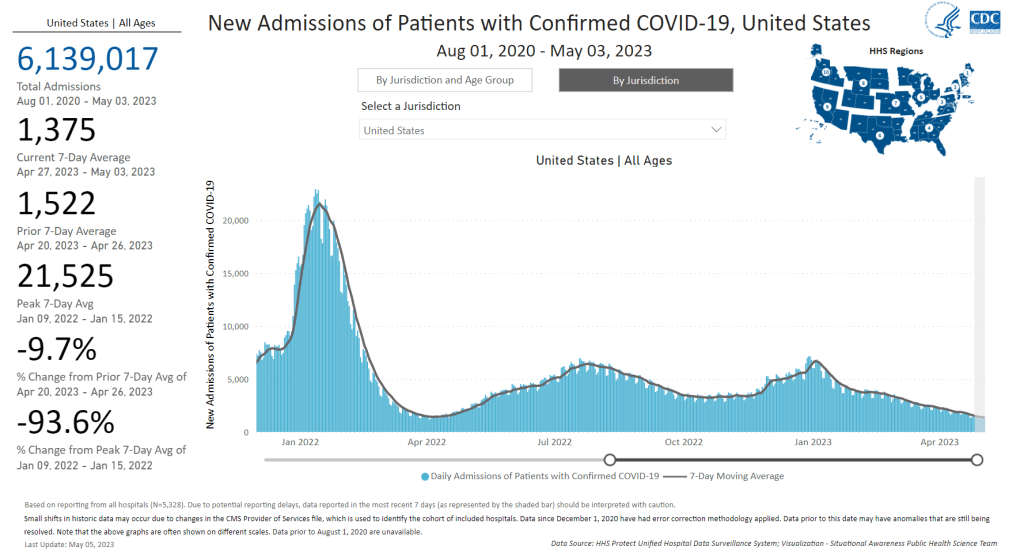
In the past week (April 30 through May 6), the U.S. reported about 9,500 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 1,400 new admissions each day
- 2.9 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 7% fewer new admissions than last week (April 22-29)
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
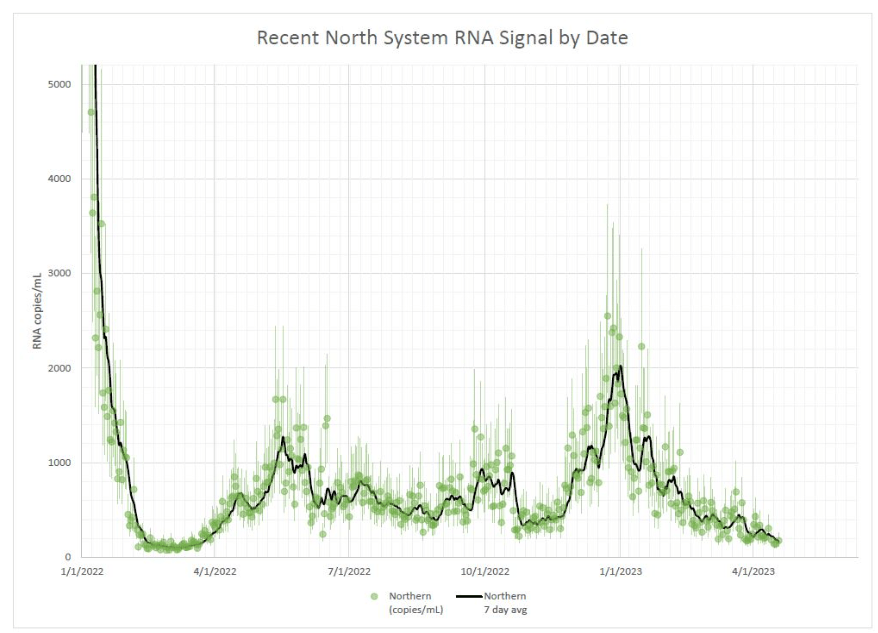
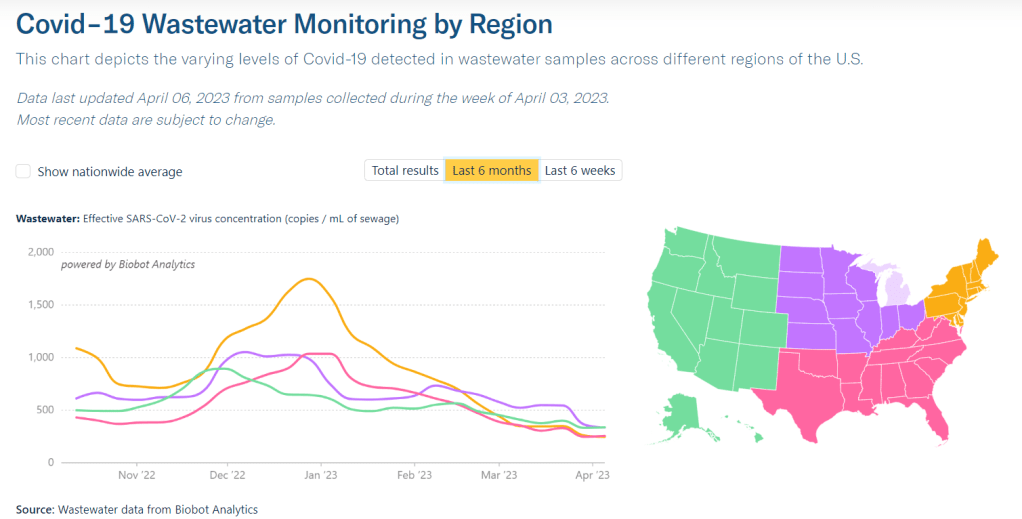
- A 14% lower concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater than last week (as of May 10, per Biobot’s dashboard)
