- CDC adds data on new booster shots: The latest addition to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker is the Omicron-specific, bivalent booster shots, authorized a couple of weeks ago. So far, the CDC has only provided a total count of Omicron booster recipients (4.4 million, as of September 21) and incorporated these boosters into total counts of Americans who’ve received “first” and “second boosters. A note at the top of the dashboard explains the CDC is working to provide more granular data about the new boosters as separated out from past boosters.
- Evidence Commons (ASU): Researchers at Arizona State University’s College of Health Solutions have compiled this detailed dashboard of scientific publications related to COVID-19 tests, supported with funding from the Rockefeller Foundation. The dashboard incorporates information from over 3,000 papers, sorted by the type of test under study, methodology, analysis location, and more. It’s a helpful tool to sort through diagnostic details that are often buried in technical documents.
- Helix announces new CDC partnership: Speaking of testing, the viral sequencing and population genomics company Helix announced this week that it has an “extended agreement” with the CDC to sequence coronavirus samples for the agency’s analysis. While Helix has been working with the CDC on variant tracking for some time, the new partnership extends this important effort: Helix (and research partners) will sequence over 3,000 coronavirus samples per week for the next year, “with the option to double the number of samples during surge moments,” according to the company’s press release.
- Pathogen Genomics Centers of Excellence: The CDC has also directed new surveillance funding to five state health departments that will test out new genomics technologies and respond to infectious disease outbreaks. These five departments—Georgia, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Virginia, and Washington—are receiving $90 million over the next five years; the funding came out of $1.7 billion allocated for genomic surveillance in the American Rescue Plan. I’m glad to see this sustained funding going beyond COVID-19, though I wish more than five states were getting the money!
- Long-term nervous system damage from COVID-19: Ziyad Al-Aly and his team at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Healthcare System have published a new paper on long-term impacts from a COVID-19 infection. The study used a large dataset of electronic health records from a national VA database, including 154,000 people with COVID-19 and over five million controls. COVID-19 patients had an elevated risk of strokes, cognition and memory problems, seizures, mental health disorders, encephalitis, and more. While the VA population isn’t the best representation for the U.S. population as a whole (it skews older and male), the study still provides evidence for long-term neurological complications from COVID-19.
- Long COVID estimates in Europe: And one more piece of Long COVID news for this week: the World Health Organization’s European division has produced new estimates on Long COVID for the continent. Between 10% and 20% of COVID-19 cases in Europe have led to mid- or long-term symptoms, the WHO found, impacting up to 17 million people. The study also found women are more likely to develop Long COVID.
Tag: Featured sources
-
Sources and updates, September 25
-
Sources and updates, September 18
- COVID-19’s impact on the workforce: Economists at the National Bureau of Economic Research released a new working paper this week, showing that COVID-19 has “persistently” reduced the U.S.’s labor supply. Using data from the Census’ Current Population Survey, the researchers found that workers who had to take off at least a week from work due to COVID-19 were seven percentage points less likely to still be in the labor force a year later, compared to those who didn’t miss a week. Overall, Long COVID pushed about 500,000 people out of the workforce, the paper estimates. Notably, this estimate is much lower than the analysis from the Brookings Institution published last month; the gap between these two reports suggests a need for more robust data collection on Long COVID and work.
- Long COVID prevalence from a population survey: Last week, I shared a new preprint from Denis Nash and his team at the City University of New York, reporting on the results of a national survey used to determine true COVID-19 prevalence during the BA.5 surge. This week, Nash et al. shared another preprint from that same survey, focused on Long COVID. Based on the nationally-representative survey (sample size: about 3,000), the researchers estimate about 7.3% of U.S. adults are currently experiencing Long COVID symptoms—matching estimates from the Household Pulse Survey. One-quarter of those Long COVID patients surveyed reported that their day-to-day life activities were significantly impacted.
