- Long COVID care access challenges: A new paper, published this week in JAMA Network Open, shares the results of a survey by the Urban Institute think tank. The researchers surveyed about 9,500 adults, including 800 with self-reported Long COVID, about their experiences accessing medical care. The long-haulers were more likely to report difficulties with accessing and paying for care, compared to adults who don’t have the condition. To address this issue, the healthcare system needs to develop clinical guidelines for Long COVID, train workers about it, address insurance barriers, and more, the researchers said.
- PolyBio announces Long COVID research agenda: Speaking of Long COVID: the PolyBio Research Foundation, a nonprofit devoted to Long COVID, ME/CFS, and other chronic conditions, has announced several research projects that it’s supporting. The projects will evaluate potential biological mechanisms underlying Long COVID symptoms, such as virus persisting in different parts of the body, changes in T cell activity, microclots, and more. PolyBio has a great reputation for pushing ahead post-viral disease research, and I’m looking forward to seeing the results of these studies.
- Bivalent boosters hold up against XBB variants: Another new study that caught my attention this week: researchers at the University of North Carolina and North Carolina state health department reported on how well the bivalent, Omicron-specific boosters worked, based on the agency’s surveillance data. The study examined data from September 2022 through February 2023, a period when the BQ and XBB subvariants were dominating coronavirus spread. North Carolina residents who received the bivalent boosters were significantly less likely to experience severe COVID-19 symptoms, the researchers found, but their protection started to wane within a month after receiving the shots.
- Resources on indoor air quality in schools: Journalist’s Resource recently updated this list of research and resources for journalists interested in covering indoor air quality in K-12 schools. The update follows a CDC report showing that many public schools across the U.S. have failed to upgrade their ventilation, despite federal funding to do so (which I covered last week). School air quality is a topic that deserves more reporting, especially from local journalists who can dig into how their school districts are doing.
- Arizona county starts monitoring for a fungus in wastewater: I’m always on the lookout for new uses of wastewater surveillance, and one promising application could be tracking Candida auris, a fungal pathogen that’s resistant to common drugs and spreads quickly in healthcare settings. The Arizona state health department and a lab at the University of Arizona recently launched a pilot program to track this fungus through Yuma County’s wastewater. Arizona and neighboring southwest states have been a hotbed for C. auris; if this pilot is successful, other states could start similar efforts.
Tag: Wastewater
-
Sources and updates, April 16
-
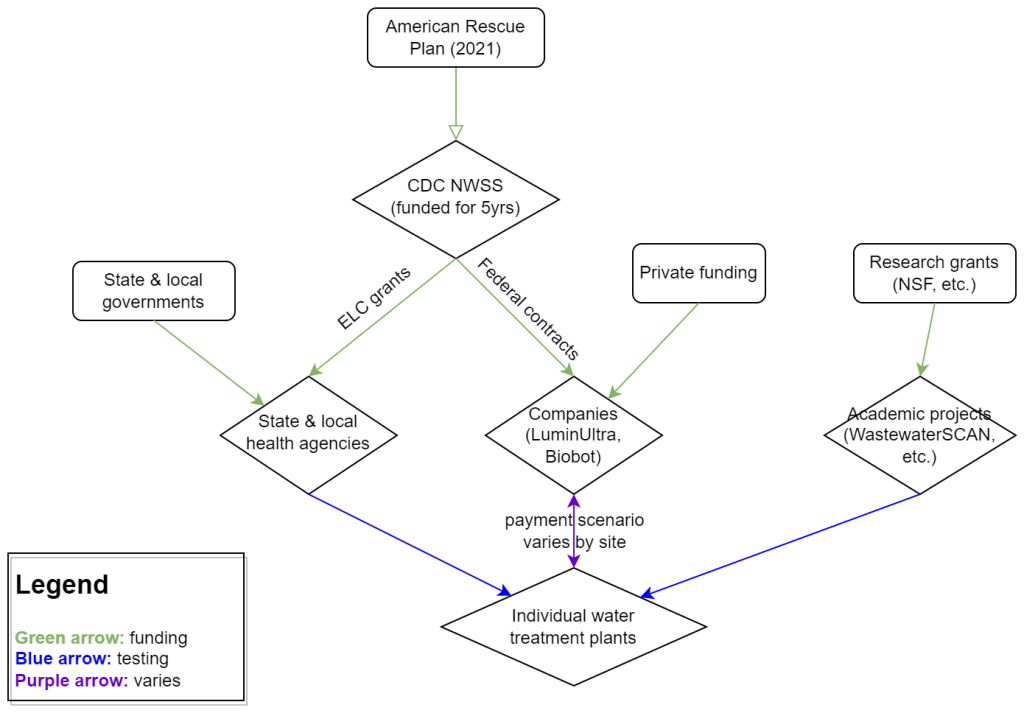
How wastewater surveillance is funded, and concerns for its future

My attempt to explain the wastewater surveillance funding ecosystem in one diagram. (Credit: Betsy Ladyzhets) This week, I have a new story out in Scientific American about why the wastewater surveillance infrastructure built during the pandemic may not last in the long term. While current monitoring projects aren’t likely to go anywhere right now, issues with funding, uneven commitments at state and local levels, and the overall novelty of this field may lead those programs to shut down in the coming years.
Here’s the story’s opening paragraphs:
During the past three years of the pandemic, testing sewage water for the virus that causes COVID has become a valuable tool: it has spotted surging infections and new variants weeks before they showed up in medical clinics, for instance. The technology has also warned of other health threats such as seasonal viruses and increased opioid use.
But now its long-term ability to protect public health is in jeopardy. Funding uncertainty from the federal government and uneven commitments from state health departments have raised the specter that wastewater monitoring programs may shut down in the future.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS), which includes the majority of wastewater testing sites in the U.S., is “fully funded through 2025,” says Amy Kirby, director of the program. But after that, “new sources of sustainable funding” are needed, Kirby says, ideally through the CDC’s regular budget rather than resources tied to COVID. Uncertainty about money—along with logistical challenges and questions about how to interpret data from this relatively novel source—has made some state governments hesitant to invest in the technology, leading to an uneven national system.
My reporting for this piece involved interviews with the CDC, state and local public health agencies, and other major wastewater organizations (Biobot, WastewaterSCAN). I learned a lot about the overall ecosystem for funding wastewater surveillance, including a lot of somewhat-technical details that didn’t make it into the SciAm story. So, I’m sharing some of those details here.
