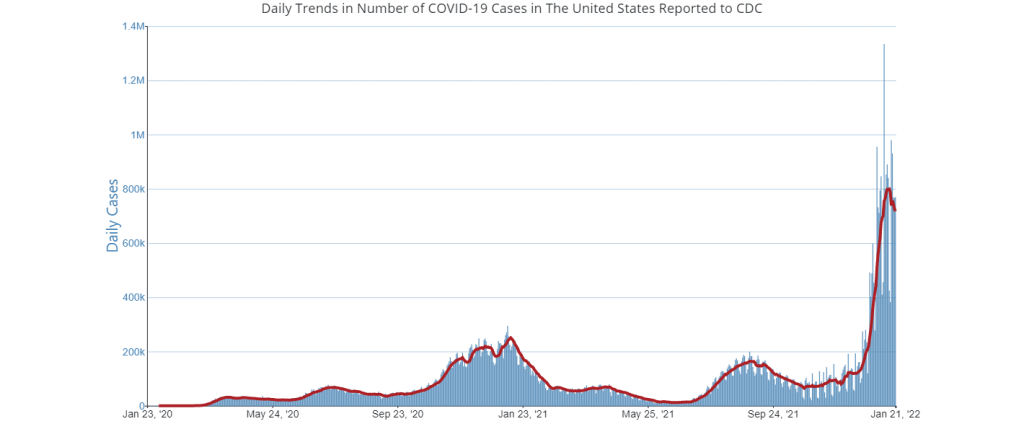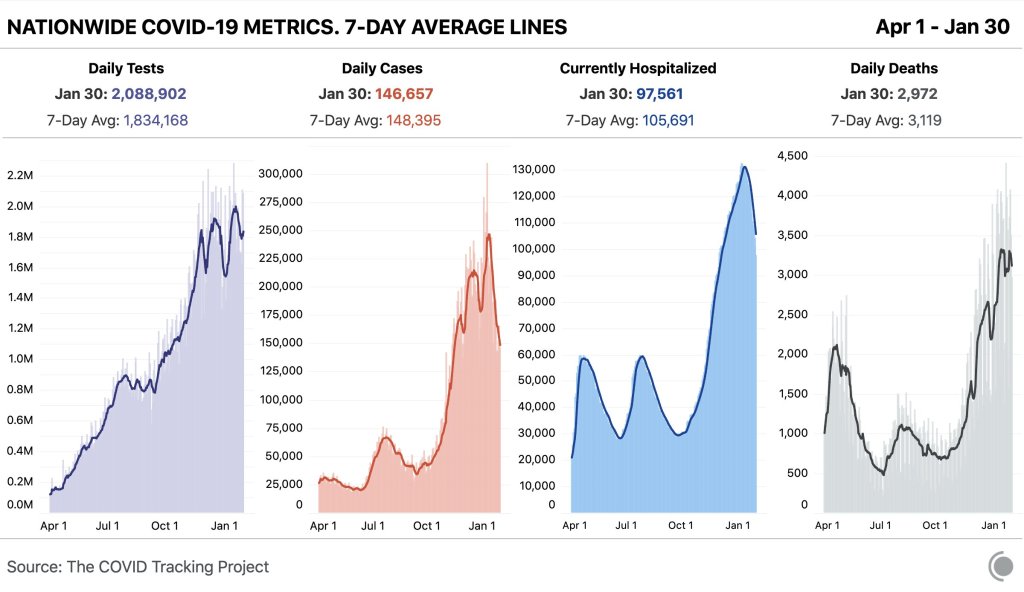
In the past week (January 19 through 25), the U.S. officially reported about 300,000 new COVID-19 cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 42,000 new cases each day
- 90 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 11% fewer new cases than last week (January 12-18)
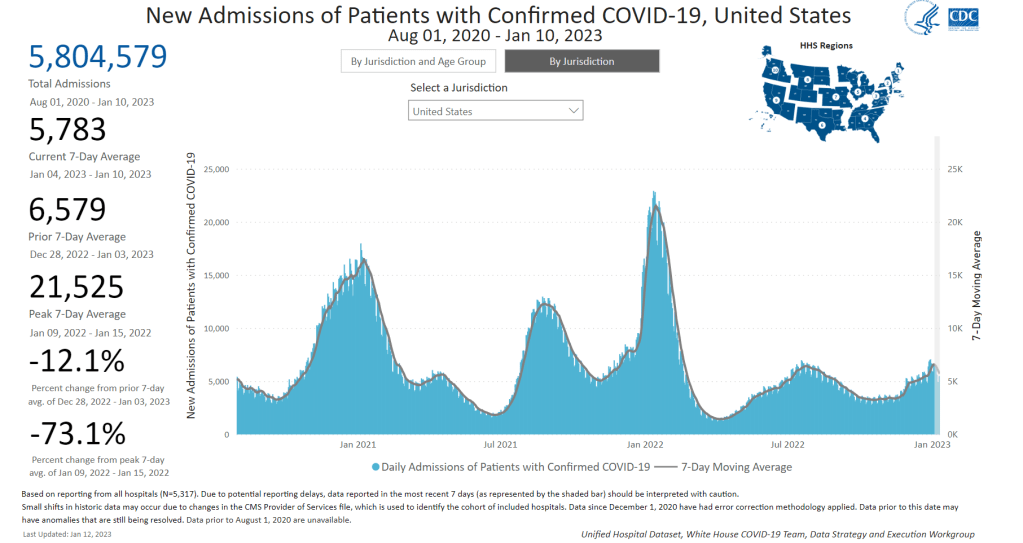
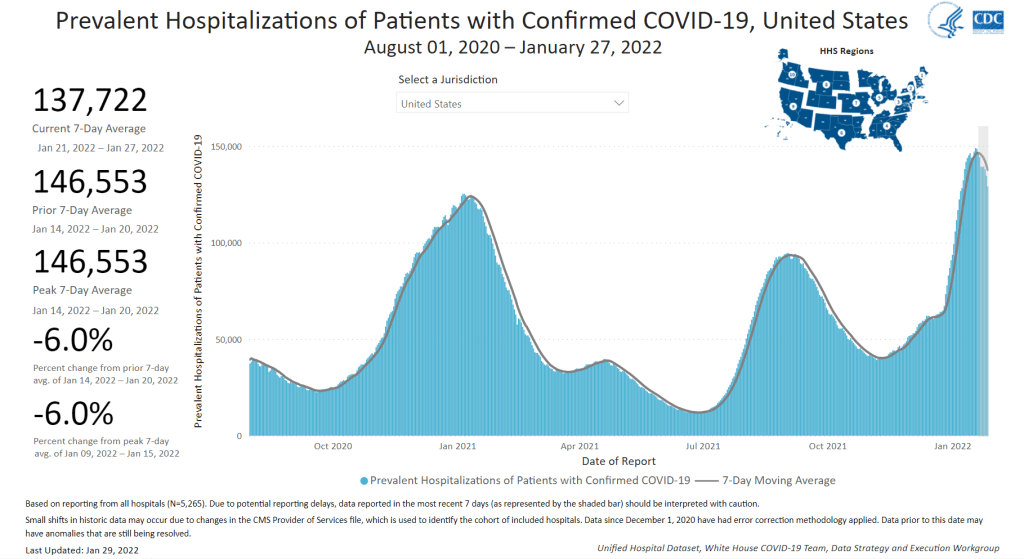
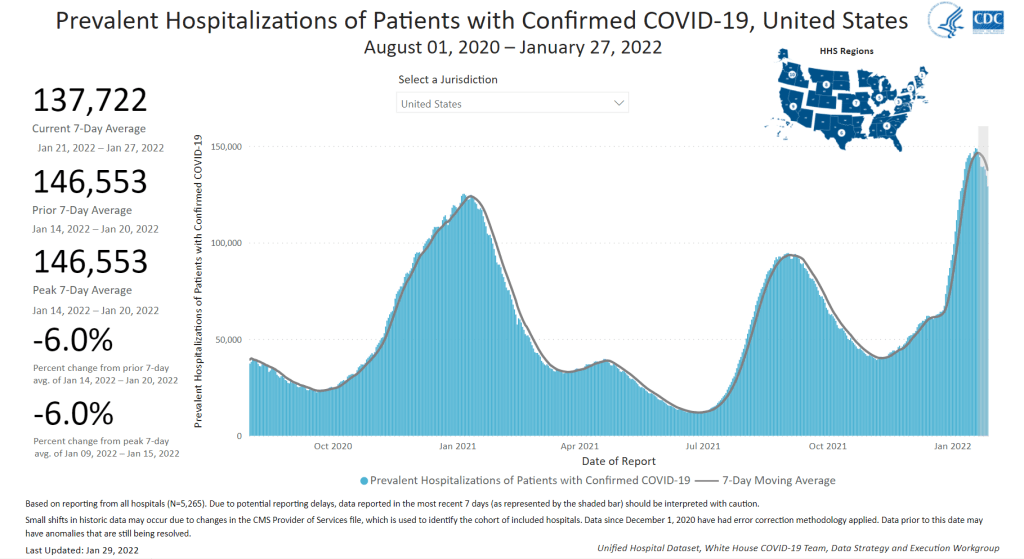
In the past week, the U.S. also reported about 30,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals. This amounts to:
- An average of 4,200 new admissions each day
- 9.0 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 14% fewer new admissions than last week
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 3,800 new COVID-19 deaths (540 per day)
- 61% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.5; 31% by BQ.1 and BQ.1.1; 2% by CH.1.1 (as of January 28)
- An average of 100,000 vaccinations per day
At the national level, COVID-19 spread appears to be approaching another plateau. New cases and hospitalizations (as reported by the CDC) are still in decline, but their descent is slowing: reported cases dropped by 11% this week, compared to 24% last week.