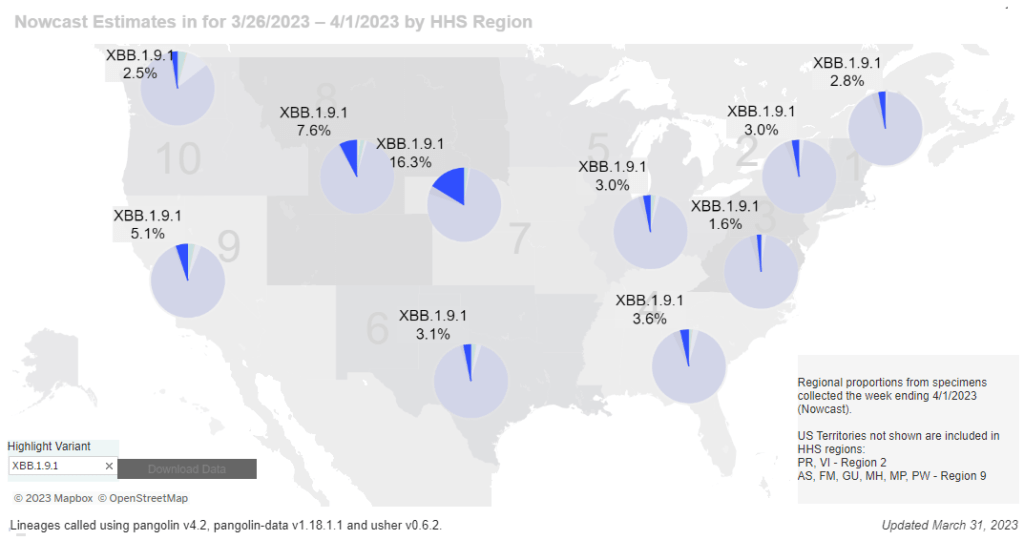
- 64% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.5; 13% by XBB.1.9; 14% by XBB.1.16 (as of May 13)
- An average of 70,000 vaccinations per day
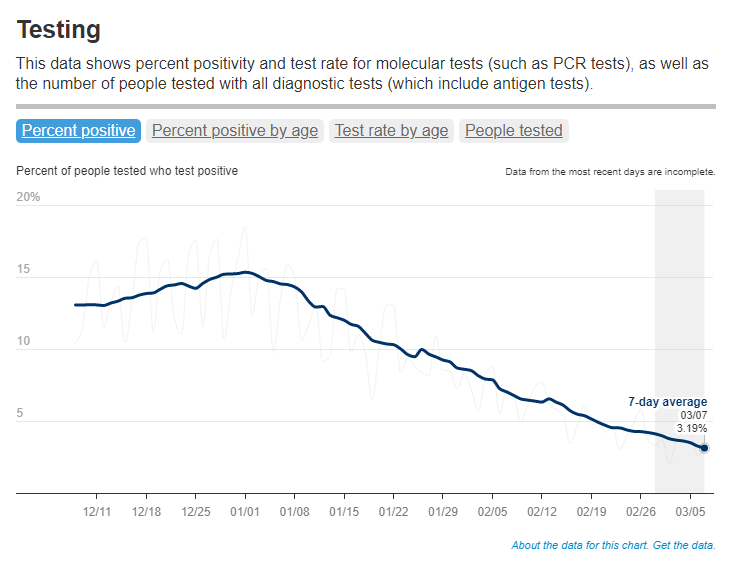
COVID-19 spread continues to trend down in the U.S., though our data for tracking this disease is now worse than ever thanks to the end of the federal public health emergency. If newer Omicron variants cause a surge this summer, those increases will be hard to spot.
