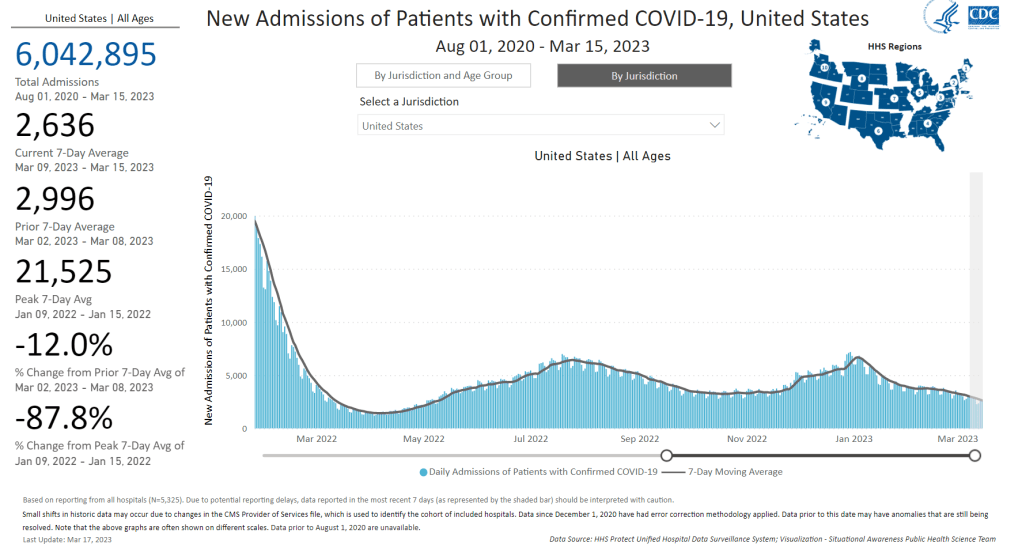
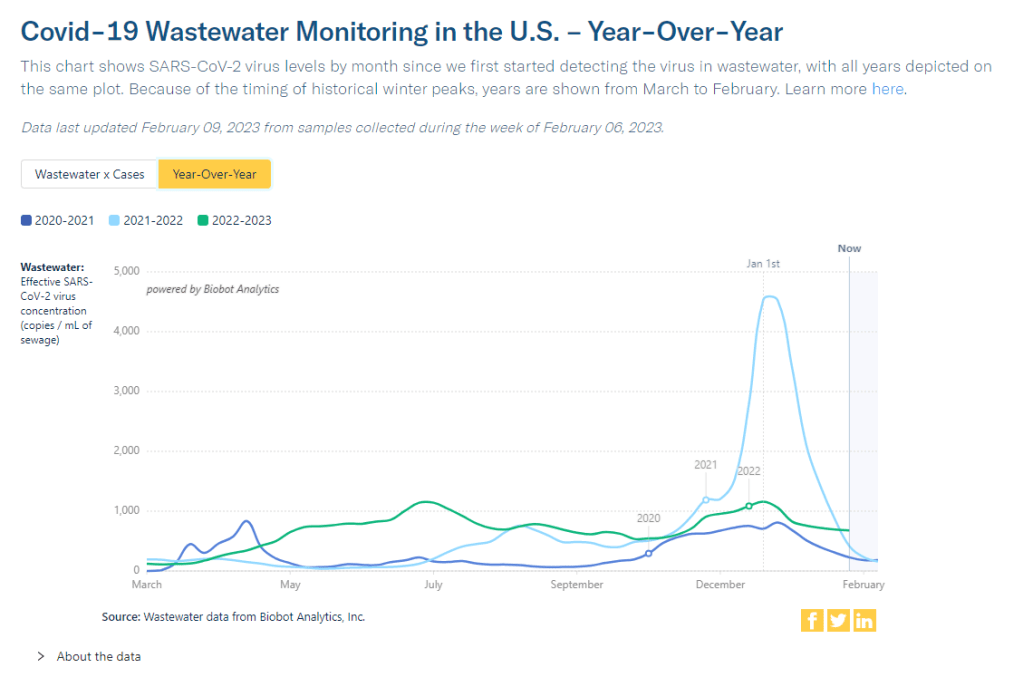
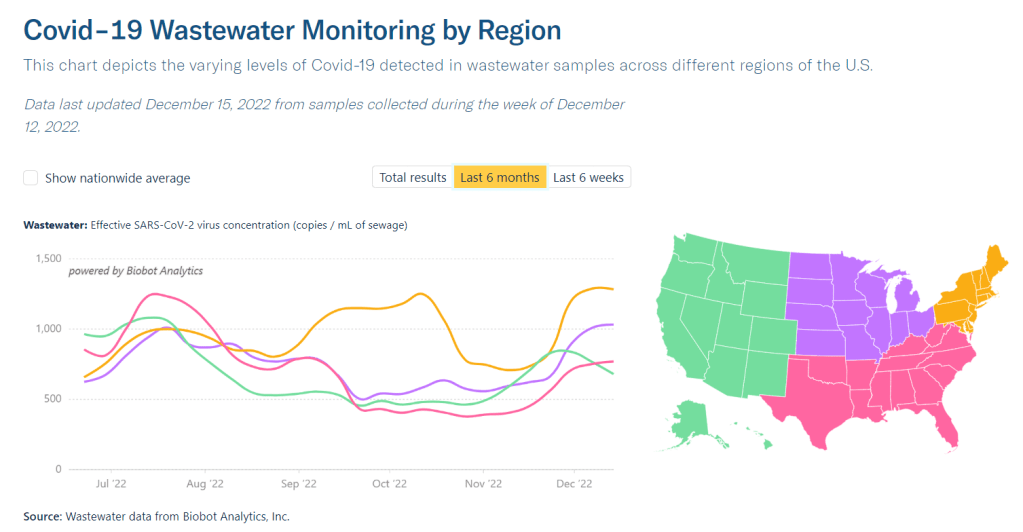
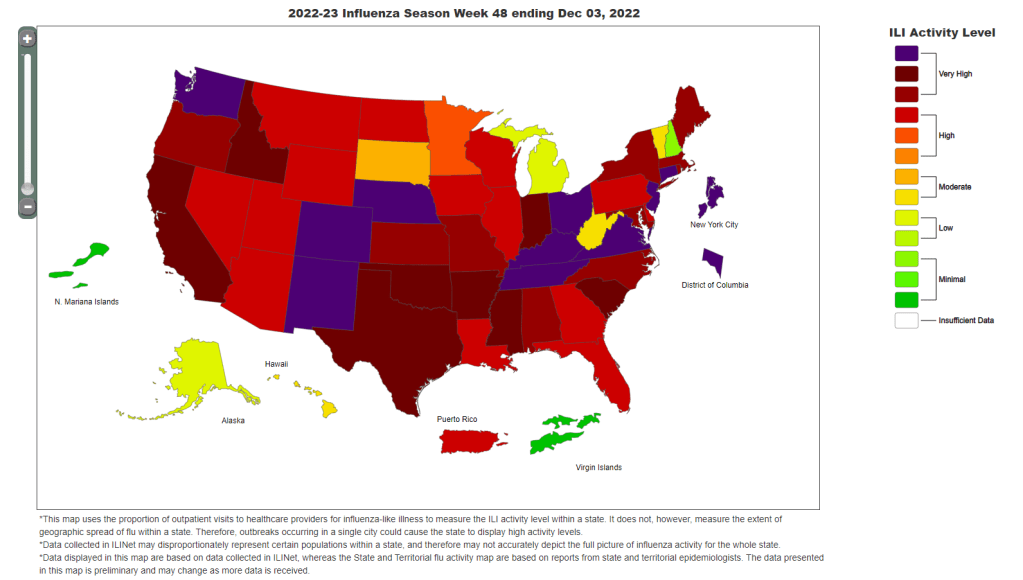
I received a couple of reader questions in recent weeks that I’d like to answer here, in the hopes that my responses will be more broadly helpful. As a reminder, if you ever have a COVID-19 question that you’d like to ask, you can email me at betsy@coviddatadispatch.com, or send it anonymously through this Google form.
COVID-19’s incubation period
One reader asked:
I’d love to learn more about COVID’s incubation period. I have read that it’s 2 to 14 days … but the median time seems to be on the low end (and could be as low as 24 hours?) How likely is it that it’s more like 14 days? I’d love to better understand this so that I know how to better handle exposures… Should I avoid someone who has had an exposure for two full weeks?
This is a tricky question for two reasons. First, the incubation period—or the time between exposure to COVID-19 and starting to show symptoms of infection—does indeed vary a lot. One review of studies on this topic, posted as a preprint in May, found a range from two to seven days, though it can be even longer. The CDC recommends precautions for up to ten days after exposure.
Second, the incubation period has changed as the coronavirus has mutated. The virus is constantly evolving to keep infecting us even as people build up immunity; shortening the incubation period is one of its strategies. Omicron has a notably shorter period than past variants; Katherine Wu at The Atlantic wrote an article about this in December 2021 that I think is still informative.