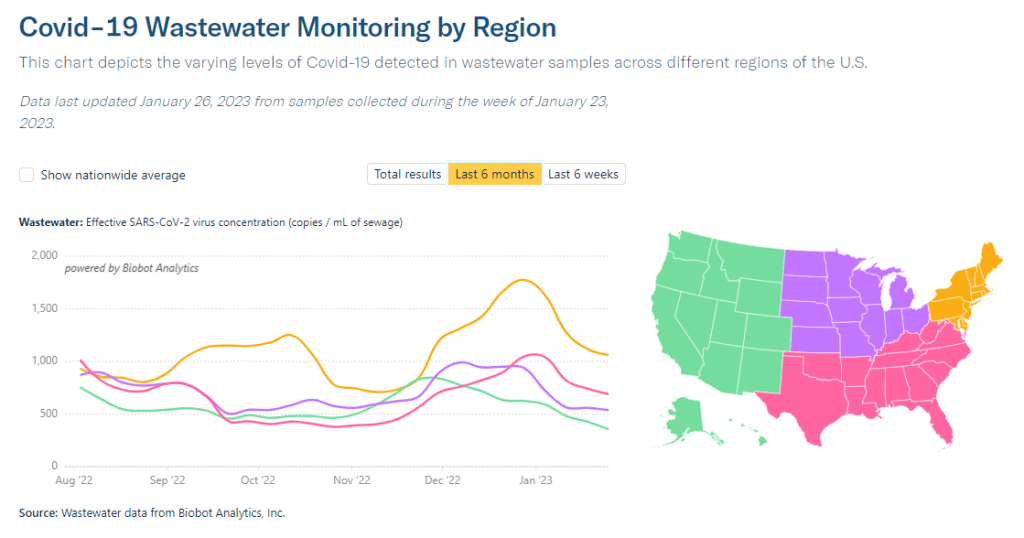
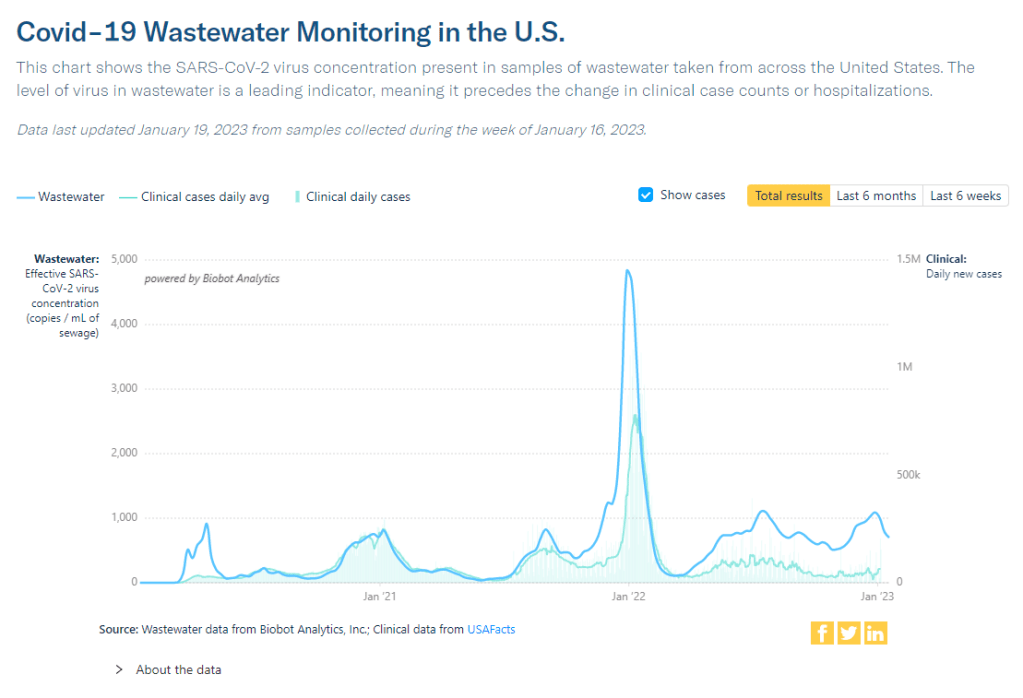
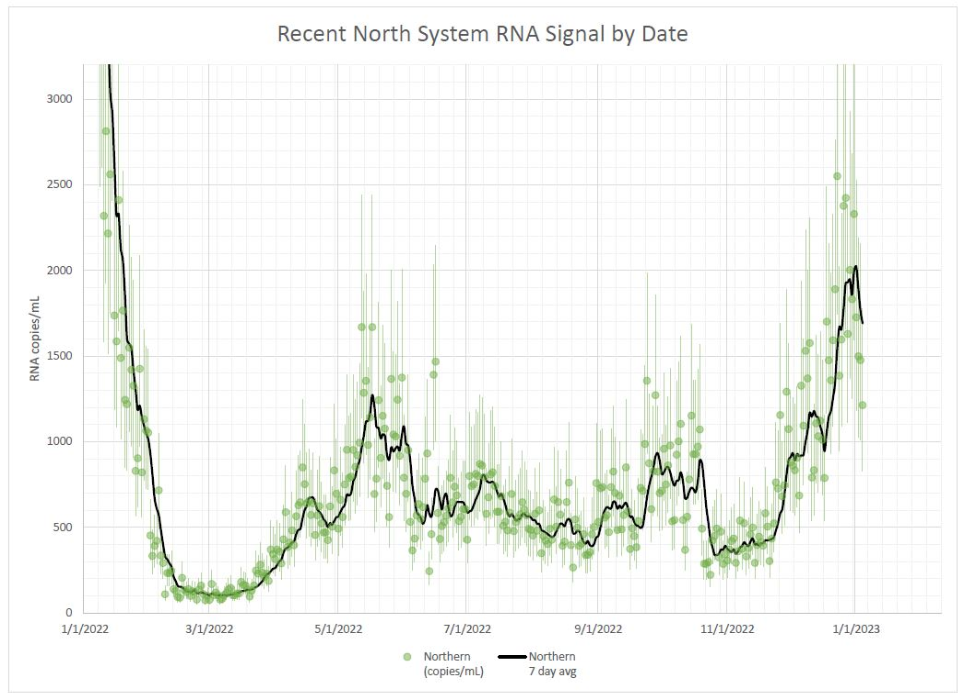
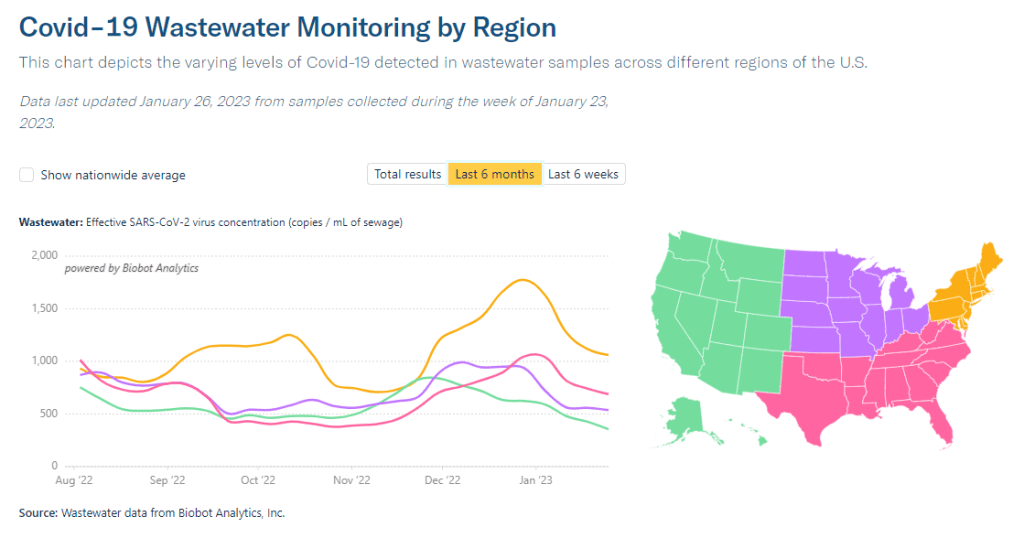
Wastewater surveillance presents the same trends. National data from Biobot suggest that COVID-19 transmission is leveling out in a similar place to where we were in October and November 2022, before the holiday surge drove up spread.
