Last week, I shared a new page from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), reporting statistics on COVID-19 therapeutic distribution in the U.S. The new dataset is a helpful step, but it falls far short of the information we actually need to examine who has access to COVID-19 treatments (particularly Paxlovid) and address potential health equity issues.
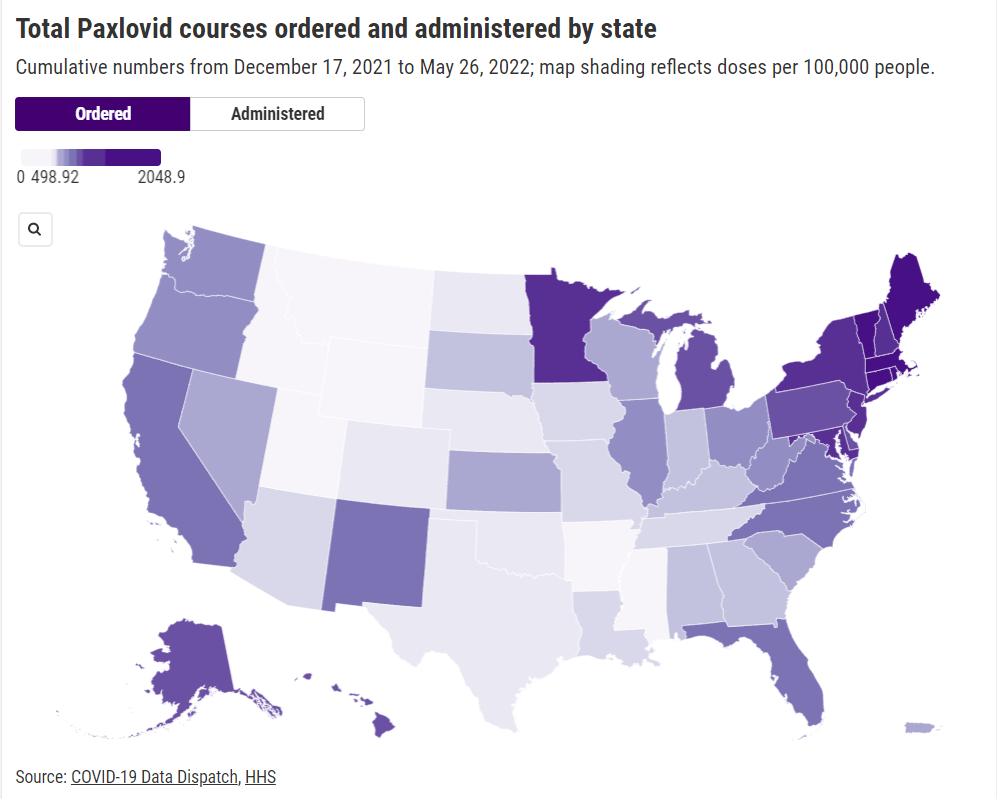
The HHS dataset includes total counts of COVID-19 drugs ordered and administered in the U.S., both nationally and by state. It also includes weekly numbers of the doses available for health providers to order from the federal government (which the HHS calls “thresholds”), over the last five weeks; again, these are available nationally and by state.
As most of the monoclonal antibodies developed for earlier variants do not provide much protection against Omicron, the majority of treatments used in the country last month were antiviral drugs Paxlovid (made by Pfizer) and Molnupiravir (made by Merck).
Paxlovid is the most effective of the two, and the most in-demand. In recent weeks, some patients have reported difficulties with accessing this antiviral as BA.2 drives rising cases across the country. For instance, one COVID-19 Data Dispatch reader wrote to me last week to share that a family member who should’ve been eligible for Paxlovid had his prescription denied, as his pharmacy said the drug was in “limited supply.”
In the first Omicron surge, during the winter, Paxlovid definitely was in limited supply. Then, as that surge waned, supplies improved: a Washington Post article last month reported that the federal government had plenty of doses going unused, and health leaders like COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha wanted to raise awareness of the antiviral with providers and patients.