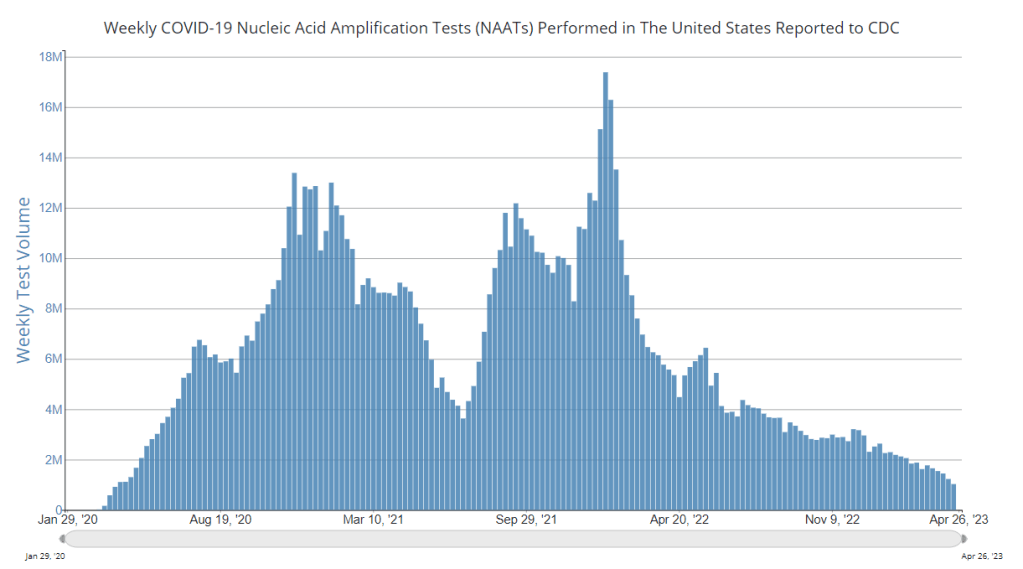
As a result of the PHE’s conclusion this week, the CDC is no longer collecting national case counts or testing data. Instead, the agency now recommends using hospitalization data to monitor how hard COVID-19 is hitting your community—even though this metric typically lags behind actual infection patterns—while variant data and wastewater surveillance may provide warnings about new surges.