Where wastewater surveillance funding comes from:
The primary funder for wastewater monitoring programs across the U.S. is CDC NWSS. The CDC itself received funding through the American Rescue Plan in 2021, sufficient to fully fund NWSS through 2025.
That CDC funding has gone in two main directions. First, the CDC has funded state and local public health agencies to set up (and maintain) their own wastewater testing projects. This is how most of the states with robust programs (places like New York, Utah, Virginia, Ohio) have funded their efforts. State and local health agencies may also receive funding from their own local governments, though most of the agencies I talked to for my story said they were primarily relying on the CDC. New York State is one major example of a state government funding wastewater surveillance right now.
And second, the CDC has set up national contracts with wastewater testing companies to supplement NWSS in places where monitoring otherwise might not be happening. The agency first contracted with LuminUltra in early 2022, then switched to Biobot Analytics last spring. Earlier this year, Biobot’s contract with the CDC was extended for six months, through July. After that, the agency plans to enter a new, five-year contract with a wastewater testing company that will cover COVID-19 as well as other emerging diseases, like mpox. This contract could go to Biobot or another company; the CDC is currently going through an application process.
Biobot and other private companies like it are also receiving funding from private sources, such as venture capital firms. In addition, individual water treatment facilities, local governments, and even businesses might set up contracts with private companies to help them test the wastewater in their jurisdiction. For example, Toronto’s Pearson Airport has contracted with LuminUltra to test wastewater from the airport terminals. In these cases, funding is coming from the specific organization that wants testing, rather than a larger program. Biobot also tests at hundreds of sites for free through its Biobot Network, in exchange for sharing the data publicly.
Finally, there’s a whole separate ecosystem of academic wastewater surveillance efforts, mostly run by university labs or research centers. WastewaterSCAN is the biggest example of this right now; the project was founded at Stanford and Emory Universities, but has since expanded through grants and philanthropic funding to cover about 150 sites across the country. Most academic projects either partner with specific treatment facilities in their areas or test the sewage on their campuses—SCAN is an exception with its broader scale.
Concerns for wastewater surveillance’s long-term future:
As you can probably tell by this description of the funding landscape, wastewater surveillance in the U.S. is pretty complicated. When scientists started testing wastewater for SARS-CoV-2 in spring 2020, this was basically a grassroots effort with different research projects across the country trying out different things. CDC NWSS has worked hard to compile data into one national system and develop standards, but the system is still far from unified.
For the CDC program to continue its efforts, the agency needs more long-term funding—and this funding shouldn’t be tied to COVID-19. The potential for wastewater surveillance to inform public health decisions goes far beyond this pandemic, and funding should reflect that potential; also, no COVID-specific funding packages have passed Congress since the American Rescue Plan, in 2021.
One way Congress could do this would be by expanding a funding system called “Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases,” or ELC. Most wastewater grants to state and local health agencies over the last couple of years have gone through ELC, though the funding came from the American Rescue Plan. Many of the health officials I talked to for my story like ELC, know how to fill out the annual applications, and would want to keep using it to receive wastewater funding.
Before the pandemic, the ELC program was drastically underfunded, I learned from experts at the Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL). States’ applications historically “vastly exceed the money that CDC is given to put out for them,” APHL policy officer Peter Kyriacopoulos told me. APHL recommends that Congress should expand the program’s funding from $300 million per year (its pre-pandemic benchmark) to $800 million per year, or more. The ELC program is up for renewal this year, which could be an opportunity for Congress to add more permanent funding for wastewater surveillance and other epidemiological efforts.
More permanent funding could go a long way in convincing more state health agencies to invest in wastewater surveillance programs, rather than relying on outside assistance from companies like Biobot or academic partners. More data and guidance on how to actually use wastewater data to inform public health decisions would help, too, since many agencies are still figuring this out. Such investment at the state level would help make the country’s wastewater infrastructure more comprehensive, and more capable of responding to new health threats.
Instead, right now, we have an uneven system. Some places are regularly monitoring for COVID-19 and easily able to expand to new testing targets, while others might lose this valuable data source in the next year or two. For any local reporters reading this, I highly recommend digging into your community’s wastewater surveillance system, and figuring out whether it’s set up for the long term.
More wastewater data
-
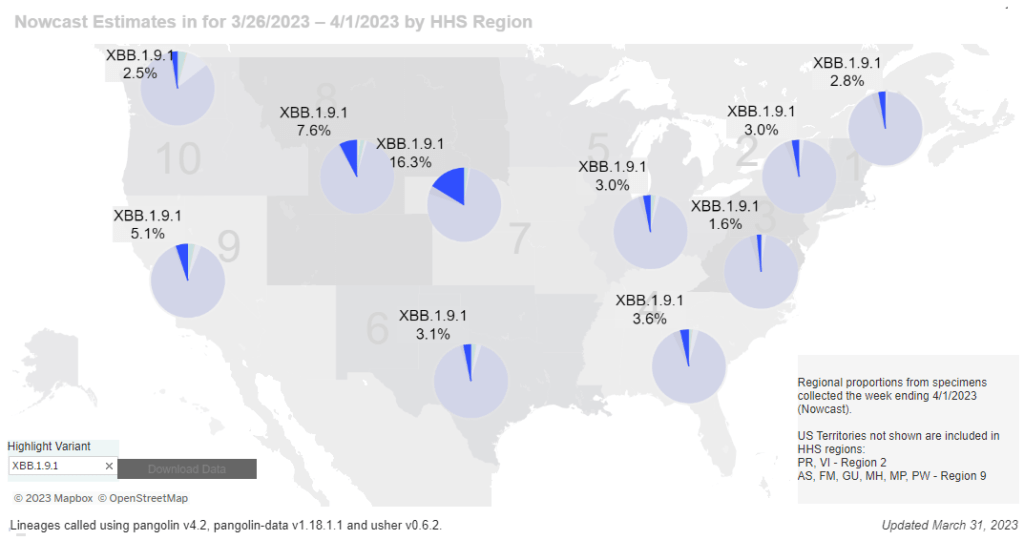
National numbers, April 2

New subvariant Omicron XBB.1.9.1 is most prevalent in the Midwest, according to CDC estimates. In the past week (March 23 through 29), the U.S. officially reported about 140,000 new COVID-19 cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 20,000 new cases each day
- 43 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 9% fewer new cases than last week (March 16-22)
In the past week, the U.S. also reported about 17,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals. This amounts to:
- An average of 2,400 new admissions each day
- 5.1 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 5% fewer new admissions than last week
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 1,600 new COVID-19 deaths (230 per day)
- 88% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.5; 5% by XBB.1.9.1; 2% by XBB.1.5.1; 0.4% by CH.1.1 (as of March 18)
- An average of 40,000 vaccinations per day
While official COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations continue to trend ever-so-slightly downward, wastewater surveillance data show potential new upticks in transmission. Despite continued minimal safety measures in most places, we have to remain wary of a potential spring surge.