Now, as BA.2 and its subvariants drive a new surge, it’s unclear whether there are still plenty of Paxlovid doses for anyone who might need them—or whether the doses must once again be rationed for only the most vulnerable patients. If the latter is true, even if it’s true only in some states or counties hardest-hit by the Omicron variants, it’s a problem: as the U.S. seems completely unwilling to put in new safety measures, Paxlovid is an important tool to at least reduce severe disease and death. Without it, high-risk people are in an even worse position.
As a data journalist, I would love to investigate this problem by digging into federal data to see where Paxlovid is getting used, and where there may be gaps. But the existing data are pretty sparse: the HHS has published only limited national and state-level data, with the only numbers on doses actually ordered and administered being cumulative (i.e. totals over a five-month period). There’s no information on how Paxlovid prescriptions have changed in different states or counties over time, or of whether the drug is actually reaching vulnerable people who need it.
KHN’s Hannah Recht explained why this data gap is a problem for health providers prescribing Paxlovid, in an article earlier in May:
Los Angeles County’s Department of Public Health has worked to ensure its 10 million residents, especially the most vulnerable, have access to treatment. When Paxlovid supply was limited in the winter, officials there made sure that pharmacies in hard-hit communities were well stocked, according to Dr. Seira Kurian, a regional health officer in the department. In April, the county launched its own telehealth service to assess residents for treatment free of charge, a model that avoids many of the hurdles that make treatment at for-profit pharmacy-based clinics difficult for uninsured, rural, or disabled patients to use.
But without federal data, they don’t know how many county residents have gotten the pills. Real-time data would show whether a neighborhood is filling prescriptions as expected during a surge, or which communities public health workers should target for educational campaigns.
Yasmeen Abutaleb’s article in the Washington Post (linked above) also discusses the need for data:
Other experts welcomed the administration’s efforts, especially as cases rise, but said simply boosting the supply wasn’t enough, noting that inequities persist in who has access to Paxlovid. People without health insurance and those who live far away from medical providers or pharmacies are among those at highest risk from covid and face some of the highest hurdles to receiving effective treatment, said Julie Morita, executive vice president of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
“It is essential that we collect and report data on who is receiving Paxlovid and other antiviral medications to swiftly pinpoint and address any disparities that emerge,” Morita said. “If done right, this can be a real turning point — but it is essential that all populations and communities have the opportunity to reap the benefits.”
In short, if health providers like community clinics and pharmacies could see data on which communities are receiving Paxlovid prescriptions and which ones are not, they could work to fill the gaps. The existing state-by-state data (published after Recht’s article) is a helpful starting point, but still has little utility for local health officials.
Indeed, the limited state-by-state data already suggest that some states in the Northeast, the West Coast, and the Great Lakes region are ordering and administering more Paxlovid (relative to their populations), compared to others in the Midwest and South. This is a pattern worth examining further, but it’s difficult when the data are so unspecific.
Here’s my wishlist of Paxlovid data that would be more useful:
- More granular geographies. State-level data is pretty useless if you run a local health clinic, or if you’re a local journalist. We need prescription information at the county level, if not even smaller regions (like census tracts or ZIP codes.)
- Demographic data. Without data on race and ethnicity, age, or other demographic factors, it’s very difficult to determine whether Paxlovid is reaching people in an equitable way—or if access to the drug is becoming another way in which the pandemic disproportionately impacts already-marginalized groups.
- Provider type. Along the same lines as demographic data, seeing how many Paxlovid doses are going through large pharmacies as opposed to community health centers, hospitals, or other types of healthcare providers could be a useful measure of equity.
- Patient health conditions. People with health conditions that predispose them to severe COVID-19 symptoms (compromised immune systems, diabetes, kidney disease, etc.) are supposed to be at the front of the line for Paxlovid. We need data to see whether they are actually getting this priority treatment.
Come on, HHS: give us the granular data!