- Lancet COVID-19 Commission shares lessons from the pandemic: The Lancet COVID-19 Commission is an interdisciplinary group of scientists convened by the journal to study the COVID-19 crisis and make recommendations for the future. In the group’s final report, released this week, the scientists focus on “failures of international cooperation” that have contributed to unnecessary illness and deaths. Those failures include delays in acknowledging that the coronavirus spreads through the air, not enough funding for low- and middle-income countries, “the lack of timely, accurate, and systematic data,” and more.
- COVID-19 archive of Dr. Fauci’s emails: The COVID-19 Archive is a project aiming to compile digital documents tracing the early phases of the pandemic. Its prototype iteration allows users to search and sort through the early-COVID inbox of Dr. Anthony Fauci, via email records contributed by investigative reporter Jason Leopold. (MuckRock, where I work part-time, is a collaborator on the project, but I’m not personally involved with it.)
- U.S. has active circulation of vaccine-derived polio: This week, the CDC and World Health Organization formally announced that the polioviruses spreading in New York state constitute active circulation of vaccine-derived polio. Most other countries that meet this WHO classification are developing nations in Africa, as well as Israel, the U.K., and Ukraine. For more on what exactly “vaccine-derived polio” means and how the disease made a comeback in the U.S., I recommend reading Maryn McKenna in WIRED.
- Neurological symptoms associated with monkeypox: Here’s one study in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that caught my eye this week: the agency has identified two cases in which monkeypox patients faced inflammation in their brains (called encephalomyelitis), leading to neurological symptoms. Both patients were hospitalized and required weeks of rehab, including use of walkers. The CDC says these symptoms are rare but worth monitoring, and is encouraging local health agencies to report any further cases.
-
Sources and updates, September 11
- White House plans for annual boosters: This week, Biden administration officials announced a plan for one COVID-19 shot each year, on a similar timeline to the flu shots distributed every fall. In this plan, this fall’s Omicron-specific boosters are the first iteration of annual boosters. Some scientists are skeptical about the plan, given that (as I discussed last week) we have very little data on how well the new boosters work. It could be preemptive to say just one shot each year will be enough, and the federal government should also be investing in next-generation vaccines that might better prevent infection and transmission.
- Urgency of Equity Toolkit: The People’s CDC, a health advocacy organization aiming to fill gaps in COVID-19 guidance left by the official CDC, has published a toolkit focused on school safety for the fall. The presentation walks readers through why public health measures are still needed in K-12 schools and potential layers of protection, such as improved ventilation, surveillance testing, and improving pediatric vaccination rates.
- Parents and caregivers lost to COVID-19: Speaking of protecting children, a new study published in JAMA Pediatrics this week estimates how many children have lost parents or caregivers during the pandemic. The researchers (an international group including experts at the World Health Organization, World Health Organization, and others) produced their estimates based on global excess mortality data—going beyond deaths officially reported as COVID-19. In total, the study estimates about 10.5 million lost parents or caregivers and 7.5 million became orphans worldwide.
- True virus prevalence during the BA.5 surge: I’ve previously cited the work of Denis Nash and his team at the City University of New York; they utilized a population survey to estimate how many New Yorkers actually got COVID-19 during the city’s spring surge. This week, the team shared a new study that uses the same approach for the whole country. While their sample size was fairly small (about 3,000 people) and the study has yet to be peer-reviewed, its findings are striking: about 17% of U.S. adults surveyed were infected by the coronavirus during a two-week period from late June to early July, around the peak of the BA.5 surge.
- New independent effort to study Long COVID: This week, a group of researchers, clinicians, and patients announced the Long Covid Research Initiative, a new collaborative effort to study the condition and identify potential treatments. The group has raised $15 million in private funding and aims to move more quickly than public or academic efforts that have been bogged down in bureaucracy (among other challenges). I’m excited to see what this new group finds.
-
Sources and updates, September 4

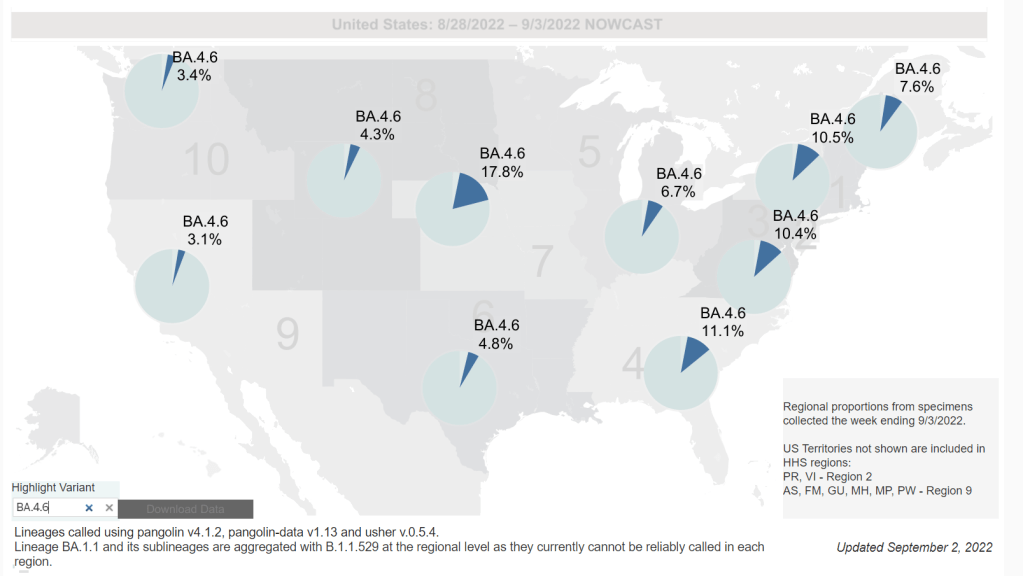
Omicron BA.4.6, a newer version of BA.4, is currently more prevalent in the Midwest than other regions of the country. Chart via the CDC, retrieved September 4. - Slow rise of BA.4.6 is worth watching: As I mentioned in today’s National Numbers post, a newer subvariant labeled BA.4.6 is gaining ground over other versions of Omicron in the U.S. BA.4.6 evolved from BA.4, and has an additional mutation in the virus’ spike protein that enables it to bypass protection from prior infections. It’s unclear whether BA.4.6 will be able to fully outcompete BA.5, which is currently causing the vast majority of U.S. COVID-19 cases—these two strains are similar enough that the competition may go slowly. So far, the subvariant has been more prevalent in the Midwest than other regions of the country, according to CDC data. Also worth watching: BA.2.75, a subvariant that is dominating some European countries but hasn’t shown up significantly in the U.S. yet.
- Up to 4 million people may be out of work due to Long COVID: Last week, policy research organization the Brookings Institute published a new report discussing the massive impacts Long COVID is having on America’s labor force. The report utilizes recent data from the Household Pulse Survey (released in June) estimating Long COVID prevalence, in conjunction with research on how many long-haulers might be out of work due to their condition. The results: between two and four million Americans potentially lost their jobs (or are working significantly less) due to Long COVID, costing at least $170 billion a year in lost wages. Even the low ends of these estimates are staggering.
- U.S. life expectancy declined again in 2021: Americans born in 2021 may expect to live for 76 years on average, according to the CDC’s National Vital Statistics System. This is the lowest life expectancy has been since 1996. CDC researchers attribute the sharp decline in the last two years to the pandemic and drug overdose deaths. Disparities in life expectancy have also increased: Native Americans born in 2021 may expect to live only 65 years on average and Black Americans may expect to live 71 years, compared to 76 years for white Americans.
- Biobot expands wastewater surveillance for opioid tracking: In the last couple of months, we’ve seen wastewater used to track monkeypox and polio, in addition to COVID-19—suggesting the technology’s capacity for broader public health surveillance. This week, leading wastewater company Biobot announced a new initiative to track opioid use and other high-risk substance use through a similar platform to its current COVID-19 efforts. Tracking the opioid crisis was actually the original focus for Biobot’s founders pre-pandemic, so it’s notable to see the company expanding in this direction now.
- New technical report on monkeypox outbreak: Speaking of monkeypox, the CDC recently released a detailed report on how the disease has spread through the U.S. and other countries. It’s a new reporting format for the CDC, with the agency releasing data more rapidly than it might have in a scientific study—possibly emulating the U.K. Health Security Agency’s Technical Briefings. Notably, the CDC Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics, the agency’s new modeling center, was a key contributor to the report. Former CFA leader Caitlin Rivers shared key findings from the report here. (And for more on CFA, see this story I wrote for FiveThirtyEight in June.)
-
Sources and updates, July 31
- KFF poll shows low vaccine uptake for young kids: This week, the Kaiser Family Foundation released an update from their COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor, an ongoing project tracking U.S. attitudes towards vaccines. This latest update focuses on children under age five, and the results are worrying: about 43% of parents with kids in this age group say they will “definitely not” get their child vaccinated, citing concerns about vaccine safety. Conservative parents and those who are unvaccinated themselves were particularly likely to be against vaccinating their young kids, KFF found.
- Vaccine side effects less common for second boosters: A new CDC study, published in this week’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, tracked reactions to COVID-19 boosters among Americans over age 50 using CDC monitoring systems. Among over 200,000 people who received third and fourth doses from the same vaccine manufacturer, side effects like a sore arm and fatigue were less common after the fourth dose compared to the third dose. Still, uptake for second boosters has been slow and potentially inequitable; the CDC recently published data on second boosters by race/ethnicity, showing that white Americans over age 50 are more likely to get this extra protection than non-white people in this age group.
- White House summit on next-generation COVID-19 vaccines: And one more piece of vaccine news for this week: the White House brought together federal officials, scientists, and pharmaceutical executives for a summit discussing next-generation COVID-19 vaccines. The summit highlighted vaccine candidates designed to work against many potential coronavirus variants, as well as those that would be delivered through the nose—potentially producing more protection against coronavirus infection and transmission. Either option would require a lot of funding from a Congress that has been hesitant to support COVID-19 efforts.
- States are letting health emergency declarations expire: While the federal declaration of COVID-19 as a public health emergency will remain in place at least through this fall, many states have let their declarations expire in recent months. These expirations impact the resources states are able to allocate for tracking and responding to COVID-19—ranging from data collection to telehealth access. The ending emergencies are certainly contributing to less frequent COVID-19 data updates in many states.
- New studies on COVID-19’s origins: Two major studies have conclusively linked the coronavirus’ early spread to the Huanan Seafood Market in Wuhan, China. These studies, both published in Science, were produced by an international group of virologists and evolutionary biologists at the Scripps Research Institute, the University of Arizona, the University of Sydney, the University of Edinburgh, and many other institutions. The experts traced early cases in the seafood market, finding evidence of spillover from animals to humans. The precise origins of COVID-19 are still unknown, but these studies go a long way in demonstrating early spread tied to animals, not a lab leak.
-
Sources and updates, July 24
- New CDC report on drug overdose deaths during the pandemic: Drug overdose deaths increased by 30% from 2019 to 2020, according to a new CDC report compiling data from 25 states and D.C. But this increase was higher for Black and Native Americans: deaths among these groups increased by 44% and 39%, respectively. The full report includes more details on how overdose deaths disproportionately occurred in Black and Native populations, as well as the need for more easily accessible treatments for substance abuse.
- CDC survey of public health workers: Another CDC report that caught my attention this week presented results from a national survey of state and local public health workers in 2021. Almost three in four of the workers surveyed were involved with COVID-19 response last year. The survey provides further evidence of burnout among public health workers: 40% of those surveyed reported that they intend to leave their jobs within the next five years.