Official data from the CDC suggested that cases and new hospital admissions dropped very slightly last week, compared to the week prior. But case data continue to be plagued with reporting delays; again this week, multiple states (Florida, Delaware, Mississippi, Oklahoma) reported no cases or had other issues. These delays make it difficult to assess patterns at state or county levels.
Wastewater surveillance data provide more accurate early warnings about potential rising transmission. This week, Biobot’s data suggest slight increases in all four major regions of the country. It’s worth noting, though, that Biobot’s most recent data are preliminary. I’ll be closely watching the dashboard’s next updates, this coming Tuesday and Thursday.
The latest Omicron variant of concern, XBB.1.9.1, could be one reason for increasing coronavirus levels. This subvariant caused an estimated 5% of new cases across the country nationwide last week, according to the CDC’s Nowcast analysis. At the same time, XBB.1.5 has declined for the first time since it emerged a couple of months ago, suggesting XBB.1.9.1 might slowly outcompete it.
XBB.1.9.1 is most prevalent in the Midwest, particularly the region including Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska. Some counties in this region are also reporting significant coronavirus increases in their wastewater, according to Biobot and WastewaterSCAN. Missouri’s wastewater dashboard similarly shows increases across the state.
In our current era of high background coronavirus spread (and few-to-no widespread safety measures), a new variant can easily cause concerning outbreaks. It’s important to remember that, no matter how much the virus evolves, simple measures like masks and ventilation can still make transmission less likely.
-
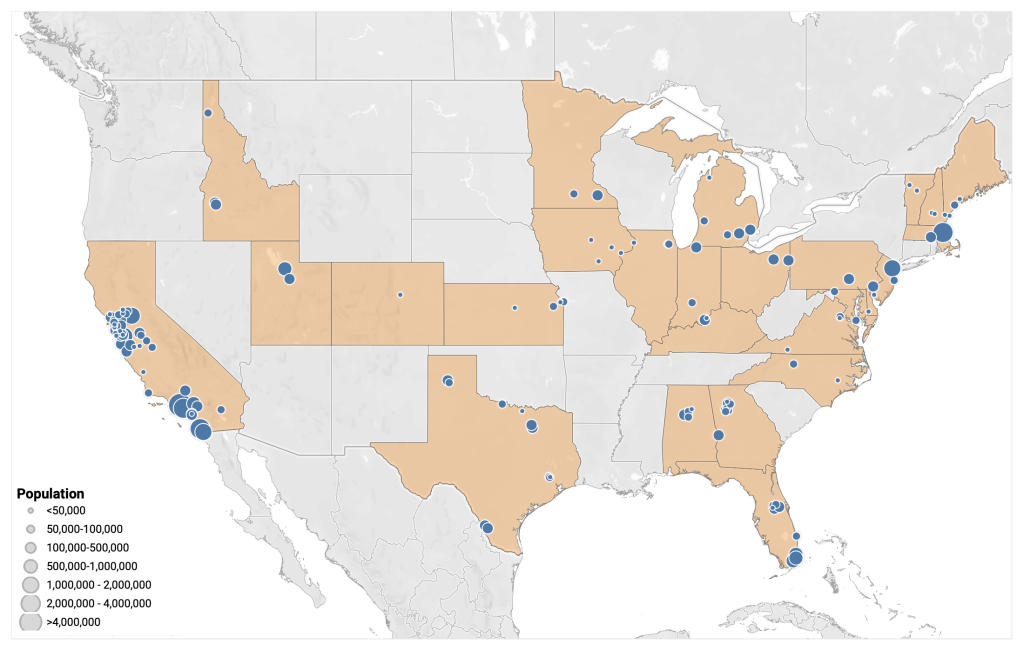
COVID source shout-out: WastewaterSCAN’s newsletter

Map of WastewaterSCAN sites, from the project’s March 24 newsletter. A few weeks ago, I learned that the WastewaterSCAN project has a newsletter, which shares updates about COVID-19 and other diseases nationally and for the Bay Area in California. It’s a helpful resource for following infectious disease trends.
WastewaterSCAN, for any readers who might be unfamiliar, is a wastewater surveillance project founded by researchers at Stanford and Emory Universities. The project started in 2020 by monitoring wastewater in the Bay Area for SARS-CoV-2, but has since expanded to about 150 sites nationwide and six testing targets: the coronavirus, flu, RSV, mpox, norovirus, and human metapneumovirus (HMPV).
In the newsletter, the SCAN team shares summary data about all of these diseases, as well as some variant analysis for SARS-CoV-2. The language is sometimes a bit technical (as its primary audience is the team’s academic and public health partners), but still very useful for seeing where diseases are rising or falling. SCAN’s local updates are especially helpful for anyone living in the Bay Area.
Also, the SCAN team recently had a paper published in the Lancet discussing their work monitoring wastewater for diseases beyond COVID-19. The new article shows this technology’s potential for broader public health surveillance.
-
Sources and updates, March 19
- Long-term effects of COVID-19 on kids: The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) recently published a report about how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted children and families. It includes a variety of health impacts (physical, behavioral, mental), interventions taken by schools and other institutions, access to healthcare coverage, impacts of COVID-related economic policies, and recommendations for addressing this issue in the future. The report’s authors note that, for “almost every outcome” related to health and well-being, COVID-19’s impacts were worse for Black, Hispanic/Latino, Native American, and low-income families.
- Shorter sleep duration during the pandemic: On a similar topic: the CDC’s Preventing Chronic Disease journal recently published an article about teenagers’ sleep habits during the pandemic. The study used data from the 2021 Adolescent Behaviors and Experiences Survey, a nationally-representative survey of high school students. About three-quarters of students surveyed slept for less than eight hours a night, and students who slept less were more likely to report that doing their schoolwork became more difficult during the pandemic. While shorter sleep was becoming an issue before COVID-19, this study shows how COVID-related stress may have exacerbated the problem.
