More than half of Americans have some antibodies from a recent coronavirus infection, according to a new CDC report. The study was published Tuesday in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), accompanied by a press conference and other fanfare. To me, this report (and its publicity) reflects the CDC’s current lack of urgency around addressing the pandemic and its continued impacts.
The CDC regularly surveys COVID-19 antibody levels among the U.S. population, a metric that scientists call seroprevalence. For these surveys, the agency works with commercial laboratories to measure antibody rates from a nationally representative sample of Americans, with updates provided about once a month. The survey specifically looks at a type of antibody that develops in response to infection, not vaccination.
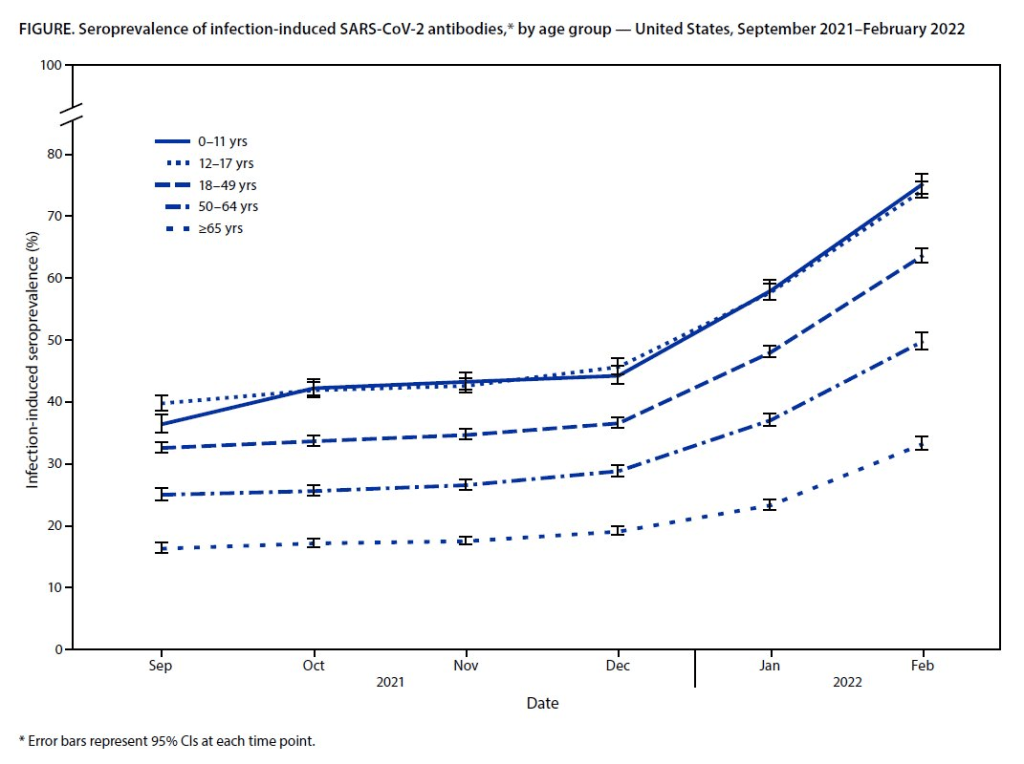
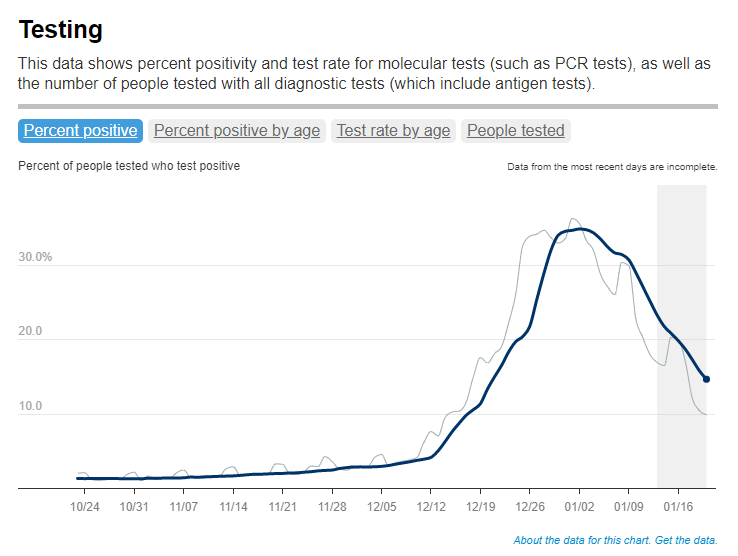
This most recent iteration of the survey, providing data from February 2022, is particularly notable: the CDC estimates that 58% of Americans had this immune system indicator of a recent COVID-19 infection, immediately after the nation’s massive Omicron wave. Not all of these people got COVID-19 during the Omicron wave, though, since some of these antibodies stem from earlier infections.
Other notable findings include:
- National seroprevalence increased from 34% in December 2021 to 58% in February 2022—the largest jump recorded in this survey—reflecting the Omicron wave’s impact.
- Children and teenagers had the highest antibody levels. For the 12 to 17 age group, seroprevalence went from 46% in December 2021 to 74% in February 2022.
There are some major caveats to this study, though, including:
- The imprecise nature of this antibody measurement. The type of antibody measured in this seroprevalence survey “stays positive for at least two years after infection,” CDC scientist Dr. Kristie Clarke said on the agency’s press call.
- Antibodies wane at different rates and levels for different people, so it’s unclear to what extent this 58% finding actually reflects the share of Americans who have gotten COVID-19 since spring 2020.