The preprint I cited above found that Omicron had an average incubation period of 3.6 days, shorter than other variants. I think it’s reasonable to assume that this period has continued to get shorter as Omicron has evolved into the many lineages we’re dealing with now. But the pace of research on this topic has slowed somewhat (with less contact-tracing data available for scientists to work with), so it’s hard to say for certain.
So, with these complexities in mind, how should one handle exposures? My personal strategy for this (noting that I’m not a doctor or qualified to give medical advice, just sharing my own experience) is to rely on a combination of timing, testing, and symptom monitoring. For the first couple of days after exposure, you wouldn’t be likely to have a positive test result even if you are infected, as it takes time for enough virus to build up in the body for tests to catch it. So, for those days, I’d just avoid people as much as possible.
After three to four days, PCR tests would start to be effective, and after five to six days, rapid tests would be. So at that point, I’d start testing: using a mix of PCR and rapid tests over the course of several days, up to two weeks after exposure. Studies have shown that the more tests you do, the more likely you are to catch an infection (and this applies to both PCRs and rapids). Daily is the best strategy, but less frequent regimens can still be useful if your access to tests is limited. At the same time, I’d keep track of any new symptoms, as that can be a sign of infection even if all tests are negative.
I’d personally be comfortable hanging out with someone who has had an exposure but consistent negative test results and no symptoms. But others who are less risk-tolerant than I am might avoid any contact for two weeks. The type of contact matters, too: a short, outdoor meeting or one with masks on is safer than a prolonged indoor, no-mask meeting.
Vaccine effectiveness
Another reader asked:
Is there any information on the effectiveness of the latest vaccines, including vaccines that combine Covid and RSV, and are there similarities between these viruses (related?)
As we head into respiratory virus season in the U.S., there will be, for the first time, vaccines available for all three major diseases: COVID-19, the flu, and RSV. I’ll talk about effectiveness for each one separately, because they are all separate vaccines for separate viruses. There’s no combined COVID-RSV vaccine on the market.
COVID-19: We know the fall boosters will target XBB.1.5, a variant that has dominated COVID-19 spread in the U.S. recently. There isn’t much data available on these vaccines yet, because the companies developing them (Pfizer, Moderna, Novavax) have yet to present about their boosters to the FDA and CDC, as is the typical process. The CDC’s vaccine advisory committee is meeting this coming Tuesday to talk fall vaccines, though, so it’s likely we will see some data from that meeting.
Also worth noting: some early laboratory studies suggest that vaccines based on XBB.1.5 will provide good protection against BA.2.86, despite concerns about differences between these variants. (More on this later in today’s issue.)
Flu: Every year, scientists and health officials work together to update flu vaccines based on the influenza strains that are circulating around the world. Effectiveness can vary from year to year, depending on how well the shots match circulating strains.
This week, we got a promising update about the 2023 flu vaccines: CDC scientists and colleagues studied how well these shots worked in the Southern Hemisphere, which has its flu season before the Northern Hemisphere. The vaccine reduced patients’ risk of flu-related hospitalization by 52%, based on data from several South American countries that participate in flu surveillance. This is pretty good by flu vaccine standards; see more context about the study in this article from TIME.
RSV: There are two new RSV vaccines that will be available this fall, both authorized by the FDA and CDC in recent months. These vaccines—one produced by Pfizer, one by GSK—both did well in clinical trials, reducing participants’ risks of severe RSV symptoms by about 90% (for the first year after infection, with effectiveness declining over time).
Both vaccines were authorized specifically for older adults, and Pfizer’s was also authorized for pregnant people as a protective measure for their newborns. We’ll get more data about these vaccines as the respiratory virus season progresses, but for now, experts are recommending that eligible adults do get the shots. This article from Yale Medicine goes into more details.
Nasal sprays as COVID-19 protection
Another reader asked:
I’m thinking of researching what foods and supplement are anti-viral anti-COVID. I’m wondering if anyone has done any research on that?
I haven’t seen too much research on about foods and supplements, since dietary options are usually not considered medical products for study. Generally, having a healthy diet can be considered helpful for reducing risk from many health conditions, but it’s not something to rely on as a precaution in the same way as you might rely on masking or cleaning air.
Another thing you might try, though, would be nasal sprays to boost the immune system. I have yet to try these myself, but have seen them recommended on COVID-19 Safety Twitter and by cautious friends. The basic idea of these nasal sprays is to kill viruses in one’s upper respiratory tract, essentially blocking any coronavirus that might be present from spreading further. People take these sprays as a preventative measure before potential exposures.
A couple of references on nasal sprays: