- Project Next Gen announces first grants: Project Next Gen, the federal government’s effort to support next-generation COVID-19 vaccines and treatments, announced its first round of scientific funding this week. The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has now allocated $1.4 billion of a total $5 billion in the program, with funding going to set up clinical trials for new vaccines and a new monoclonal antibody developed by Regeneron. HHS hasn’t actually selected vaccine candidates yet; that will come in a later announcement. Notably, as I reported on Twitter, HHS officials said during a press conference that they do not anticipate future Project Next Gen funding going towards Long COVID research.
- Biobot Analytics expands to other respiratory viruses: Biobot Analytics, one of the leading COVID-19 wastewater surveillance companies, launched a new testing panel this week for a broader range of respiratory pathogens. The panel will allow health agencies to monitor their local sewersheds for COVID-19, flu, and RSV at the same time. Biobot is rolling this testing option out in time for this year’s respiratory virus season. While the company hasn’t announced this yet, I suspect Biobot will make some data from the respiratory virus testing available online, similar to its current COVID-19 and mpox dashboards.
- KFF launches health misinformation tracker: The Kaiser Family Foundation has announced a new polling effort focused on health misinformation, and released the first round of data from this initiative. This release includes data about COVID-19 and vaccines, as well as other key areas of misinformation like reproductive health and firearms. According to KFF’s surveys, a majority of Americans have heard false claims about COVID-19, such as that the vaccines caused many sudden deaths in otherwise healthy people; smaller but still significant shares of people (around 20% to 30% depending on the statement) say these false claims are true.
- Excess deaths in China after ending restrictions: Last winter, China abruptly ended its “zero COVID” policy (which had included strict quarantines, testing, and other measures), leading the coronavirus to spread widely—but with limited official data tracking its impacts. A new study from researchers at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Washington state examines excess deaths in China, or deaths above historical norms, following that policy change. About 1.87 million excess deaths occurred among Chinese adults over age 30 in just two months after the end of the zero COVID policy, the researchers estimated. These deaths mainly impacted older residents, many of whom weren’t vaccinated against newer variants.
- Long COVID without a positive test: Another notable study from this week: researchers at Northwestern Medicine’s Long COVID clinic compared immune responses and symptoms among patients who did and did not have proof of their initial coronavirus infections. While this was a small study (including just 29 patients), the researchers found that the majority of those without proof of infection had COVID-related immune system signals similar to those patients who did have initial proof. The study offers further evidence to a trend that I’ve long heard in interviews with people with Long COVID: many patients weren’t able to get positive tests during their initial infections but still clearly have Long COVID, and they should not be excluded from research.
- COVID-19 risk for essential workers: One more new study: researchers at the University of Gothenburg, in Sweden, used available occupational data to examine how people in specific jobs were at higher risk for COVID-19 cases. The study included 550,000 cases from October 2020 through December 2021. People working in public-facing jobs such as bus drivers, school staff, and nurses were at higher risk for getting COVID-19—and developing severe symptoms that required hospitalization—than those in less public-facing professions, the researchers found. Essential workers receive less attention now than they did early in the pandemic, but they still need protections to stay safe, the study suggests.
Tag: excess deaths
-
COVID source callout: NYT continues to push misleading information
Longtime readers may remember that I am no fan of “The Morning,” a daily newsletter from the New York Times that has frequently downplayed COVID-19 in recent years. Last summer, for example, I called out the newsletter for misleading reporting about who was dying most from COVID-19.
Well, this week, the newsletter’s primary author, David Leonhardt, has done it again. Leonhardt wrote on Monday that “the pandemic really is over.” As evidence, he pointed to excess deaths (i.e. deaths above expected norms from past years), writing that this metric has returned to a pre-COVID-19 baseline.
It is true that excess deaths have been low since early 2023, when the country’s holiday COVID-19 surge concluded. And sure, this is good news about COVID-19’s current impact on mortality. You can see the CDC’s estimates here. However, Leonhardt’s newsletter fails to mention several caveats:
- If the pandemic were truly “over,” excess deaths would actually be below historical averages, not at them, to reflect people who had died prematurely of COVID-19 in the last three years. (Health law scholar Blake Murdoch pointed this out on Twitter.)