- Maternal mortality keeps getting worse: This week, the CDC released its most recent, official statistics on maternal mortality in the U.S. The new data reflect deaths in 2021, and show that mortality rates rose to about 33 deaths per 100,000 births, compared to rates closer to 20 per 100,000 births in 2020 and 2019. Mortality rates were more than 2.5 times higher for Black women compared to white women. For more recent data (and additional demographic figures), see this story and GitHub repository from MuckRock, also shared in last week’s newsletter.
- WHO updates its variant tracking system: The World Health Organization announced on Thursday that it will start classifying subvariants of Omicron as distinct Variants of Interest (VOIs) and Variants of Concern (VOCs), and will assign new Greek-letter names to VOCs. Omicron lineages have accounted for the vast majority of coronavirus circulating globally since early 2022, but all subvariants have previously been clustered under that one Greek-letter name. Now, the WHO will give us new names as needed, hopefully making future variants a bit easier to talk about. The WHO also updated its definitions for classifying new subvariants as VOCs or VOIs.
- Wastewater monitoring continues to expand: Two updates about local wastewater surveillance programs caught my attention this week. First, the City of Chicago’s public health department has announced it will start monitoring wastewater for polio, in collaboration with the University of Illinois, state health department, and national CDC. And second, two local agencies in the Bay Area, California recently started testing wastewater for traces of drugs, including fentanyl, methamphetamine, cocaine, and nicotine. We’ll likely see more announcements like this across the U.S. as agencies continue to expand their wastewater surveillance programs beyond COVID-19.
-
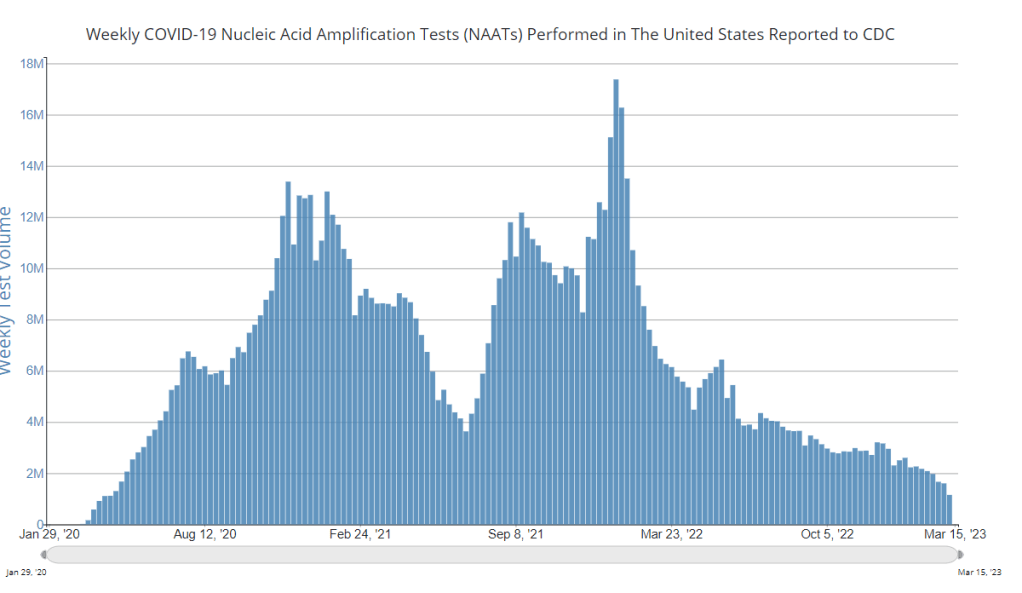
At-home tests, wastewater: COVID-19 testing after the public health emergency ends

Nationwide, fewer people are getting lab-based COVID-19 tests now than at any time since the start of the pandemic. Chart via the CDC. When the public health emergency ends this spring, COVID-19 testing is going to move further in two separate directions: rapid, at-home tests at the individual level, and wastewater testing at the community level.
That was my main takeaway from an online event last Tuesday, hosted by Arizona State University and the State and Territory Alliance for Testing. This event discussed the future of COVID-19 testing following the public health emergency, with speakers including regulatory experts, health officials from state agencies, and executives from diagnostic companies.
“The purpose of testing has shifted” from earlier in the pandemic, said Dr. Thomas Tsai, the White House’s COVID-19 testing coordinator, in opening remarks at the event. Public health agencies previously used tests to monitor COVID-19 in their communities and direct contact-tracing efforts; now, individual tests are mostly used for diagnosing people, and the resulting data are widely considered to be a major undercount of true cases.
While the speakers largely agreed about the continued value of rapid, at-home tests (for diagnosing people) and wastewater surveillance (for tracking COVID-19), they saw a lot of challenges ahead for both technologies. Here are some challenges that stuck out to me.
Challenges for rapid, at-home tests:
The public health emergency’s end won’t have an immediate impact on which COVID-19 tests are available, health policy researcher Christina Silcox from Duke University explained at the event. But, in the coming months, the FDA is likely to also end its emergency use authorization for COVID-19 diagnostics. As a result, companies that currently have tests authorized under this emergency will need to apply for full approval. Relatively few rapid tests are currently approved in this way, so the change could lead to fewer choices for people buying tests.
At the same time, it will become harder for many Americans to access rapid tests. After the federal emergency ends, private insurance companies will no longer be required to cover rapid tests. Some insurance providers might still do this (especially if large employers encourage it), said Amy Kelbik from McDermott+Consulting, but it will no longer be a universal option. At the same time, Medicare will stop covering rapid tests; Medicaid coverage will continue through fall 2024.
In light of these federal changes, state health officials at the ASU event talked about a need for continued funding to support rapid test distribution from state and local agencies. “Testing will continue to inform behavior, but will become drastically less available,” said Heather Drummond, testing and vaccine program leader at the Washington State Department of Health. Washington has led a free test distribution program, but it’s slated to end with the conclusion of the federal health emergency, Drummond said; she’d like to see services like this continue for the people who most need free tests.
Drummond and other health officials also discussed the challenges of educating people about how to interpret their test results, as COVID-19 guidance becomes less widely available. The vast majority of rapid, at-home test results are not reported to public health agencies—and, based on the event’s speakers, this isn’t a problem health agencies are particularly interested in devoting resources to solving right now. But as rapid tests become the default for diagnosing COVID-19, continued outreach will be needed on how to use them.
Also, as I’ve written before, some PCR testing infrastructure should still be maintained, for cases when someone needs a more definitive test result or wants documentation in case of long-term symptoms. PCR test access will likely get even worse after the federal health emergency ends, though, as insurance plans will also stop covering (or cover fewer costs for) these tests.