- COVID-19 testing options: COVID-19 Testing Commons is a research group at Arizona State University’s College of Health Solutions that has compiled comprehensive information about COVID-19 tests available worldwide. You can search the database for tests by company, platform, type of specimen collected, regulatory status, and more. The group also recently compiled a report summarizing these testing options in the pandemic to date.
- Congressional hearing on Long COVID: This week, Congress’s Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Crisis held a hearing specifically about Long COVID. Congressmembers heard from Long COVID patient advocates and researchers about the impacts of this condition and the urgent need for more research and support. I highly recommend reading or listening to the testimony of Hannah Davis, cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, for a powerful summary of these impacts and needs. (If you’re watching the video: her testimony starts at about 28:50.)
- CDC recommends Novavax vaccine: The CDC has officially authorized Novavax’s COVID-19 vaccine, following the FDA authorization that I mentioned in last week’s issue. Novavax’s vaccine is protein-based, which is an older type of vaccine but has been less common for COVID-19; some experts are hopeful that people who have hesitated with the mRNA vaccines may be more likely to get Novavax. Dr. Katelyn Jetelina has a helpful summary of this vaccine’s potential impact at Your Local Epidemiologist.
- NYC prevalence preprint updated: I’ve linked a couple of times to this study from a group at the City University of New York, with the striking finding that an estimated one in five New Yorkers got COVID-19 during a two-week period in the BA.2/BA.2.12.1 surge. The researchers recently revised and updated their study, based on some feedback from the scientific community. Their primary conclusions are unchanged, lead author Denis Nash wrote in a Twitter thread, but the updated study includes some context about population immunity and NYC surveillance.
-
Sources and updates, July 17
- COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance: The pandemic resulted in major losses for the fight against antimicrobial resistance, according to a new CDC report published last week. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR), in which bacteria evolve the ability to bypass commonly-used antibiotics, is a significant public health concern in the U.S. and globally. The CDC is still missing data for several major AMR threats during the pandemic, but data the agency was able to compile present a concerning picture about resistant infections in U.S. hospitals during the pandemic.
- CDC’s air travel contact tracing needs work: And now, a report about the CDC: the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that the agency’s data system for contact tracing on flights “needs substantial improvement.” Without a comprehensive, singular data source for airplane passenger contact information, the CDC has to do extra research and extend contact tracing time after a passenger tests positive for COVID-19.
- State COVID-19 data reporting continues slowing: New York Times reporter Adeel Hassan and colleagues described how states are reporting their COVID-19 data less frequently and closing public testing sites, leaving more gaps and delays in their numbers. This article provides a helpful summary of a trend I’ve alluded to in various blog posts for the last few weeks.
- Private companies step up to assist with PCR testing: Two major testing companies, Quest Diagnostics and Color Health, announced this week that they will provide free COVID-19 testing to some Americans without health insurance at hundreds of sites across the country; these site locations will be determined by the CDC’s Social Vulnerability Index. The CDC is picking up the tab for these testing costs, according to press releases. (H/t the COVID Weekly Testing Newsletter.)
- FDA authorization for Novavax vaccine: Novavax’s protein-based COVID-19 vaccine has been granted Emergency Use Authorization by the FDA. While this vaccine option is unlikely to substantially increase uptake in the U.S., the FDA’s authorization opens the door for Novavax shots to be used as fall booster shots—an idea that seemed promising to some members of the agency’s advisory committee in a recent meeting.
-
Sources and updates, July 10
- CDC adds (limited) Long COVID data to its dashboard: This week, the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker added a new page, reporting data from a study of “post-COVID conditions” (more colloquially known as Long COVID). The study, called Innovative Support for Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infections (INSPIRE), follows patients who test positive for up to 18 months and tracks their continued symptoms. Among about 4,100 COVID-positive patients in the study, over 10% still had symptoms at three months after their infections, and over 1% still had symptoms at 12 months. This is just one study among many tracking Long COVID, but it is an important step for the CDC to add these data to their dashboard.