- Current death data are seriously undercounting COVID-19 deaths, thanks to the now-very-limited availability of COVID-19 tests combined with limited surveillance following the end of the federal public health emergency. The CDC revises up its estimates every week.
- Excess death data, in general, are typically considered preliminary estimates for about a year. So, the data Leonhardt sites are preliminary and likely to be revised up once the CDC compiles more information from death certificates.
- The pandemic has disproportionately impacted people of color and other vulnerable groups. Analysis from APM Research Lab shows that this pattern has continued through the first half of 2023.
- Plenty of other metrics (including wastewater surveillance, hospitalizations, and the virus’ continued evolution) suggest that COVID-19 is still circulating and still making people sick. The U.S. is likely heading into a summer surge right now, in fact.
- Leonhardt fails to mention Long COVID, one of the most dire outcomes of COVID-19. Even though millions of people are still dealing with prolonged symptoms.
So, for whom is the pandemic really “over”? It might be over for Leonhardt himself, but it’s not over for people with Long COVID, people still mourning lost loved ones, high-risk people still taking every precaution, people who will get infected this summer, and so many more. All of these people challenge the NYT’s misleading narrative.
-
COVID source shout-out: excess deaths estimates
This week, a team of demography researchers published a paper sharing excess death estimates by county, for the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. The team, led by Andrew Stokes at Boston University, has been analyzing excess death data for years in order to understand the true toll of COVID-19 on the U.S.
To measure excess deaths, researchers compare the number of deaths that they’d expect to occur in a given place, over a given timeframe—based on modeling from historical data—to the number of deaths that actually happened. This metric is a helpful one for COVID-19 research, because official COVID-19 deaths are undercounted for a variety of reasons. (To name a few: lack of standards for death certificates, politicization of the pandemic, health equity issues.)
Especially now that official COVID-19 data are becoming less and less reliable, I see excess deaths as a useful avenue for continued reporting on the pandemic. And for any journalists or researchers interested in looking into this issue, Stokes and his team’s work is a great starting point. I collaborated with them for MuckRock’s Uncounted project, using a preprint iteration of the paper published this week.
For more info on this topic, see the Uncounted project and this 2021 post about excess death data from the CDC.
-
Sources and updates, April 30
- Local COVID-19 resources from the People’s CDC: In advance of the federal public health emergency’s end, advocacy and communications organization the People’s CDC has compiled a list of COVID-19 resources for people still seeking to stay safe during the ongoing pandemic. The list includes testing and treatments, food support, mutual aid, advocacy organizations, and links to other People’s CDC resources.
- Premature deaths during the pandemic: A new analysis from the Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker examines the impact of COVID-19 on premature deaths, or deaths that occurred before the person reached age 75. This analysis included all excess deaths (so, not just those deaths officially reported as COVID-19, but also deaths from other diseases, drug overdoses, violence, etc.). All demographic groups experienced an increase in premature mortality during the pandemic, the researchers found, but deaths increased more for people of color than for white people. Hispanic and Native Americans had the highest impact, with premature all-cause mortality rising 33% betweeen 2019 and 2022.
- Youth risk behaviors during COVID-19: This week, the CDC published a wealth of data and analysis from its 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System, a regular survey examining health-related behaviors among U.S. high school students. The survey asks questions about gun violence, unstable housing, mental health, sexual behaviors, dietary behavior, drug use, and more. As this survey is conducted every two years, the 2021 iteration was the first to capture youth behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic, and it included some questions specifically designed to look at COVID-19’s impacts.
- Lessons from COVID-19 report: A new book, published this week, explores what went wrong (and right) from the U.S.’s COVID-19 response. 34 leading experts from a variety of backgrounds collaborated on the book; the group originally convened in anticipation of a 9/11 Commission-style inquiry into the federal government’s COVID-19 response, and continued to investigate what went wrong even though that commission did not actually come into being. For highlights from the book, see this Q&A between two of the authors and STAT’s Helen Branswell.
- Long-term financial issues after COVID-19: A new paper, published this week in the Journal of Hospital Medicine, finds that a COVID-19 diagnosis may lead to financial challenges. Researchers at the University of Michigan and Johns Hopkins studied this issue by linking healthcare records from a large Michigan-based insurance network with financial records from the credit company Experian. The study included over 132,000 Michigan residents. People who had COVID-19 were more likely to see their credit score drop following that infection, the researchers found; those who were hospitalized with severe symptoms had the highest risk of this financial impact.