Challenges for wastewater surveillance:
Overall, wastewater surveillance is the best source for community-level COVID-19 data, speakers at the ASU event agreed. Official case numbers represent significant undercounts of true infections, and hospitalizations (while more reliable) are a delayed indicator. Wastewater data are unbiased, real-time, population-level—and the technology can be expanded to other common viruses and health threats, health officials pointed out at the event.
But wastewater surveillance is still very uneven across the U.S. It’s clear just from looking at the CDC’s map that some states have devoted resources to detailed wastewater testing infrastructure, with a testing site in every county—while others just have a handful of sites. Funding uncertainty likely plays a role here; speakers at the event expressed some confusion about the availability of CDC funds for long-term wastewater programs.
The CDC’s wastewater surveillance system has also faced challenges with standardizing data from different testing programs. And, at state and local agencies, health officials are still figuring out how to act on wastewater data. Agencies with more robust surveillance programs (such as Massachusetts, which had two officials speak at the ASU summit) may be able to provide success stories for other agencies that aren’t as far along.
Broader testing challenges:
For diagnostic company leaders who spoke at the event, one major topic was regulatory challenges. Andrew Kobylinski, CEO and co-founder of Primary.Health, said that the FDA’s test requirements prioritize highly accurate tests, even though less sensitive (but easier to use) tests might be more useful in a public health context.
Future COVID-19 tests—and tests for other common diseases—may need a new paradigm of regulatory requirements that focus more on public health use. At the same time, health agencies and diagnostic companies could do more to collect data on how well different test options are actually working. While it’s hard to track at-home tests on a large scale, more targeted studies could help show which tests work best in specific scenarios (such as testing after an exposure to COVID-19, or testing to leave isolation).
Company representatives also talked about financial challenges for developing new tests, particularly as interest in COVID-19 dies down and as recession worries grow this year. While a lot of biotech companies dove into COVID-19 over the last three years, they haven’t always received significant returns on their investments. For example, Lucira, the company behind the first flu-and-COVID-19 at-home test to receive authorization, recently filed for bankruptcy and blamed the long FDA authorization process.
Mara Aspinall, the ASU event’s moderator and a diagnostic expert herself, ended the event by asking speakers whether COVID-19 has led to lasting changes in this industry. The answer was a resounding, “yes!” But bringing lessons from COVID-19 to other diseases and health threats will require a lot of changes—to regulatory processes, funding sources, data collection practices, and more.
More testing data
-
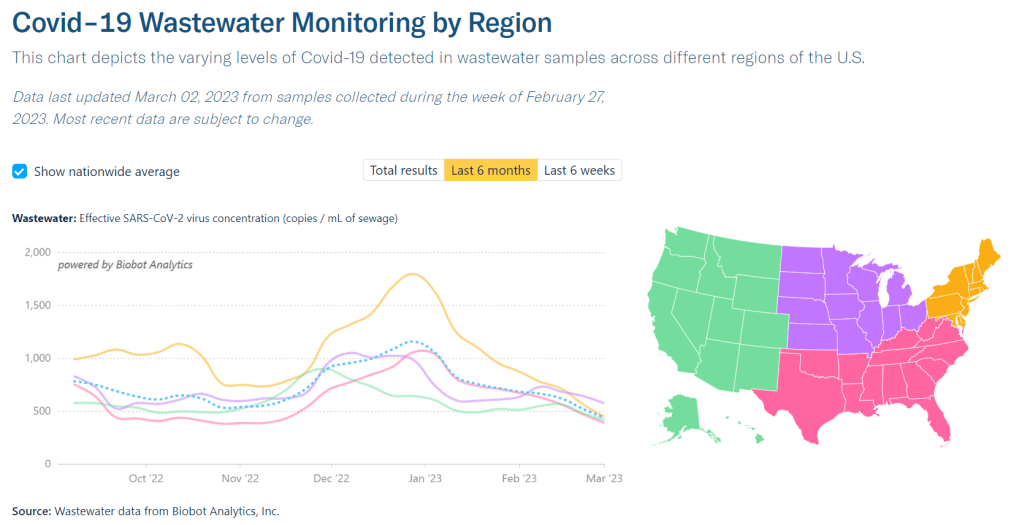
National numbers, March 5

Wastewater data from Biobot suggest that COVID-19 spread is still declining throughout the country, but slowly. In the past week (February 23 through March 1), the U.S. officially reported about 230,000 new COVID-19 cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 32,000 new cases each day
- 69 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 5% fewer new cases than last week (February 16-22)
In the past week, the U.S. also reported about 23,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals. This amounts to:
- An average of 3,300 new admissions each day
- 7.1 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 8% fewer new admissions than last week
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 2,300 new COVID-19 deaths (330 per day)
- 90% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.5; 8% by BQ.1 and BQ.1.1; 1% by CH.1.1 (as of March 4)
- An average of 50,000 vaccinations per day
At the national level, major COVID-19 metrics continue to indicate slow declines in transmission. As I’ve been writing for the last few weeks, we’re at a “low tide” point in COVID-19 spread: clearly lower than the peaks that occur after holidays or new variants, but much higher than the baselines that we experienced before the Omicron era.
Official cases reported by the CDC dropped by 5% last week compared to the week prior, while new hospital admissions dropped by 8%. Wastewater data from Biobot show declining coronavirus levels nationally, but viral concentrations in wastewater are twice as high as they were at this point in 2021 or 2022.
Biobot’s regional data suggest that the Midwest has overtaken the Northeast in coronavirus concentrations for the first time since late summer 2022. Both regions are seeing declines, but the declining spread in the Northeast has accelerated a bit faster than that in the Midwest.
While most individual states and counties are reporting COVID-19 declines as well, a few have reported increased coronavirus in their wastewater in recent weeks. This includes counties in Idaho, Wyoming, Montana, Florida, Texas, and others in the Midwest and South.
Omicron XBB.1.5 continues to be the dominant variant in the U.S., now accounting for about 90% of new cases in the last week, per CDC estimates. Viral evolution experts will be watching to see if XBB.1.5 mutates further, or if some other variant arrives to compete with it.
As we head into the spring, U.S. COVID-19 data continue to get harder to find and less reliable. Last week, the Department of Health and Human Services announced that it would retire its Community Profile Reports, which I used to rely on as a regular source for this newsletter.
Meanwhile, a study from Denis Nash and his team at the City University of New York that estimated true COVID-19 prevalence during the BA.4/BA.5 surge last summer was recently published in the journal Preventative Medicine. I covered this study when it was released as a preprint last fall, and find it striking that no other estimates like this have emerged since then.
-
Sources and updates, February 26
- Deaths in U.S. prisons: Throughout the pandemic, the UCLA COVID Behind Bars Data Project has been a leading source for data on COVID-19 cases and deaths in carceral settings. As COVID-specific data on prisons and jails have become more sporadic, the project recently turned its attention to overall mortality data in these settings. Last week, the UCLA team released a new dataset sharing all-cause deaths in prisons through 2020, which combines data from public reports and records requests. The full dataset is available on GitHub, and a summary of this project’s findings on all-cause mortality was published in the New York Times last weekend.
- BIOFIRE syndromic trends data: BIOFIRE Diagnostics is a biotech company focused on diagnostic testing, offering tests for a variety of viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens. The company publishes anonymized test results from its labs on its Syndromic Trends dashboard; this dashboard is a helpful way to get an overview of test positivity for COVID-19 compared to other common diseases. (H/t Force of Infection.)
- R&D roadmap for COVID-19 vaccines: The University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy has published a new report outlining the research and development steps needed for the world to produce coronavirus vaccines that are “broadly protective,” not tied to a specific variant. It includes recommendations for research on virology, immunology, and vaccine technologies, along with information on using animal models and guidance on vaccine policy. Related: the CDC’s Advisory Community on Immunization Practices met this week to discuss COVID-19 and other vaccines.
- CDC reports on travel surveillance: Two new studies about COVID-19 among international travelers to the U.S. were published in this week’s CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Both studies describe results from the agency’s Travel Surveillance program, which is a collaboration with biotech company Ginkgo Bioworks and testing company XpresCheck. One report compares traveler test results from before and after the U.S. ended its pre-departure testing requirement for international flights, finding that travelers were much more likely to have COVID-19 after the requirement was lifted. The second report provides results from a pilot program testing airplane wastewater at JFK Airport; this report found that the vast majority of plane samples tested were positive for SARS-CoV-2, and researchers identified a variety of Omicron variants. More work is needed to really get airplane wastewater testing going in the U.S., but it’s good to see early results showing this program’s feasibility.
- Early data from XBB.1.5 in NYC: Another notable study in CDC MMWR this week provided analysis from New York City’s health department on Omicron XBB.1.5. The subvariant was first identified in the city in October 2022 (though it may have evolved somewhere else), and quickly spread through the region; it accounted for 81% of sequenced COVID-19 test samples by early January. The NYC health department linked sequencing data with patient outcomes data, finding that people infected with XBB.1.5 were not significantly more likely to be hospitalized or to die from COVID-19 compared to those infected with other variants. In other words, XBB.1.5 appears to not cause more severe disease, based on this report.
- Predicting COVID-19 cases based on wastewater results: One more newsworthy study to share this week: researchers at Hokkaido University developed a mathematical model to predict COVID-19 cases based on coronavirus concentration levels in Sapporo, Japan. I’m always on the lookout for studies like this, as wastewater data become increasingly important to track true infection numbers. (Here’s a prior example, from the University of Florida.) Of course, it’s worth noting that the Hokkaido researchers had consistent wastewater and case data from spring 2020 through 2022 to use for their model; for wastewater researchers working in the U.S. now, that consistency is often harder to achieve.
-
COVID-19 is inspiring improvements to surveillance for other common viruses
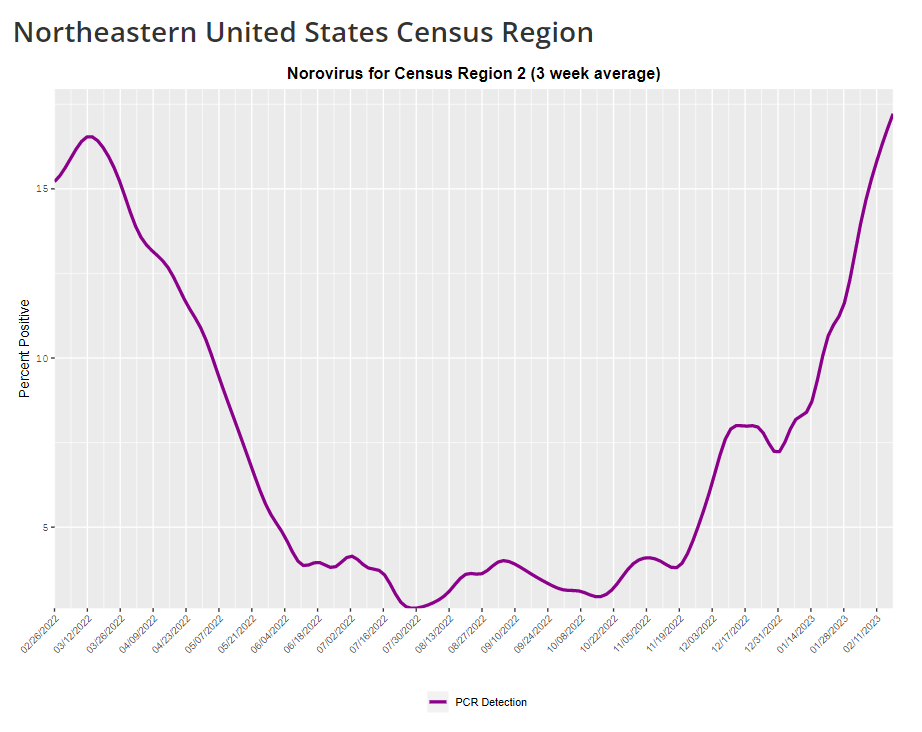
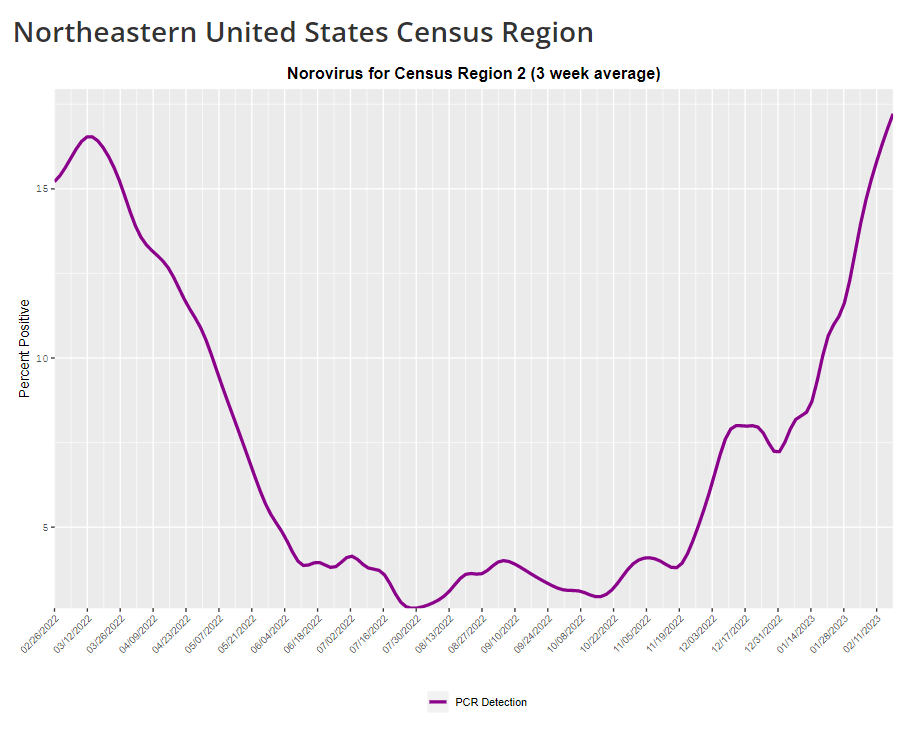
The CDC provides norovirus test positivity data from a select number of labs that report test results for this virus. Due to limited reporting, data are only available at the regional level. This week, I have a new story out in Gothamist and WNYC (New York City’s public radio station) about norovirus, a nasty stomach bug that appears to be spreading a lot in the U.S. right now. The story shares some NYC-specific norovirus information, but it also talks more broadly about why it’s difficult to find precise data on this virus despite its major implications for public health.
