nose could reduce the amount of virus that gets inhaled, if the coronavirus is present in the space. (This “inhalation dose” might correlate with one’s chances of infection and/or severity of symptoms if infected, though research is still ongoing on these questions.)
Achieving a sealed filter over the nose is easier said than done, though. You can’t just use a standard mask, since that’s designed for the nose and mouth. One commenter shared a system that he uses, an elastomeric nose mask held in place with a headband. Another suggested using nasal filters designed to block allergens. As far as I know, there hasn’t been any research showing what might be most successful—unlike the extensive research that has gone into showing the value of high-quality face-masks and respirators.
In addition to the discussion of designing a nose-only mask, this reader’s question led to some discussion about the careful behavior needed to use it successfully. One commenter pointed out that, if you’re eating alone, it’s easier to stay focused on breathing patterns than if you’re eating in a group and engaged in conversation. I also appreciated this reply from a Louisiana-based behavioral scientist:
So, to summarize, I’d say that a nose filter could be helpful for situations like a dentist appointment and could be helpful (but trickier) for indoor dining—but it’s hard to say for sure. A much easier conclusion: avoid indoor dining as much as possible during COVID-19 surges like the one we’re in right now.
More reader responses
-
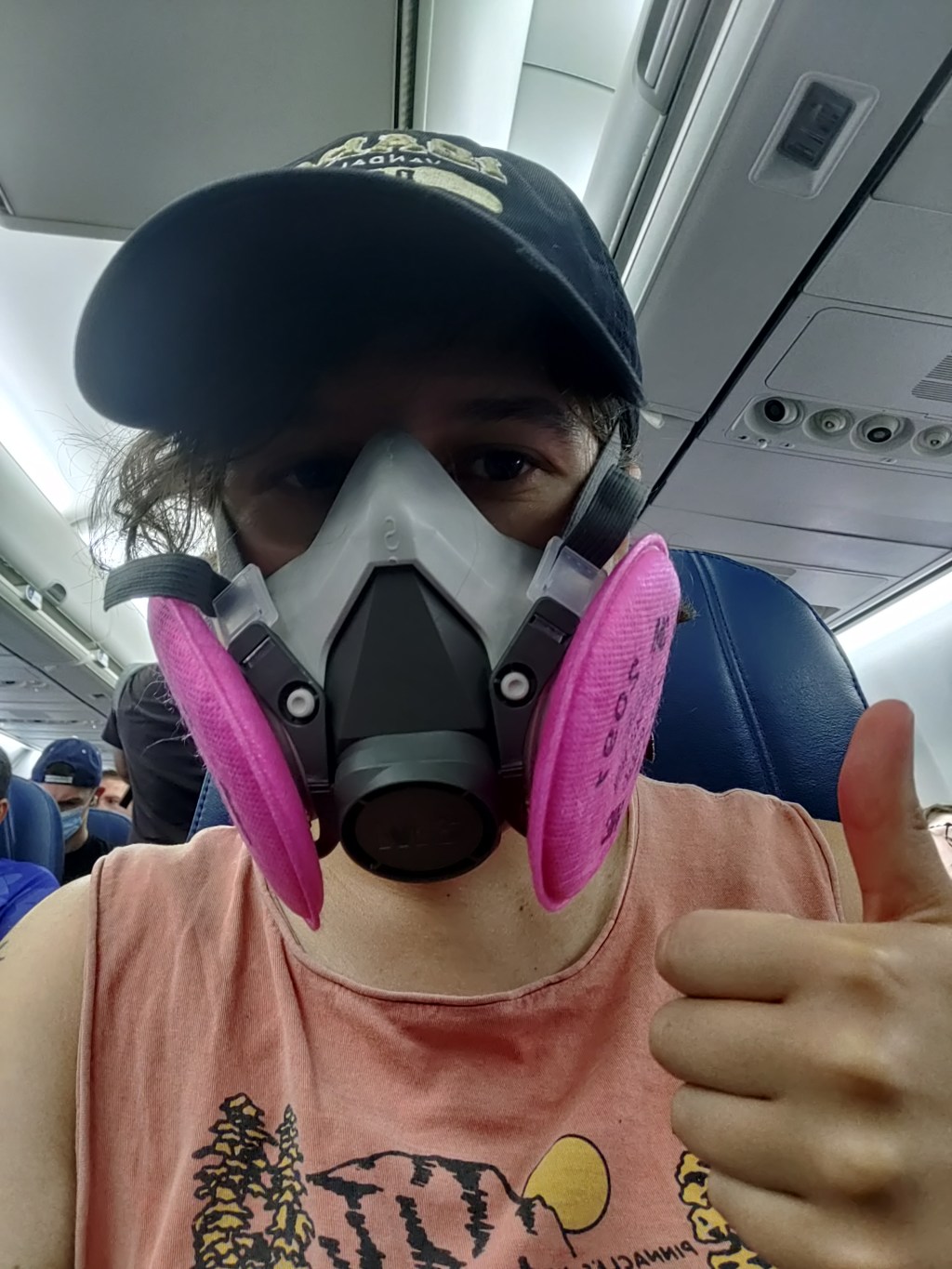

Tips for safe plane travel during the BA.5 surge

The author in a 3M respirator (with P100 filters), on the plane to Denver, Colorado. This weekend, I traveled to Denver, Colorado for the final trip in an early-career fellowship which has covered some travel and trainings for me this past year.