-
Sources and updates, April 2
- CDC publishes list of archived data pages: As the CDC prepares to shift its COVID-19 data publication efforts when the federal public health emergency ends in May, the agency has published a list of COVID-19 data and visualization pages that are no longer receiving updates. These archived pages include vaccination demographics, COVID-19 outcomes among pregnant people, data from correctional facilities, and more. I expect the list will get longer as we approach May 11, though the CDC is still updating core COVID-19 metrics (like cases, deaths, wastewater surveillance, etc.).
- One federal COVID-19 emergency may end sooner: Speaking of ending emergencies: you might have seen some news this week about a Republican bill to end COVID-19’s emergency status, which President Biden has announced he would not veto if it comes to his desk. It’s important to note that this is actually a different emergency declaration than the public health one, which is under the control of the federal Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The public health emergency is still slated to end on May 11, and its implications for COVID-19 tests, treatments, and vaccines have not changed. Also, related: this story in STAT explains the federal funding that’s currently left over for COVID-19 response.
- Firearm injuries rose during COVID-19: A new report from the CDC shows how emergency department visits due to firearms rose during the pandemic. Compared to a 2019 baseline, these vitis were 37% higher in 2020, 36% higher in 2021, and 20% higher in 2022, the researchers found. Firearm injuries and deaths are another example of how COVID-19 contributed to higher excess morbidity and mortality; while these injuries weren’t directly caused by the coronavirus, they may be connected to the social and economic unrest that the U.S. faced over the last three years.
- County Health Rankings 2023: This week, the County Health Rankings initiative at the University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute released its 2023 data. These rankings cover a wide array of health-related metrics, from health behaviors like alcohol and drug use to physical environment factors like air quality. The database may be a helpful resource for reporters or researchers looking to understand how their communities compare to others, while the organization’s 2023 report offers national health trends.
- Global health workforce statistics: This database from the World Health Organization details how many health workers are employed around the world and over time. Statistics cover a variety of different health professions (doctors, specialists, nurses, dentists, pharmacists, etc.) and up to 20 years of data, depending on the country. While the dataset doesn’t cover through the pandemic—2020 is the most recent year included —it still shows how health workers have declined in many places over the last couple of decades. (H/t Data Is Plural.)
- Public health worker declines: Speaking of health workers: a new study, published in the journal Health Affairs, shows how the public health workforce in the U.S. has severely declined during the pandemic. The researchers used data from a workforce survey conducted in 2017 and 2021, comparing past “intent to leave or retire” with actual rates of workers leaving. Nearly half of the state and local public health workers in the survey sample left between 2017 and 2021, the researchers found. This paper shows how recruitment and retention among health workers drastically needs improvement.
-
Sources and updates, January 22
- New CDC dashboards track respiratory illness hospitalizations: This week, the CDC released two new dashboards that combine COVID-19 data with data on other respiratory illnesses. First, the RESP-NET dashboard summarizes information from population-based hospital surveillance systems in 13 states for COVID-19, the flu, and RSV; it includes overall trends and demographic data. Second, the National Emergency Department Visits dashboard provides data on emergency department visits for COVID-19, the flu, RSV, and all three diseases combined; this dashboard includes data from all 50 states, though not all hospitals are covered.
- Early results from NIH at-home test self-reporting: Last week, ABC News shared early results from MakeMyTestCount.org, an online tool run by the National Institutes of Health allowing Americans to self-report their rapid, at-home test results. Between the site’s launch in late November and early January, “24,000 people have reported a test result to the site,” according to ABC. (While the article says “people have reported,” I think this number actually represents the number of test results reported, given that the website doesn’t track when one person submits multiple test results over time.) The majority of results reported are positive and women are more likely to self-report than men, per ABC. It’s unclear how useful these early data may be for any analysis, but I’m glad to see some numbers becoming public.
- New preprint updates county-level excess death estimates: A new preprint from Boston University demographer Andrew Stokes and colleagues, posted this week on medRxiv, shares updated estimates on excess deaths and COVID-19 deaths by U.S. county. According to the analysis, about 270,000 excess deaths were not officially attributed to COVID-19 during the first two years of the pandemic, representing 24% of all excess deaths during that time. And the analysis reveals regional patterns: for example, in the South and in rural patterns, excess deaths were less likely to be officially attributed to COVID-19. For more context on these data, see MuckRock’s Uncounted project (which is a collaboration with Stokes and his team).