- Air change guidance by state: In recognition of the role ventilation can play in reducing COVID-19 spread, some states have put out recommendations for minimum air changes per hour (ACH), a metric for tracking indoor air quality. Researcher Devabhaktuni Srikrishna has compiled the recommendations on his website, Patient Knowhow, with a map showing ACH guidance by state. (I recently interviewed Srikrishna for an upcoming story about ventilation.)
- COVID-19 is a leading cause of death in the U.S.: A new study from researchers at the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute confirms that COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the U.S., in both 2020 and 2021. The researchers utilized death records from the CDC in their analysis, comparing COVID-19 to common causes such as cancer and heart disease. COVID-19 was a top cause of death for every age group over age 15, the study found.
- COVID-19 disparities in Louisiana: Another notable study this week: researchers at the University of Maryland, College Park examined the roles of social, economic, and environmental factors in COVID-19 deaths in Louisiana, focusing on Black residents. “We find that Black communities in parishes with both higher and lower population densities experience higher levels of stressors, leading to greater COVID-19 mortality rate,” the researchers wrote. The study’s examination of environmental racism in relation to COVID-19 seems particularly novel to me; I hope to see more research in this area.
- Tracking coronavirus variants in wastewater: And one more new study: a large consortium of researchers, led by scientists at the University of California San Diego, explores the use of wastewater surveillance to track new variants. Variants can show up in wastewater up to two weeks earlier than they show up in samples from clinical (PCR) testing, the researchers found. In addition, some variants identified in wastewater are “not captured by clinical genomic surveillance.”
- Global COVID-19 vaccine and treatment initiative ending: The ACT-Accelerator, a collaboration between the World Health Organization and other health entities and governments, has run out of funding. This is bad news for low- and middle-income countries that relied on the program for COVID-19 vaccines and treatments—many of which are still largely unvaccinated, more than a year after vaccines became widely available in high-income countries. Global health equity initiatives will likely continue in another form, but funding will be a continued challenge.
-
Sources and updates, July 3
- Report on race and ethnicity data collection: Researchers at Boston University’s Center for Antiracist Research, who worked on collecting race and ethnicity data from states during the pandemic, have produced a report about the challenges of this work. I was a long-time volunteer for the COVID Tracking Project’s Racial Data Tracker, which became the first stage of a larger project for the BU center, and I’m glad to see this report highlight the issues with destandardized, incomplete data that I remember well.
- Global impact of vaccines in 2021: In a new paper, published in The Lancet in late June, researchers at Imperial College London evaluate the lives saved by COVID-19 vaccines on a global scale during the first year that this technology was available. Vaccines prevented about 14 million COVID-19 deaths in 185 countries and territories, the researchers found. If global health initiatives like COVAX had met their goals, the lives saved could have been far greater.
- COVID-19 spread from a cat: Scientists in Thailand have identified the first documented case of a human getting the coronavirus from a pet cat. In this case, the cat from a family going through isolation for COVID-19 infected a veterinarian who was caring for it; genetic analysis confirmed that three humans (father, son, and veterinarian) and the cat were infected with the same viral strain. While cases like this are likely rare, the documented transmission demonstrates why we need better tracking of COVID-19 in animals, as I noted last week.
- Potential new approach for tracking variants: A new study in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, funded by the National Institutes of Health, presents the potential for monitoring coronavirus variants through a PCR testing-based approach. Compared to the techniques labs currently use to track variants—which involve sequencing an entire viral genome—this new approach would be faster, cheaper, and could be performed by more labs. The researchers are eager to share their work “as a public health tool,” they said in an NIH press release.