Of course, going anywhere on a plane right now, during an intense COVID-19 surge, is not something I’d normally choose to do. This is basically my one plane trip of the summer; all my other travel has been by train and/or car. (And the fellowship event itself had some safety measures in place, eg. required masks and rapid tests.)
But I know a lot of people are traveling by plane right now—I know, because I saw so many of them at JFK Airport. So, I wanted to share a few things I did on this trip to reduce my risk.
First: I bought a respirator. These devices, considered to be a step above N95s/KN95s, are intended for use in occupational settings, such as for workers in chemical plants or firefighters going into smoke. You can read more about them on this CDC NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) page.
I think of mine like a reusable N95 mask, with great longevity and an excellent seal to my face. I ordered one from 3M, which has several NIOSH-approved options. I also learned more about different respirators at Patient Knowhow, a site with reviews of a few major N95-equivalent options. (I recently talked to the site’s founder, Devabhaktuni Srikrishna, for an upcoming article on ventilation.)
It’s important to note that, if you get one of these respirators, you may need to order air filters separately. I got P100 filters, which are the highest grade. Another add-on may be an exhalation valve filter, which cleans the air you exhale out of your respirator (basically, further ensuring that you aren’t getting other people sick as you wear it).
Now, one challenge with these respirators is that they may freak people out a little. I feel like a bug-eyed sci-fi villain with mine on; though I’m well-accustomed to NYC’s blase attitude towards weird behavior, so I don’t mind if I freak people out. For others, this could be a greater concern.
Respirators also aren’t common mask options yet, though they seem to be growing more popular—my Twitter selfie of me in my respirator on the plane got over 200 likes. But they aren’t yet well-known in transit settings. While I personally didn’t have issues (other than a bit of confusion at JFK’s security screening), I know that others have been told to take these off on flights. It’s good to have a backup N95/KN95 in case that happens.
Second: I follow guidance from ventilation experts. If you’d like to read about how plane ventilation works, masking options, and other small ways to improve travel safety, you can find a lot of this advice on Twitter. “Ventilation Twitter,” as I recently described it to a journalist friend, is generally very welcoming and willing to triage questions.
One key piece of advice: while I kept my respirator on throughout my flights (seriously, the briefest breaks possible for water and food), I made especially sure to stay masked while planes were at the gate or landing. These are the points in a flight when the plane’s ventilation system isn’t switched on, making masking more important.
Saahil Desai provides a helpful explanation of these priority periods for masking in a recent Atlantic article. Though I’d like to note, some experts have suggested that the article downplays the importance of masking as much as you can throughout a flight and using other safety strategies as well.
More helpful threads on this subject…
Third: I avoid indoor dining as much as possible. This is, of course, one of the highest-risk settings for catching the coronavirus, because you have to take your mask off to eat or drink—while others nearby are also unmasking to eat or drink.
Sometimes, one can be put into tricky situations when there are truly no outdoor dining options (such as on a long airplane trip). But even in that scenario, there are ways to reduce risk. For example, when I needed to eat breakfast at JFK Airport, I found a corner of an unused gate where I could be relatively far from other people, rather than sitting in a crowded food court area.
I also appreciated that the other fellows in my group followed my recommendation for an outdoor dinner on Thursday evening, before our official activities started!
And finally: lots of testing. Remember, rapid tests can indicate whether you’re actively spreading the coronavirus, but PCR tests are still the gold standard for accuracy. I try to get PCR tests before and after travel or large gatherings, to be certain of my status. (Though I acknowledge that I live in NYC, where public testing is still available, albeit in decline.)
This trip went from Thursday to Saturday, with the riskiest event being an indoor dinner on Friday evening. My tests included: PCR test on Wednesday (same-day results); rapid test on Thursday morning; rapid test on Friday morning; rapid test on Friday evening (right before the dinner); rapid test on Saturday morning; and a planned PCR test for next Wednesday or Thursday. Rapid tests and symptom monitoring were also required for the rest of my group.
Is all of this inconvenient? Sure, somewhat. But I consider it worthwhile to have a safe trip and protect the people around me. If you have other safety tips or questions on this topic to share, please reach out and let me know.
-
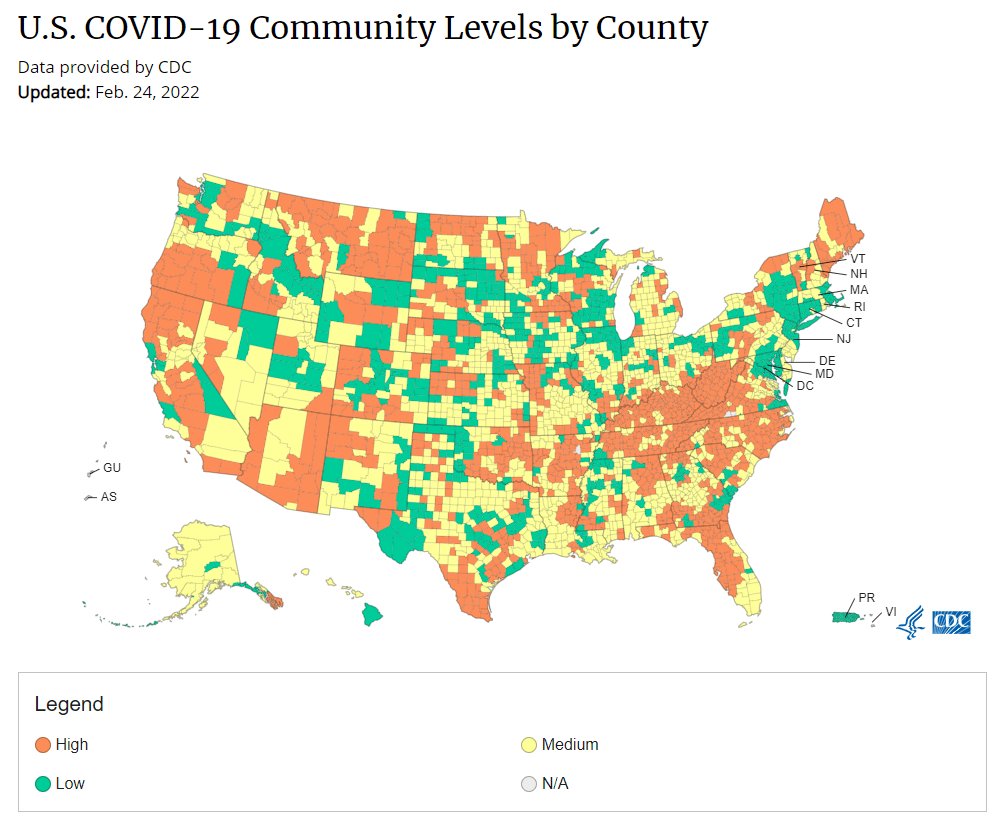
Why the CDC changed its masking guidance, and which metrics to follow right now
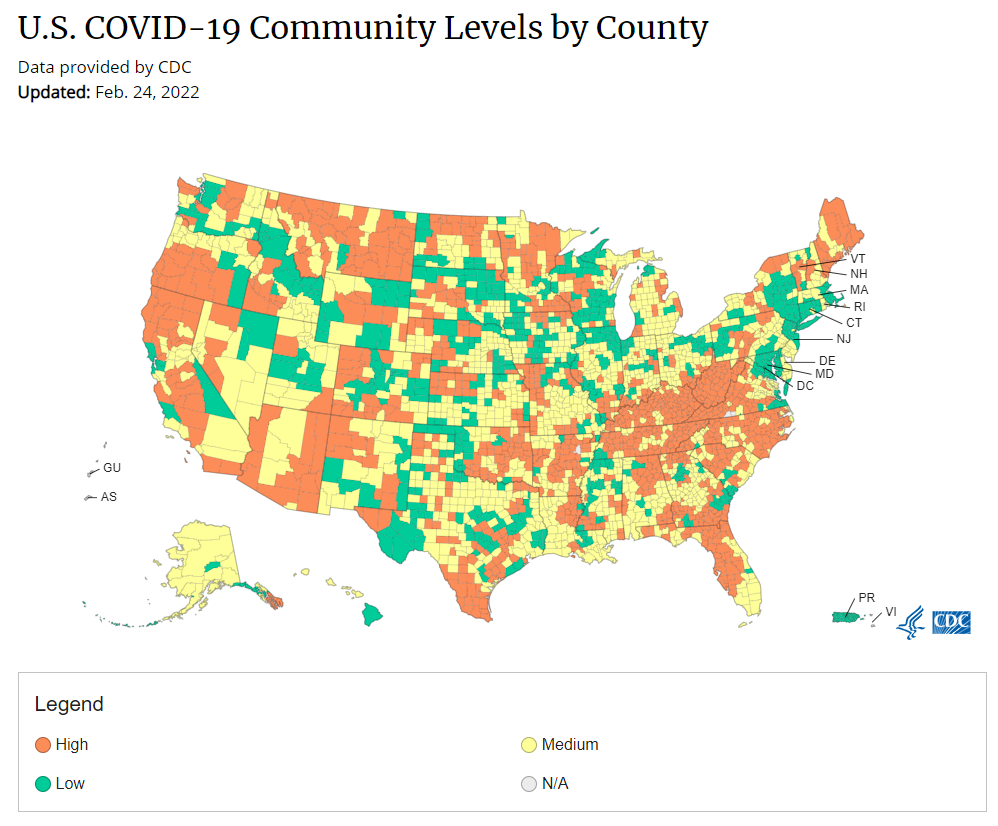
Under the new CDC guidance, about 70% of Americans live in counties where they can go unmasked in public. Chart via CDC.gov. This past Friday, the CDC announced a major shift to its guidance for determining COVID-19 safety measures based on county-level community metrics. The new guidance is intended to replace COVID-19 thresholds that the agency developed last summer, during the Delta wave; here, the CDC is promoting a shift from using cases and test positivity for local decision-making to using metrics tied directly to the healthcare system.
This shift away from cases isn’t new: state health departments have been moving in this direction recently, as I wrote last week. Similarly, the CDC’s recommendation for when Americans should feel safe in taking off their masks aligns with recent guidance changes from state leaders.
The new guidance is essentially a lot more lenient when it comes to mask removal. Overnight, the U.S. goes from under 5% of counties in “low” or “moderate” transmission (under the old guidance) to over 60% of counties, representing 70% of the population, in a “low” or “medium” COVID-19 community level.