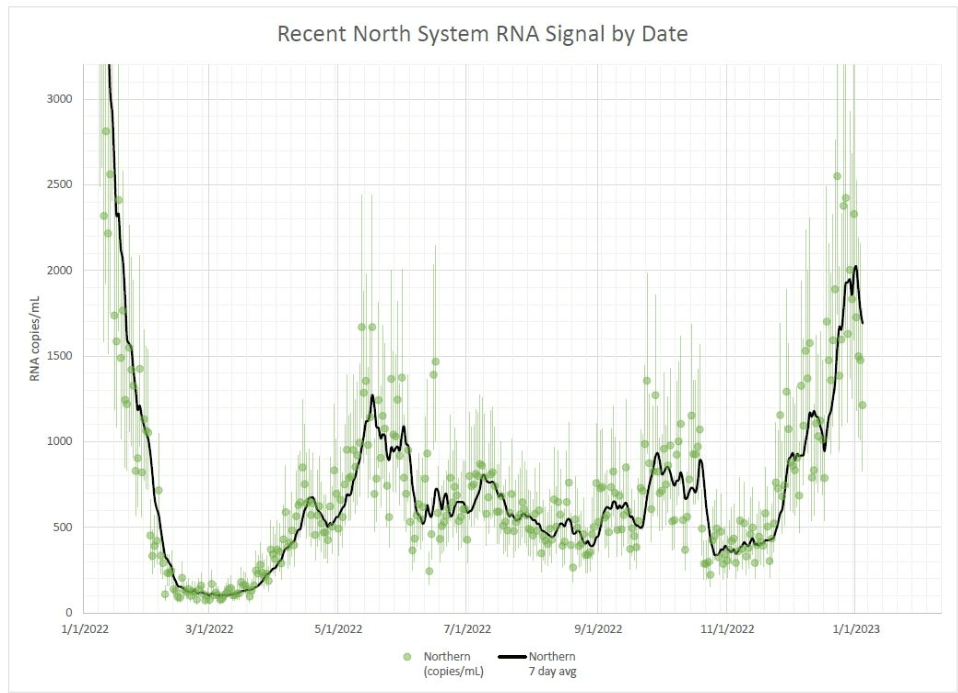
Biobot’s regional data show a slowing decline in the Northeast, plateaus in the Midwest and South, and a somewhat-more-pronounced decline in the West. And wastewater surveillance data from the CDC shows that COVID-19 spread is going up in some places, down in others: out of about 1,000 sites reporting data in the last two weeks, 48% reported decreases in coronavirus levels while 40% reported increases.
Unlike in recent weeks where every state has reported declines in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations, a few places are now reporting definitive upticks, according to the latest Community Profile Report. These states include Alaska, Vermont, Maine, South Dakota, North Dakota, Nevada, Oklahoma, Minnesota, and Indiana.
Why might some states report COVID-19 upticks just after we emerged from a surge over the holidays? One explanation could be the XBB.1.5 variant, which continues to outcompete other Omicron lineages. XBB.1.5 now comprises about 60% of new cases nationwide (according to the CDC’s estimates); while it is most dominant in the Northeast, it’s growing—and likely reinfecting people—in other regions.
The CDC’s latest variant estimates also now include Omicron CH.1.1, which has been connected to rising cases in the U.K. and New Zealand in recent months. Per the CDC, CH.1.1 has been present in the U.S. at low levels (like, 1% or less) for a few weeks now, without posing a major challenge to XBB.1.5. But it is still a variant worth keeping an eye on.
As flu and RSV cases continue to trend down, the U.S. is confronted with the final weeks of a respiratory disease-heavy winter that was pretty rough on our healthcare system—but fell short of the mind-boggling case numbers that we saw in the prior two winters. Yes, we didn’t see a repeat of “the first Omicron wave”; but still, millions of people got sick, thousands died. Many will likely experience Long COVID as a consequence of their infections this winter.
Is this an acceptable baseline for future winters? Or should we do better? (This recent article in The Atlantic by Katherine Wu expands on the problem of expectations, and makes a case for doing better.)