-
Sources and updates, June 26

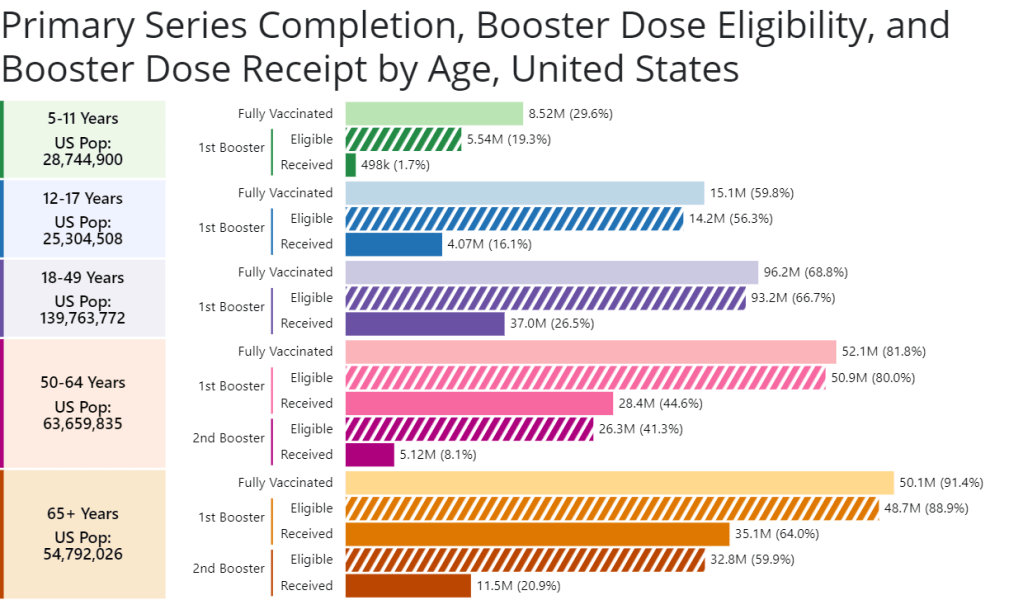
A new chart from the CDC shows booster shot eligibility and uptake by age. Retrieved on June 26. - CDC report on Paxlovid distribution: A major study from the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report this week: researchers at the CDC and collaborators studied the distributions of antiviral COVID-19 drugs Paxlovid and Lagevrio (also called Molnupiravir) by ZIP code, comparing ZIP codes with the CDC’s Social Vulnerability Index. More than one million prescriptions were dispensed between late December 2021 and late May 2022, the study found. But, by the end of that period, prescription rates were twice as high in low- and medium-vulnerability ZIP codes as in high-vulnerabilty ZIP codes—indicating that these antivirals are not reaching the people who most need them.
- CDC booster shot data update: The CDC has added a new chart to its “COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States” page, showing booster shot eligibility and uptake by age. The chart includes two rounds of boosters for seniors; according to the data, 64% of eligible seniors have received their first booster, but only 21% have received their second booster. The data are also available for download.
- COVID-19 vaccinations among children: I also recently learned about this CDC page focused on kids’ vaccinations, including vaccination coverage by demographic factors such as poverty status, parents’ education level, and insurance. The data come from a national survey previously used to monitor flu vaccinations among children. Data are updated monthly, and don’t yet include figures for children under 5; but existing data for children ages 5-17 affirm that vaccine uptake for kids has been low so far.
- Guide to finding government COVID-19 documents: The Digital Public Library of America has released a free ebook with an archive of over 3,000 government documents related to the pandemic response. These documents were collected by the COVID Tracking Project during its year of work, and have been meticulously categorized and indexed in true CTP fashion. CTP alum Jennifer Clyde was the project’s editor.
- Commonwealth Fund report on improving our public health system: A new report from healthcare-focused foundation The Commonwealth Fund provides recommendations for improving the country’s public health system. It focuses on organizing local agencies, providing more funding, improving trust, and other key topics.
- History of exposure notification apps: Jenny Wanger, whom I interviewed about COVID-19 exposure notification apps back in spring 2021, sent me this paper she wrote about the technology, which was published earlier in June. The paper provides a report of how exposure notification protocols were developed, how states used the technology, and how limited data made it difficult to assess the technology’s success.