This shift will embolden more states, local health departments, and individual organizations to lift safety measures and change how they track COVID-19. In this post, I’ll unpack why I believe the CDC made certain choices with this new guidance, what critiques I’m seeing from public health experts, and some recommendations for thinking about your COVID-19 risk during this highly confusing pandemic era.
Rationale for the CDC’s new guidance
With this new framework, the CDC is essentially telling Americans to watch hospitalization numbers—not case numbers—as the most important metric to inform how hard COVID-19 is hitting their community. One piece of their logic is, I suspect, that case numbers are less reliable in this pandemic era than they have been since March 2020.
That lack of reliability largely stems from the rise of at-home rapid antigen tests, which gained popularity during the Omicron surge and are now largely unconstrained by supply issues. (For example: iHealth Labs, one major at-home test provider, now allows shoppers to buy up to 50 test kits per person, up from a limit of 10 during Omicron’s peak.)
Unlike PCR test results, which are systematically processed in labs and reported to public health agencies, at-home test results typically do not travel beyond a patient’s trash can. And while a few local jurisdictions (like D.C.) have given residents options to self-report their antigen tests, the majority have opted not to take on this challenge. As a result, current case numbers for almost everywhere in the U.S. are not very reflective of actual infections in the community.
In previous pandemic eras, researchers could use PCR test positivity as an indicator of how reliable case numbers might be for a particular jurisdiction: higher test positivity usually means that more cases are going unreported. But in the era of widespread rapid tests, test positivity is also less reliable, because rapid tests aren’t accounted for in the test positivity calculations either.
Case numbers do still have some utility, because people who have COVID-19 symptoms or need a test result to travel will continue seeking out PCR tests. The CDC guidance reflects this by keeping cases as one factor of its COVID-19 community level calculation. But cases are no longer the star of the show here.
Instead, the CDC is focusing on hospitalizations: specifically, new COVID-19 admissions per 100,000 people and the share of inpatient beds occupied by COVID-19 patients. New hospital admissions are a more reliable—and more timely—metric than the total number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19, because admissions reflect only the people coming in with symptoms that recently started, not the people who have been hospitalized for days or weeks.
The share of inpatient beds occupied by COVID-19 patients, meanwhile, reflects the strain that this disease is currently putting on a hospital system. The CDC is choosing to include all COVID-19 patients here, not only those who are hospitalized for COVID-specific symptoms (the correct choice, in my view). Agency director Dr. Rochelle Walensky gave a good explanation for this at a media briefing on Friday:
We are considering anybody in a hospital bed with COVID, regardless of the reason for admission, and the reason that we landed there is multifold. First, many jurisdictions can’t differentiate, so that was important for us to recognize and realize. Second, whether or not a patient is admitted with COVID or for COVID, they increase the hospital capacity and they’re resource intensive. They require an isolation bed. They require PPE. They probably require a higher staff ratio. And so they are more resource intensive and they do take a COVID bed potentially from someone else.
Interestingly, as well, as we have less and less COVID in certain communities, the amount of people who are coming into the hospital with COVID will necessarily decrease. We will not have as many people walking around asymptomatically because there will just be less disease out there. So increasingly, as we have less disease in the community, we anticipate that more of the people who are coming into the hospital are going to be coming in because of COVID.
And then finally, as we have even less disease in the community, we anticipate that not every hospital is going to screen every patient for COVID as they walk in the door, especially if we have less and less disease in the community. And when that happens, we won’t actually be able to differentiate. In fact, people who are coming in, who are tested will necessarily be coming in for COVID. So for all of those reasons, comprehensively, we decided to stay with anybody coming in with a COVID diagnosis.
Also, a note on wastewater: I’ve seen some commentators express surprise that the CDC didn’t include wastewater in its new guidance, as this sewage surveillance can be a useful leading indicator for COVID-19 that’s more reliable than cases. The problem here is, wastewater surveillance is not available in much of the country—just look at all the empty space on this map. To use wastewater for decisionmaking, a county or state needs to have enough wastewater collection sites actually collecting these data, and most states are not there yet.
Critiques of the new guidance
While hospitalizations are a more reliable COVID-19 metric than cases, especially in our rapid testing era, they come with a few major issues. First, hospitalizations are a lagging indicator, meaning that they start to rise a couple of weeks after a new surge has started. If we rely on hospitalizations as a signal to put mask requirements or other safety measures in place, those changes will come weeks delayed.
As Boston University epidemiologist Dr. Ellie Murray put it in a recent Twitter thread: “Using lagging indicators like hospitalizations could be okay for turning *off* precautions IF we are sure that no new surge has begun. But that means we need leading indicators, like infection surveillance to guide turning *on* precautions.”
Another issue with relying heavily on this lagging indicator is, new COVID-19 safety measures may come too late to protect essential workers, children in schools, and others who face high risk of coronavirus exposure. “These high exposure populations get COVID first and most,” writes health policy expert Julia Raifman.
In other words, by the time case and hospitalization rates are high enough for a community to institute new safety measures under this new CDC guidance, those high-risk people are likely to be the ones already in the hospital. Raifman points to data from the U.S. Census’ Household Pulse Survey, showing that low-income workers were most likely to miss work for COVID-19 throughout last year.
Beyond this lagging indicator issue, another challenge with relying on hospitalizations is that, for many Americans, the hospitals that they might go to if they come down with severe COVID-19 are not located in their county. Plenty of counties, particularly in rural areas, don’t have hospitals! To deal with this, the CDC is actually using regional hospitalization figures, compiling statistics from multiple counties that rely on the same healthcare facilities.
University of South Florida epidemiologist Jason Salemi lays out this calculation in an excellent Twitter thread, linked below. While it makes sense that the CDC would need to use regional instead of local figures here, the agency is being pretty misleading by labeling this new guidance as county-level metrics when really, the metrics are not that localized.
There are more equity concerns embedded in the new CDC guidance as well. For counties with “low” or “medium” community COVID-19 levels, the CDC recommends that most Americans do not need to wear masks in public. But people who are immunocompromised or at high risk for severe disease should “talk to a healthcare provider” about the potential need to wear a mask indoors, stock up on rapid tests, or consider COVID-19 treatments.
For one thing, telling people, “talk to your doctor” is not a great public health strategy when one in four Americans do not have a primary care physician, and one in ten do not even have health insurance! For another thing, one-way masking among immunocompromised and otherwise high-risk people is also not a great strategy, because masks protect the people around a mask-wearer more than they protect the mask-wearer themselves. (I recommend this recent Slate piece on one-way masking for more on this topic.)
It is also pretty unclear how the CDC landed on a case threshold for “low transmission” that is much higher in this new guidance than in the old guidance, as Dr. Katelyn Jetelina points out in a recent Your Local Epidemiologist post. If anything, honestly, I would expect that the CDC needs to lower its case threshold, given that current case numbers are not accounting for millions of rapid tests done across the country.
Finally, the new CDC guidance completely fails to account for Long COVID. Of course, it would be very difficult for the CDC to do this, since the U.S. basically isn’t tracking Long COVID in any comprehensive way. Still, overly focusing this new guidance on hospitalizations essentially ignores the fact that a “mild” COVID-19 case which does not lead to hospitalization can still cause major, long-term damage.
Which metrics you should follow right now
Here are my recommendations of COVID-19 metrics to watch in your area as you navigate risk in this confusing pandemic era.
- Both the old and new CDC thresholds. While the CDC pushes its new guidance with a brand-new page on CDC.gov, community transmission metrics calculated under the old guidance are still available on the CDC’s COVID-19 dashboard. If you’re not feeling comfortable taking off your mask in public and want to wait until transmission is seriously low in your area, you can look at the old thresholds; though keep in mind that case data are seriously unreliable these days, for the reasons I explained above.
- Remember that masks are useful beyond COVID-19. Not a metric, but an additional note about thinking through risk: masks reduce risk of infection for a lot of respiratory diseases! We had a record-low flu season last winter and many Americans have avoided colds for much of the pandemic, thanks in part to masking. Helen Branswell has a great article in STAT News that unpacks this further.
- Wastewater data, if available to you. As I mentioned above, wastewater surveillance data are not available in much of the country. But if you live somewhere that this surveillance is happening, I highly recommend keeping an eye on those trends to watch for early warnings of future surges. You can look at the CDC dashboard or Biobot’s dashboard to see if your county is reporting wastewater data.
- Vaccination levels. It makes sense that vaccination was not included in the CDC guidance, because vaccinated people can still spread highly contagious variants like Omicron. Still, more highly-vaccinated counties—particularly those with high vaccination rates for seniors—are likely to have less burden on their healthcare systems when a surge arises, so knowing the vaccination rate in your county can still be useful when thinking about your risk tolerance.
- Rapid test availability. This is a bit more anecdotal rather than an actual data source, but: looking at rapid test availability in your local pharmacies may be another way to get a sense of community transmission in your area. Right now, these tests are easy to find in many places as case numbers drop; if finding these tests becomes more competitive again, it could be a signal that more people are getting sick or having exposures.
As always, if you have any questions or topics that you’d like me to tackle in this area, please reach out.
More federal data
-
Answering reader questions: Encouraging policy changes

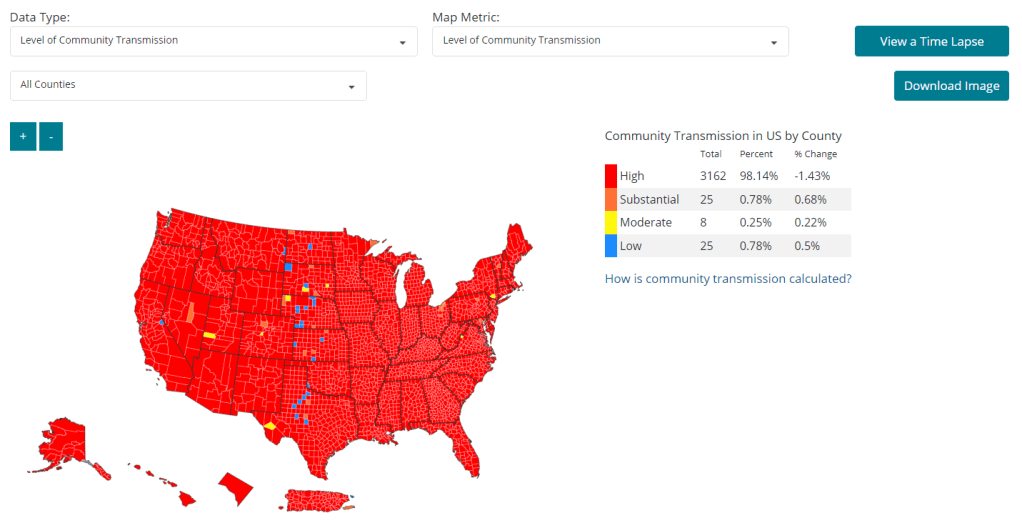
As of February 11, 98% of U.S. counties are seeing high COVID-19 transmission, according to the CDC. Chart from the CDC COVID-19 dashboard. In January, I invited readers to fill out a survey asking what you’d like to see from the COVID-19 Data Dispatch in 2022. Thank you to everyone who responded—your feedback gave me some great ideas for topics to focus on and new CDD-related initiatives to pursue this year!