- Plus, some people infected by the coronavirus never seroconvert, meaning that they don’t develop antibodies at all (and thus wouldn’t show up in this study).
- While we know that the COVID-19 antibodies identified in this study confer some protection against new infections, it’s unclear how long that protection lasts or how it might hold up against new variants.
To me, this study (and the CDC’s choice to promote it with one of the agency’s infrequent press calls) exemplifies the Biden administration’s COVID-19 response right now.
As I listened to the press call, the CDC’s interpretation of this study was clear: more than half of Americans have some protection against COVID-19 from a prior infection, and many of those people also have protection against vaccination. Much of that protection applies specifically to Omicron and will likely help us avoid a crisis from BA.2, so it gives the U.S. additional reason to relax safety measures, the CDC suggested.
(Worth noting: the CDC still recommends vaccination and booster shots for anyone who had a previous coronavirus infection, including children. But that message is not getting across right now, as evidenced by our low booster shot uptake.)
When you ask for more specifics on that “protection” from prior infections, though, the CDC isn’t able to provide much information. Again, we don’t know how long the protection lasts or how it holds up against other variants. And we have no idea how many people had mild or asymptomatic COVID-19 cases, then did not seroconvert.
The CDC’s press call also failed to mention Long COVID, which is a risk from any COVID-19 case—no matter how mild. Some Long COVID researchers have also suggested that lack of seroconversion, or even a prior infection in general, may increase a patient’s future risk for prolonged symptoms the next time they get infected.
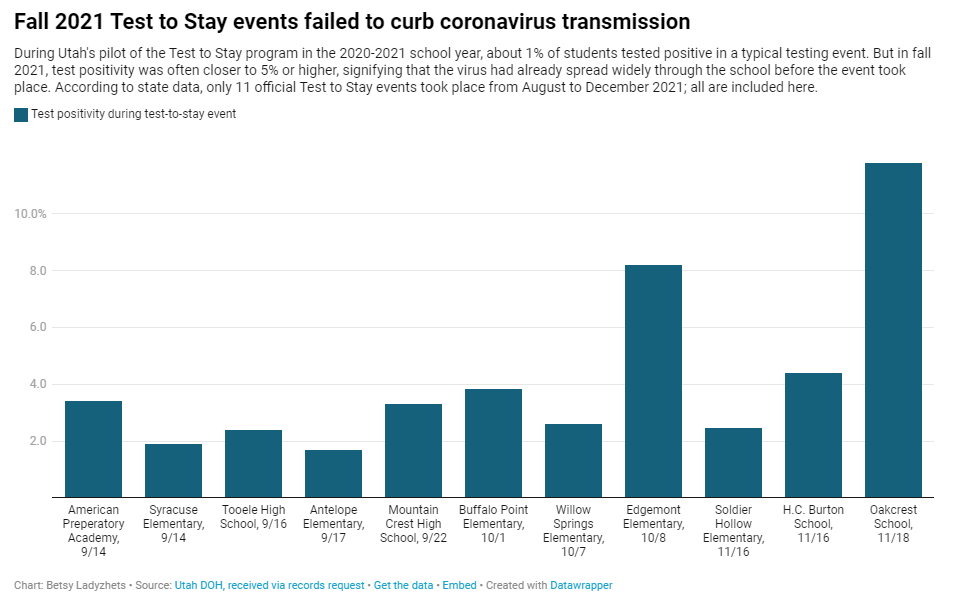
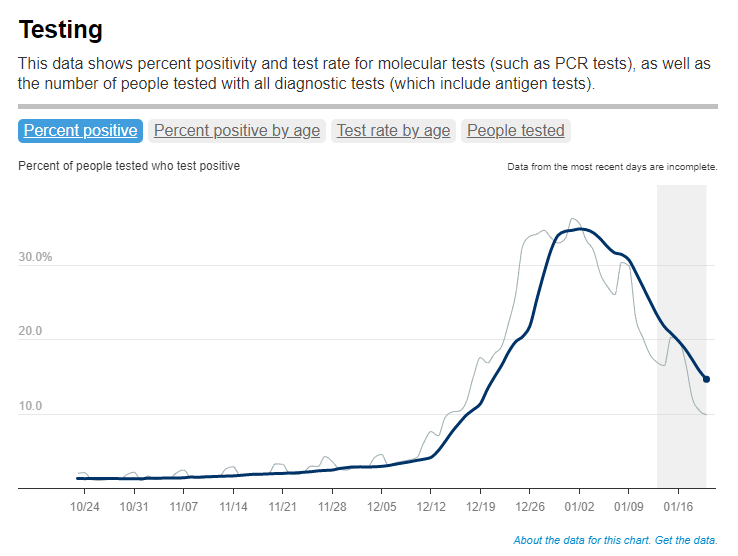
And, of course, the CDC report also exemplifies our current lack of surveillance. How many of those Omicron infections between December and February were actually caught by PCR testing and reported to the CDC? A small fraction. At the press call. Dr. Clarke mentioned an upcoming CDC study that estimates how many infections go uncounted for every one reported case:
In the Omicron period, we found that over that time period, the infection to case ratio was the highest that it’s been, at over three estimated infections per reported case. And that varied by region, so depending on which US census region the estimates were, you know, the ratios were higher or lower.
Surely that ratio is getting even higher now. To me, this forthcoming study, combined with the seroprevalence report, is a reminder that the cases we see in our datasets and dashboards are a very incomplete picture of actual coronavirus transmission in the U.S. And yet the CDC is using this incomplete picture to suggest we all relax, take our masks off, and forget about the pandemic.