- Factors contributing to low bivalent booster uptake: Another notable paper from this week: results from a survey of Americans who were previously vaccinated about their reasons for receiving (or not receiving) a bivalent, Omicron-specific booster this fall, conducted by researchers at Duke University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and others. Among about 700 people who didn’t get the booster, their most common reasons were a lack of awareness that the respondent was eligible for this vaccine, a lack of awareness that the bivalent vaccine was widely available, and a perception that the respondent already had sufficient protection against COVID-19. This survey shows how governments at every level have failed to advertise the bivalent boosters, likely to dire results.
- More wastewater surveillance on airplanes: And one more notable paper: researchers at Bangor University tested wastewater from three international major airports in the U.K., including samples from airplanes and airport terminals. About 93% of the samples from airplanes were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while among the airport terminal samples, 100% at two airports were positive and 85% at the third airport were positive. Similar to the study from Malaysia I shared last week, this paper suggests that there’s a lot of COVID-19 going around on air travel—to put it mildly. The paper also adds more evidence that airplane/airport wastewater can be a useful source for future COVID-19 surveillance.
- Nursing home infections ran rampant early in the pandemic: A new report from the Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General examines how much COVID-19 spread through nursing homes in 2020. The report’s authors used Medicare data from about 15,000 nursing homes nationwide, identifying those with “extremely high infection rates” in spring and fall 2020. In more than 1,300 of these facilities, 75% or more of the Medicare patients had COVID-19 during these surges; the same facilities had way-above-average mortality rates. “These findings make clear that nursing homes in this country were not prepared for the sweeping health emergency that COVID-19 created,” the authors write in the report’s summary.
-
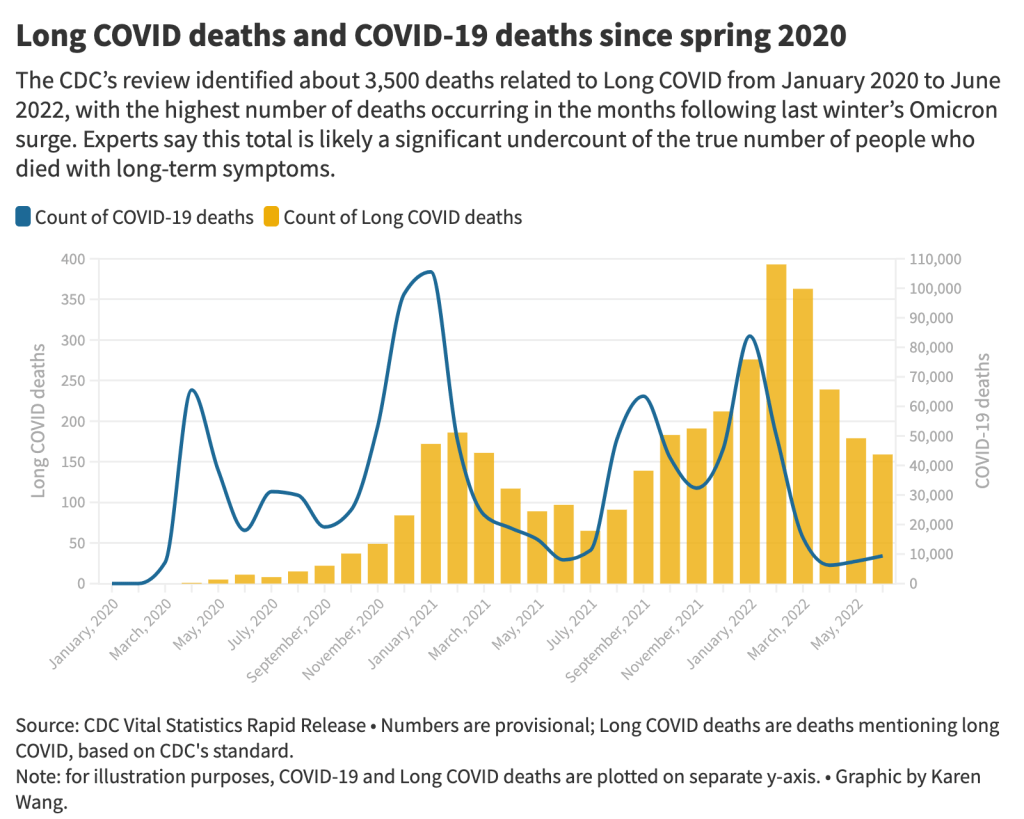
New CDC report vastly underestimates deaths with Long COVID

The 3,500 Long COVID-related deaths identified by the CDC’s review of death certificates are likely a significant undercount of mortality caused by this condition, experts say. Chart by Karen Wang; see the interactive version on MuckRock. On Wednesday, the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics (NHCS) released a major report on deaths from Long COVID. To identify a small (but significant) number of deaths, NCHS researchers searched through the text of death certificates for Long COVID-related terms. Their study demonstrates how bad our current health data systems are at capturing the results of chronic disease.