This week, though, I want to focus on a topic that multiple readers brought up in the survey: how individuals can impact COVID-19 policies. One reader asked, “What can I as an individual do to make better the lacking local, state, federal, and international societal responses to COVID-19?” Another reader asked, along the same lines, “What can I do to encourage policy changes that keep people safer?”
These questions feel particularly pertinent this week, as leaders of several states loosen up on mask mandates and other COVID-19 safety measures. Governors in New Jersey, Connecticut, Delaware, Oregon, and Massachusetts have all announced that they’re ending mask mandates in public schools, and in some cases, in other public spaces. New York Governor Kathy Hochul is keeping the state’s K-12 school mask mandate in place for now, but ending a mandate for New York businesses.
Policy changes like these go against long-standing guidance from the CDC. In summer 2021, the agency recommended that communities base their levels of COVID-19 safety measures on two primary metrics: new cases per 100,000 people in the last week, and the percent of PCR tests that returned positive results in the last week. A high case rate indicates a lot of COVID-19 in the community, while a high test positivity rate can indicate the community’s testing infrastructure is not picking up a large share of cases—both suggest that measures should be put in place to control the virus’ spread.
At the time, this guidance was instituted as a response to the CDC’s preemptive recommendation that vaccinated people could go maskless. The agency said that counties seeing “high” or “substantial” transmission, according to the CDC’s metrics, should mandate masks for all, while counties with lower transmission could allow vaccinated people to go maskless. Gotta be honest: I do not know of a single state or county that’s actually following this guidance. Still, this combination of metrics is, I find, a useful and simple way to evaluate community spread.
As I’ve pointed out in recent National Numbers updates, even though case numbers in the U.S. have dropped significantly since the Omicron peak in January, they are still at very high levels across the country. You can see on the CDC’s dashboard that, as of this week, about 98% of counties fall into the “high transmission” category—with over 100 new cases per 100,000 people and test positivity over 10%. And beyond the case numbers: many hospitals are currently recovering from record Omicron surges, while over 2,000 Americans are dying of COVID-19 each day.
According to the CDC’s own guidance, 98% of U.S. counties should have a mask mandate right now. But instead, among the small number of Democrat-led states that have retained mandates, safety measures are now being lifted. The CDC itself is having a hard time commenting on this situation, and is reportedly “considering updating its guidelines on the metrics states should use,” according to POLITICO.
During this time of “opening” the small number of places that were not already fully open, what can individuals do to make their voices heard—or at least improve COVID-19 safety in their own communities? I have three suggestions:
1. Call your political representatives and tell them how you feel.
If your state, city, or other local region is considering lifting some COVID-19 safety measures, you have a representative whose job literally includes listening to your complaints about this issue—whether that’s a state assembly member or city councilor.
You can use this website to find your national and state representatives, and many localities have their own equivalents (for example, this site for New York City). Once you’ve found the contact information for your representatives, call or email them to express your support for continued COVID-19 precautions. This document offers a couple of potential phone call and email scripts; it’s New York-specific, but can easily be translated to other states.
In the last couple of years, conservative Americans have often been more politically active at the local level than more left-leaning Americans. Republicans often show up to school board meetings, call their representatives, and make their anger heard—sometimes supported by astroturfing campaigns. Anecdotal reports suggest that public health officials tend to hear more from community members who hate mandates than from those who actually want to see COVID-19 safety in their communities. You can push back against this trend.
And if you want to do some additional phone-calling or emailing beyond political representatives, consider reaching out to your state or local public health department and offering some support! They can probably use it.
2. Volunteer for local organizations helping to provide vaccinations, masks, tests, and other resources.
About 80% of Americans ages five and up have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the CDC. This number may sound impressive, but’s more concerning when we look at the other side of the statistic: 20% of eligible Americans have not yet received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose. Plus, among those Americans who have been fully vaccinated, more than half haven’t received a booster shot.
A lot of unvaccinated Americans are conservatives whose minds are very hard to change, this is true. But many of them are low-income workers with intense schedules, lingering health concerns, and other barriers to actually getting the shots that are surmountable, health policy expert Julia Raifman told me for a FiveThirtyEight story last month.
As a result, volunteer organizations around the country are still working to get their communities vaccinated and boosted. For example, Bed-Stuy Strong, a mutual aid group in my Brooklyn neighborhood, has hosted vaccination drives focused on local seniors and disseminated information on vaccinations and testing in the area.