Reporting this story led me to reflect on how COVID-19 has revealed cracks in the country’s infrastructure for tracking a lot of common pathogens. I’ve written previously about how the U.S. public health system monitored COVID-19 more comprehensively than any other disease in history; the scale of testing, contact tracing, and innovation into new surveillance technologies went far beyond the previous standards. Now, people who’ve gotten used to detailed data on COVID-19 have been surprised to find out that such data aren’t available for other common pathogens, like the flu or norovirus.
It might feel disappointing to realize how little we actually know about the impacts of endemic diseases. But I choose to see this as an opportunity: as COVID-19 revealed gaps in public health surveillance, it inspired development in potential avenues to close those gaps. Wastewater surveillance is one big example, along with the rise of at-home tests and self-reporting mechanisms, better connectivity between health systems, mobility data, exposure notifications, and more.
Norovirus is a good example of this trend. Here are a few main findings from my story:
- Norovirus is a leading cause of gastrointestinal disease in the U.S., and is estimated to cause billions of dollars in healthcare and indirect societal costs every year.
- People who become infected with norovirus are often hesitant to seek medical care, because the symptoms are disgusting and embarrassing. Think projectile vomit, paired with intense diarrhea.
- Even when patients do seek medical care, norovirus tests are not widely available, and there isn’t a ton of incentive for doctors to ask for them. Testing usually requires a stool sample, which patients are often hesitant to do, one expert told me.
- The virus is not a “reportable illness” for the CDC, meaning that health agencies and individual doctors aren’t required to report norovirus cases to a national monitoring system. (So even when a patient tests positive for norovirus, that result might not actually go to a health agency.)
- The CDC does require health agencies and providers to report norovirus outbreaks (i.e. two or more cases from the same source), but national outbreak estimates are considered to be a vast undercount of true numbers.
- Even in NYC, where the city’s health agency does require reporting of norovirus cases, there’s no recent public data from test results or outbreaks. (The latest data is from 2020.)
As I explained in an interview for WNYC’s All Things Considered, the lack of a national reporting requirement and other challenges with tracking norovirus are linked:
It seems like the lack of a requirement and the difficulty of tracking kind-of play into each other, where it’s not required because it’s hard to track—but it’s also hard to track because it’s not required.
The lack of detailed data on pathogens like norovirus can be frustrating on an individual level, for health-conscious people who might want to know what’s spreading in their community so that they can take appropriate precautions. (For norovirus, precautions primarily include rigorous handwashing—hand sanitizer doesn’t work against it—along with cleaning surfaces and care around food.)
These data gaps can also be a challenge for public officials, as more detailed information about where exactly a virus is spreading or who’s getting sick could inform specific public health responses. For example, if the NYC health department knew which neighborhoods were seeing the most norovirus, they could direct handwashing PSAs to those areas. In addition, scientists who are developing norovirus vaccines could use better data to estimate the value of those products, and determine who would most benefit.
So, how do we improve surveillance for norovirus and other viruses like it? Here are a few options I found in my reporting:
- Wastewater surveillance, of course. The WastewaterSCAN project is already tracking norovirus along with coronavirus and several other common viruses; its data from this winter has aligned with other sources showing a national norovirus surge, one of the project’s principal investigators told me.
- Better surveillance based on people’s symptoms. The Kinsa HealthWeather project offers one example; it aggregates anonymous information from smart thermometers and a symptom-tracking app to provide detailed data on respiratory illnesses and stomach bugs.
- At-home tests, if they’re paired with a mechanism for people to report their results to a local public health agency. Even without a reporting mechanism, at-home tests could help curb outbreaks by helping people recognize their illness when they might be asymptomatic.
- Simply increasing awareness and access to the tests that we already have. If more people go to the doctor for gastrointestinal symptoms and more doctors test for norovirus, our existing data would get more comprehensive.
Are there other options I’ve missed? Is there another pathogen that might be a good example of common surveillance issues? Reach out and let me know.