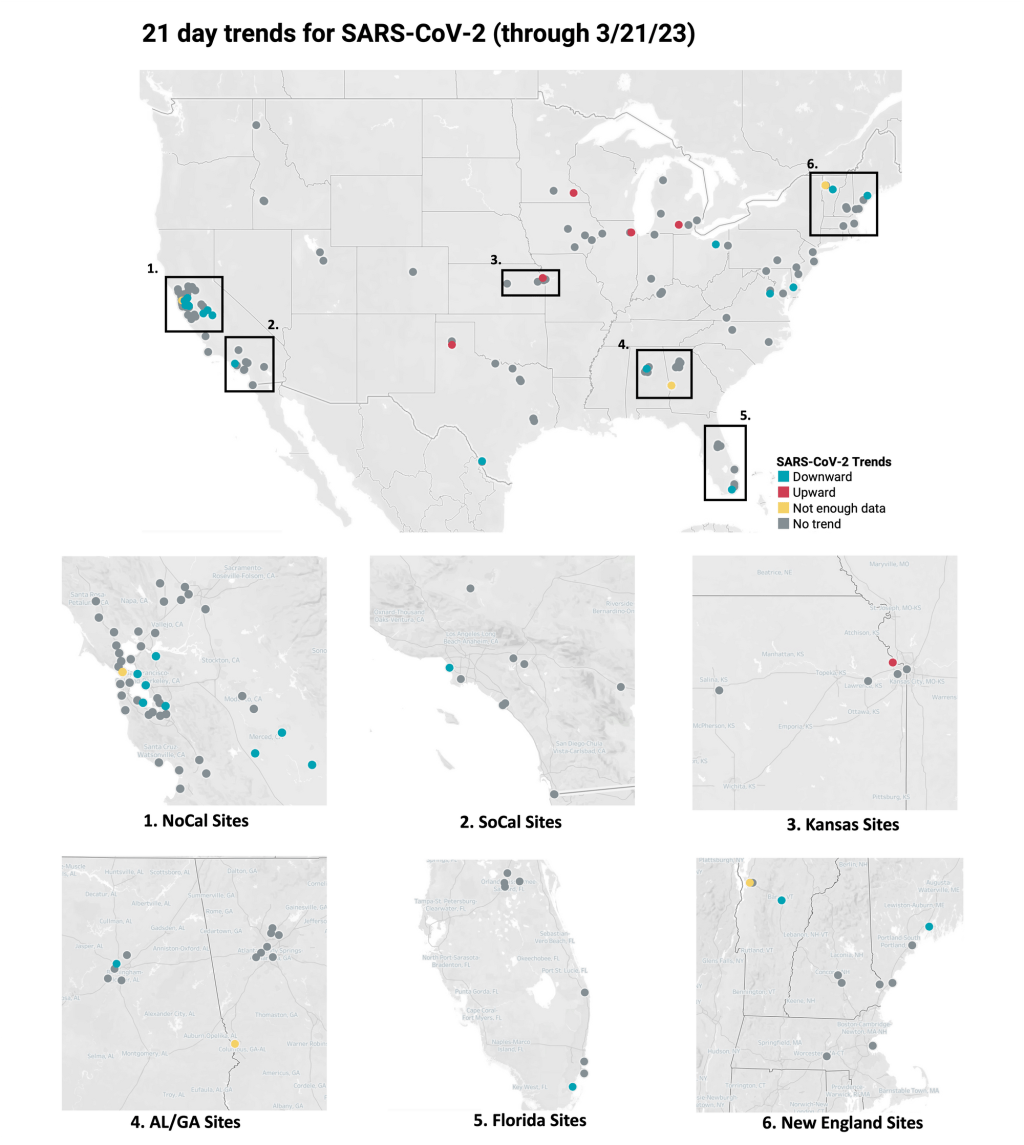
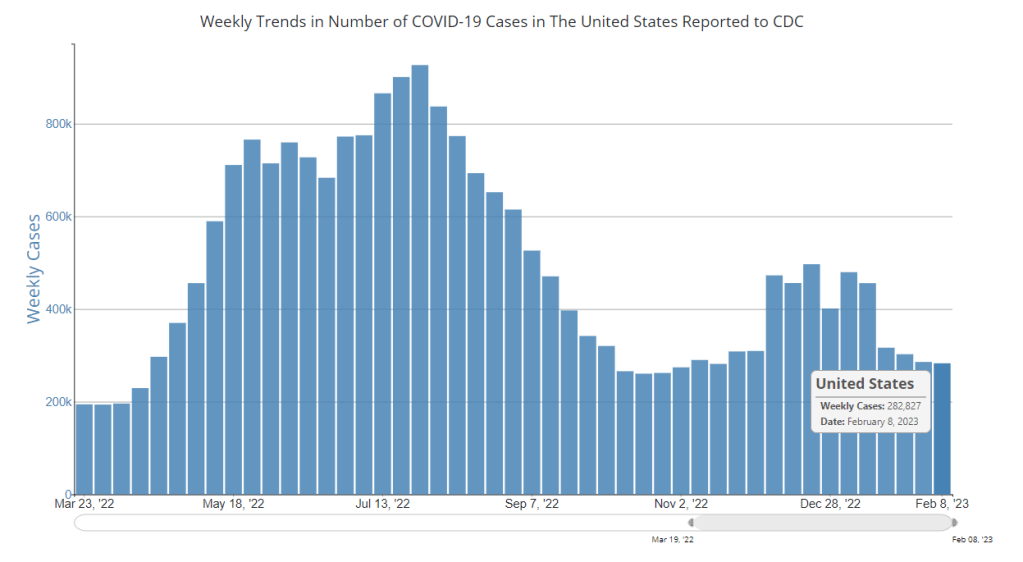
My national updates will take a similar approach. This week, hospital admissions continue their national plateau, with a decrease of about 7% from the week ending April 29 to the week ending May 6. The CDC’s national map show that admissions are low across the country, with 99% of counties reporting fewer than 10 new admissions per 100,000 residents.