Look for an effort like this that you might be able to join in your community! Or, if nothing like this currently exists, reach out to a local organization—like a public school, library, community center, etc.—and see if they might want to host a vaccine drive. Your local public health department could likely provide the supplies.
3. Educate your friends, family, and community members.
Beyond political and volunteer efforts, you can increase COVID-19 safety in your community simply by spreading the word about tools like high-quality masks and rapid tests. It might seem obvious, at this point in the pandemic, that we should all be stocking up on KN95s and testing kits, but many people do not have access to these tools—or simply don’t know why they’re useful.
You can send friends, family, and community members to websites like Project N95, which sells masks and other PPE, and Bona Fide Masks, a family business and leading KN95/N95 distributor. You can also tell them about antigen test distributors like iHealth Labs and Walmart, which are seeing fewer delays and supply crunches as the Omicron surge wanes.
In addition, if you have the resources, you can buy these masks and rapid tests in bulk and give them out. I recently gave out a couple of KN95 masks to contractors who were sent to look at a water issue in my apartment building, because I had the masks to spare. It’s that easy!
If you take any of these suggestions and see some impact, please email me (betsy@coviddatadispatch.com) and tell me about it!
More on federal data
-
Vaccines aren’t enough: What Biden can do about Omicron
This past Monday, President Biden gave a speech about the Omicron variant. He told America that Omicron is “cause for concern, not a cause for panic,” and thanked the South African scientists who alerted the world to this variant. (Though a travel ban is not a great way to thank those scientists!)
Towards the end of the speech, he said: “We’re throwing everything we can at this virus, tracking it from every angle.” Which I, personally, found laughable. As I’ve pointed out in a previous post about booster shots, the U.S.’s anti-COVID strategy basically revolves around vaccines, and has for most of 2021.
My Tweet about Biden’s vaccine-only strategy got more attention than I’m used to receiving on the platform, so I thought it was a worthwhile topic to expand upon in the COVID-19 Data Dispatch. Why aren’t vaccines enough to address Omicron—or our current surge, for that matter—and what else could the Biden administration be doing to slow the coronavirus’ spread?
Why aren’t vaccines enough?
Prior to Delta’s spread, there was some talk of reaching herd immunity: perhaps if 70% or 80% of Americans got fully vaccinated, it would be sufficient to tamp down on the coronavirus. But Delta’s increased capacity to spread quickly, combined with the vaccines’ decreased capacity to protect against infection and transmission, have shown that vaccines are not enough to eradicate the virus.
In thinking about this question, I returned to an article that Ed Yong wrote for The Atlantic back in August:
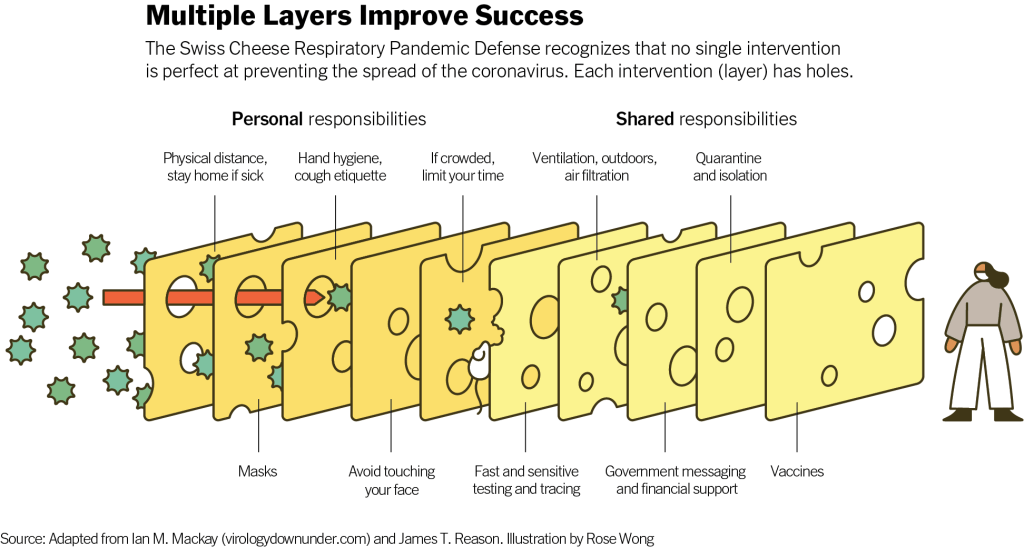
Here, then, is the current pandemic dilemma: Vaccines remain the best way for individuals to protect themselves, but societies cannot treat vaccines as their only defense. And for now, unvaccinated pockets are still large enough to sustain Delta surges, which can overwhelm hospitals, shut down schools, and create more chances for even worse variants to emerge. To prevent those outcomes, “we need to take advantage of every single tool we have at our disposal,” [Shweta Bansal of Georgetown University] said. These should include better ventilation to reduce the spread of the virus, rapid tests to catch early infections, and forms of social support such as paid sick leave, eviction moratoriums, and free isolation sites that allow infected people to stay away from others.
Remember that Swiss cheese model of pandemic interventions? Vaccines may be the best protection we have against the coronavirus, but they’re still just one layer of protection. All the other layers—masks, testing, ventilation, etc.—are still necessary, too. Especially when we’re dealing with a new variant that might not respond as well to our vaccines.