-
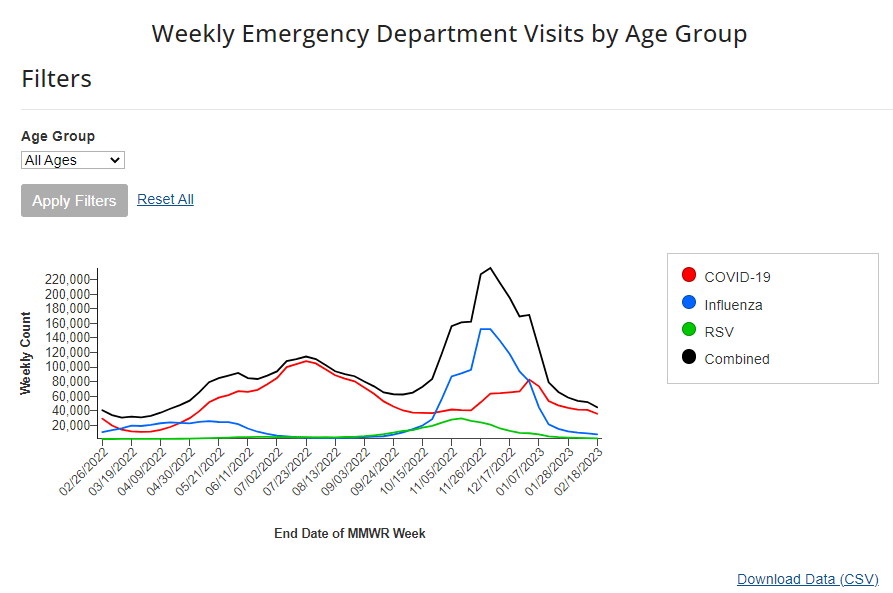
National numbers, February 26
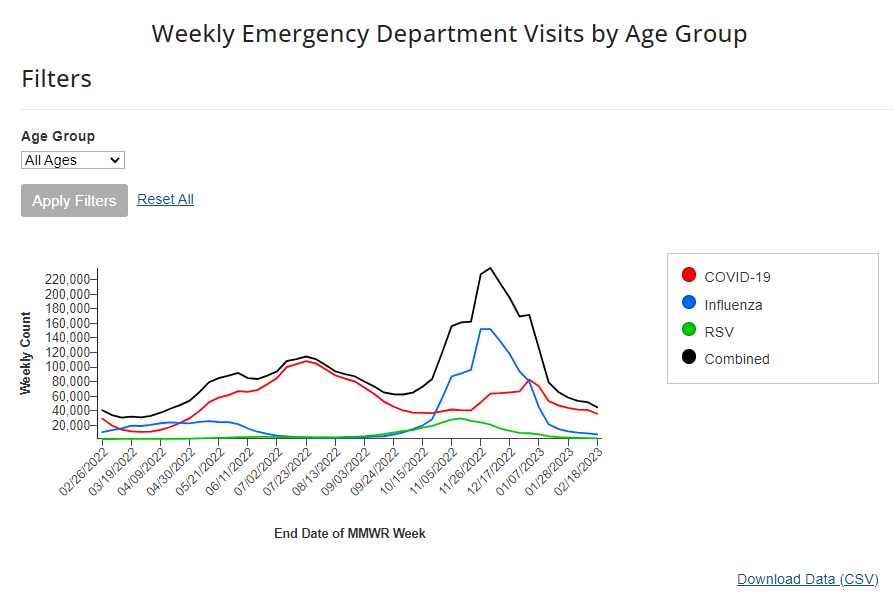
According to the CDC’s data on hospital emergency department visits for respiratory viruses, COVID-19 visits have plateaued while flu and RSV have returned to low levels. In the past week (February 16 through 22), the U.S. officially reported about 240,000 new COVID-19 cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 34,000 new cases each day
- 72 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 9% fewer new cases than last week (February 9-15)
In the past week, the U.S. also reported about 25,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals. This amounts to:
- An average of 3,500 new admissions each day
- 7.5 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 5% fewer new admissions than last week
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 2,400 new COVID-19 deaths (350 per day)
- 85% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.5; 12% by BQ.1 and BQ.1.1; 1% by CH.1.1 (as of February 25)
- An average of 60,000 vaccinations per day
The national COVID-19 plateau continues. As I’ve been saying for a few weeks now, COVID-19 spread has dropped significantly from its high during the winter holidays, but it has not fallen to the low levels we’ve previously seen this time of year due to a combination of lax precautions and the latest Omicron variant, XBB.1.5.
Case and hospitalization data from the CDC, along with wastewater surveillance data, all show COVID-19 spread declining—but very slowly. Cases declined by 9% this week compared to the week prior, while new hospital admissions declined by 5%. Biobot’s wastewater surveillance dashboard shows slight declines or plateaus in all four major regions of the country.
Respiratory virus season is clearly waning in the U.S., according to hospital emergency room visit data from the CDC’s National Syndromic Surveillance Program. ER visits for the flu and RSV have pretty much returned to baseline after their winter peaks. But COVID-19 ER visits have plateaued at a higher level, close to the visit numbers reported in September and October—another sign of the elevated “low tide” we’ve now been dealing with since spring 2022.
On the variant front: Omicron XBB.1.5 continues to dominate in the U.S. It caused an estimated 85% of new cases nationwide in the week ending February 25, according to the CDC, and is the main variant circulating in every region. After several months of “variant soup” with a number of Omicron subvariants competing, XBB.1.5 has emerged as the clear victor; no other single lineage is causing more than 10% of new cases in the country, per the CDC’s estimates.
I continue to write about COVID-19 case numbers from the CDC here, mostly because A) the directional patterns (i.e. upticks and downturns) of these data are still a decent representation of actual directional patterns in infections, and B) the CDC’s case numbers are more nationally representative (when it comes to geography) than data from the National Wastewater Surveillance System.
But I have to stress that these case numbers are increasingly undercounting actual infections. The last decent estimates I’ve seen comparing cases to infections, dated from last fall, suggested that case numbers are undercounted by a factor of 10 to 20. These days, I expect we’re likely closer to a factor of 20, if not higher. As evidence, test positivity for the entire U.S. has been at 10% for a couple of weeks now.
Other evidence for this continued undercounting comes from wastewater data. From resources like the Biobot dashboard, which compares wastewater surveillance trends to case trends, it’s abundantly clear that these two metrics used to align closely—but now coronavirus levels in wastewater are consistently much higher. In New York City, for example, wastewater data show that the city experienced one of its greatest COVID-19 surges this winter.
Speaking of unreliable numbers: the team behind the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review has begun to update its readers on how the end of the federal public health emergency will impact COVID-19 data. The first update, published on Friday, explains that some data, including hospitalization and vaccination numbers, “may be reported less frequently” or with new gaps. I anticipate we’ll get more details about this in the coming weeks, as the CDC negotiates new data-sharing requirements with other health agencies.
The CDC’s data tracking newsletter is also shifting from a weekly newsletter to biweekly, starting March 3. It continues to boggle my mind how I, a single freelance journalist writing this publication in my spare time, am able to keep up more regular data updates than a massive federal agency.