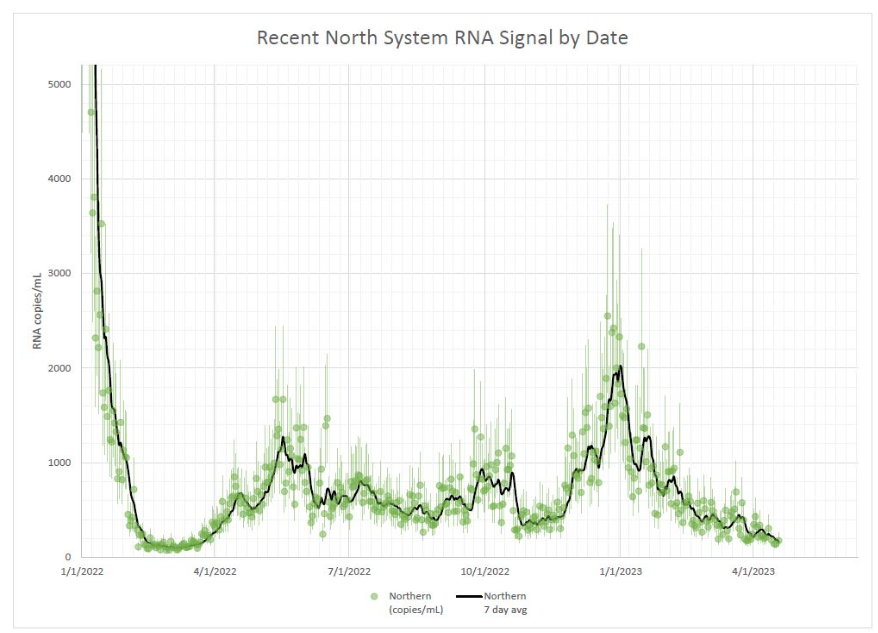
Wastewater surveillance also suggests that, while there’s still a lot of COVID-19 in the U.S., disease spread is still on a plateau or slight decline in most of the country. Biobot’s data show a minor national downturn in recent weeks; trends are similar across the four major regions, though the decline is a bit steeper on the West Coast.
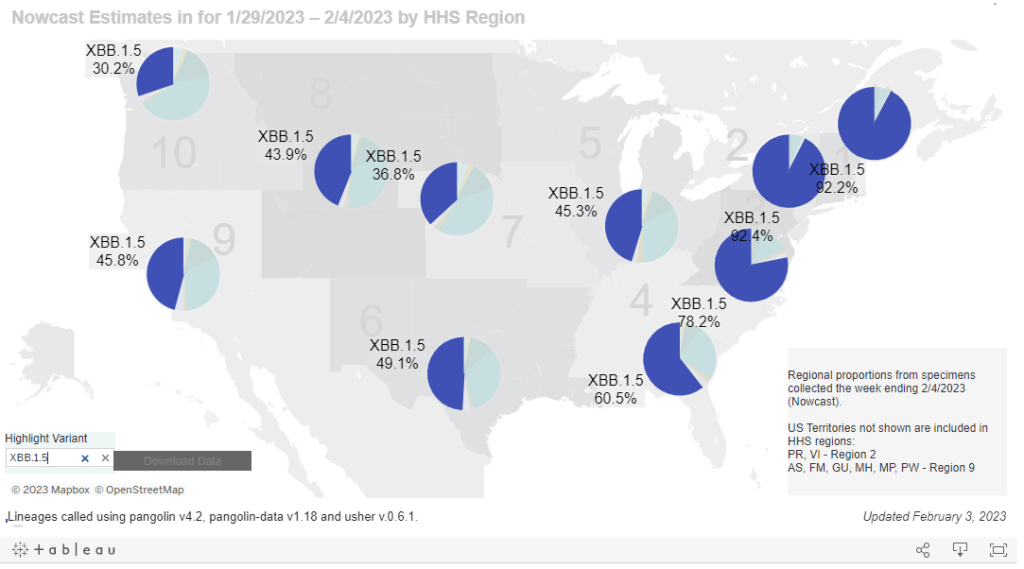
The variant picture also hasn’t changed much: XBB.1.5 caused about two-thirds of new cases in the last two weeks, according to the CDC’s estimates. XBB.1.6 caused about 14% and XBB.1.9 caused 13%; these newer versions of Omicron are gaining ground, but fairly slowly. Regionally, XBB.1.6 is most prevalent in the Northeast and on the West Coast, while XBB.1.9 is most prevalent in the Midwest.