What we could do: better masks
One strategy that we could employ against Omicron, as well as against the current Delta surge, is better masks. While cloth masks certainly make it less likely for the coronavirus to spread from one person to another, their efficacy varies greatly depending on the type of material, the number of layers, and the mask’s fit.
N95 masks do the best job at stopping the coronavirus from spreading, followed by KN95 masks. Surgical masks do a better job than cloth masks, but making sure these masks fit properly can be a challenge for some people (including yours truly, who has a very narrow face!). Layering a surgical mask and cloth mask may be a safer option to get both good fit and protection, though two layers of mask can be challenging to wear for long periods of time.
Some experts have recommended that the U.S. mail N95 or KN95 masks to all Americans, or at least require these masks in high-risk areas, such as on flights. Germany and other European countries established similar requirements last summer.
What we could do: more widely available testing
In many countries—including the U.K., Germany, India, and others—rapid tests are freely available. Here in the U.S., on the other hand, the tests are quite expensive (often upwards of $10 for one test) and difficult to find, with pharmacies often limiting the number of packages that people can buy at once.
Biden has attempted to increase rapid testing access as part of his latest COVID-19 plan: in January, private insurance companies will be required to cover the cost of rapid tests. But this doesn’t solve the supply issue, and it doesn’t really make the tests more accessible, either. The measure would still require people to buy tests out of pocket, then fill out insurance reimbursement forms to maybe get their money back. Can you imagine anyone actually doing this?
In addition, as some experts have pointed out, the people most likely to need rapid tests—essential workers and others in high-risk environments—are also those less likely to have insurance. Biden is also distributing some rapid tests to community health centers, but that’s not enough to meet the need here.
Ideally, the Biden administration would mail every American a pack of, like, 20 rapid tests, along with that pack of N95 or KN95 masks I mentioned above. Free of charge.
And at the same time, of course, we need more readily available PCR testing. Even in New York City, which has a better testing infrastructure than most other parts of the country, the lines at free testing sites are getting long again as cases go up. Any American who wants to get tested should be able to easily make an appointment within a day or two, and get their results within another day after that.
Increased testing is not only important for identifying Omicron cases (and cases of any other new variant); it’s also key for the Merck and Pfizer antiviral treatments due to be approved in the U.S. soon. Without efficient testing, patients won’t be able to start these treatments within days of their symptoms starting.
What we could do: improve genetic surveillance
The U.S. is doing a lot more coronavirus sequencing than we were in early 2021: we’ve gone from under 5,000 cases sequenced a week to over 80,000. The CDC worked with state and local health agencies, as well as research organizations and private companies, to increase sequencing capacity across the country.
But that capacity is still concentrated in specific states and cities, as I noted in the previous post. In a recent STAT News story on sequencing, Megan Molteni writes:
Urban centers close to large academic centers tend to be well covered, while rural areas are less so. That means public health departments in large parts of the country are still flying blind, even as they are figuring out ways to prioritize Omicron-suspicious samples.
A lack of testing compounds this problem. If someone doesn’t confirm their COVID-19 case with a PCR test, their genetic information will never make it to a testing lab, much less a sequencing lab. While rapid tests are very useful for quickly finding out if you’re infected with the coronavirus, you need a PCR test for your information to actually be entered into the public health system.
In addition, even where the U.S. is sequencing a lot of samples, the process can take weeks. Vox’s Umair Irfan writes:
Still, it takes the US a median time of 28 days to sequence these genomes and upload the results to international databases. Contrast that with the United Kingdom, which sequences 112 genomes per 1,000 cases, taking a median of 10 days to deposit their results. A delay of only a few days in detection can give variants time to silently spread within communities and across borders.
Despite sequencing shortfalls in the U.S., we’re still doing much more surveillance than the majority of countries. Many nations in Africa, Asia, South America, and other parts of the world are sequencing fewer than 10 cases per 1,000, Irfan reports. As the U.S. should be doing more to get the world vaccinated, the U.S. should also do more to help other countries increase their sequencing capacity—monitoring for the variants that will inevitably follow Omicron.
What we could do: stricter domestic travel requirements
Starting on Monday, all international travelers coming into the U.S. by air will need to show a negative COVID-19 test, taken no more than one day before their flight. This includes all travelers regardless of nationality or vaccination status. At the same time, any non-U.S. citizens traveling into the country must provide proof of their vaccination against COVID-19.
But travelers flying domestically don’t face any such requirements. There are mask mandates on airplanes, true, but people can wear cloth masks, often pulled down below their noses, and airports tend to have limited enforcement of any mask rules.
Both experts and polls have supported requiring vaccination for domestic air travel, though the Biden administration seems very hesitant to put this requirement in place. Speaking for myself, I felt very unsafe the last time I flew domestically. A vaccine mandate for air travel would make me much more likely to fly again.
What we could do: more social support
In the U.S., a positive COVID-19 test usually means that you’re in isolation for 10 to 14 days, along with everyone else in your household. This can pull kids out of school, and pull income from families. As has been the case throughout the pandemic, support is needed for people who test positive, whether that’s a safe place to isolate for two weeks, grocery delivery, or rapid tests for the rest of the household.
This type of support could make people actually want to get tested when they have symptoms or an exposure risk, rather than avoiding the public health system entirely.
More variant reporting