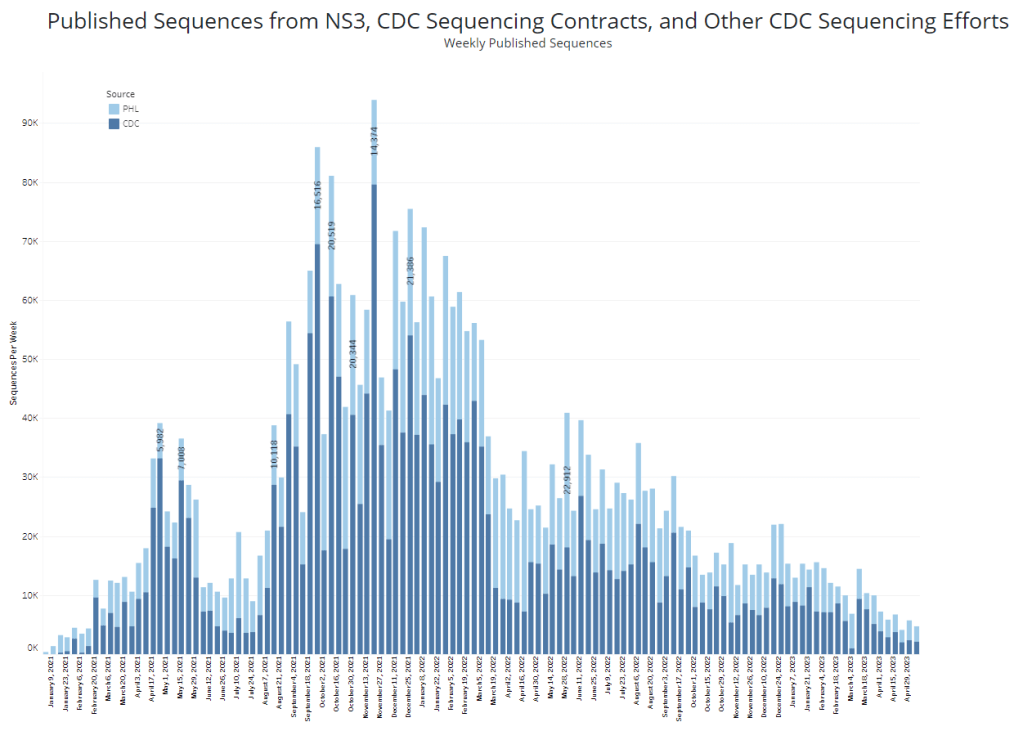
It’s worth noting, though, that the CDC has switched its variant reporting from weekly to every other week, as fewer patient specimens are going through sequencing for variant identification. The agency and its surveillance partners are sequencing around 5,000 samples every week, compared to over 80,000 a week at the height of the first Omicron surge.
Limited sequencing efforts will make it harder for the CDC to quickly identify (and respond to) new variants of concern. The same challenge is happening around the world, as PCR tests become less broadly available. Sequencing coronavirus samples from wastewater may help, but that’s only happening in a small subset of sewage testing sites right now.
One last bit of good news: vaccine administration numbers are up in the last couple of weeks, as seniors and other eligible high-risk people get their second bivalent boosters. About 70,000 people received vaccines each day this week, compared to around half that number a few weeks ago. If you’re eligible for a second booster, this is a good time to make an appointment!