My colleagues and I at MuckRock did a similar analysis to the CDC’s, searching death certificate data that we received through public records requests and partnerships in Minnesota, New Mexico, and counties in California and Illinois. You can read our full story here and explore the death certificate data we analyzed on GitHub.
Here are the main findings from both analyses:
- The CDC study is an important milestone in recognizing the reality of Long COVID: this is a serious, chronic disease that can lead to death for some patients. It’s not just an outcome of acute COVID-19.
- From its national death certificate search, NCHS identified 3,544 deaths with Long COVID as a cause or contributing factor. This is almost certainly a major undercount, experts told me (and told other reporters who wrote about the study.)
- This number is an undercount because we’re essentially seeing two poor-quality data systems intersect. Long COVID is undercounted in clinical settings because we lack standard diagnostic tools and widespread medical education about it—most doctors wouldn’t think to put it on a death certificate as a result. And the U.S.’s death investigation system is uneven and under-resourced, leading to inconsistencies in tracking even well-known medical conditions.
- On top of these problems, when Long COVID is diagnosed, it tends to be among people who had severe cases of acute COVID-19 followed by difficulty recovering, experts told me. David Putrino and Ziyad Al-Aly, two leading Long COVID researchers, both pointed to the NCHS’s trend towards identifying Long COVID deaths among older adults (over age 75) as an example of this pattern in action, since this group is at higher risk for more severe acute symptoms.
- The NCHS count of deaths thus misses Long COVID patients with symptoms similar to myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), which often arises after a milder initial case. It also misses people who have vascular impacts from a COVID-19 case, like a premature heart attack or stroke months after infection—something Al-Aly and his team have studied in depth. And, crucially, the NCHS count misses people who died from suicide, after suffering from severe mental health consequences of Long COVID.
- While the NCHS count of Long COVID deaths is far too low to be accurate, the researchers did find more deaths as the pandemic went on—with the highest number in February 2022, following the first Omicron surge. This pattern could suggest increased recognition of Long COVID among the medical community.
- The NCHS primarily identified Long COVID deaths among white people, even though acute COVID-19 has disproportionately impacted people of color in the U.S. Experts say this mismatch could reflect gaps in access to a diagnosis and care for Long COVID: if white people are more likely to be seen by a doctor who can accurately diagnose them, they will be overrepresented in Long COVID datasets. Putrino called this “a health disparity on top of a health disparity.”
- MuckRock’s analysis of death certificate data in select states similarly found that most deaths labeled as Long COVID were among seniors and white people. The trends varied by state, though, reflecting differences in populations and in local death reporting systems. For example in New Mexico, which has a statewide medical examiner’s office (rather than a looser system of county coroners), three-fourths of the Long COVID deaths were among Hispanic or Indigenous Americans.
- Our story also includes details about the RECOVER initiative’s autopsy study, which aims to use extensive postmortem testing on people who might have died from acute COVID-19 or Long COVID to identify biological patterns. Like the rest of RECOVER, this study is moving slowly and facing logistical challenges: about 85 patients have been enrolled so far, an investigator at New York University said.
Overall, the NCHS study suggests an urgent need for more medical education about Long COVID, especially as the CDC works to implement a new death code specific to this chronic condition. We also need broader outreach about the consequences of Long COVID. To quote from the story:
“Institutions like the CDC should do more to educate people about the long-term problems that could follow a COVID-19 case, said Hannah Davis, the patient researcher. “We need public warnings about risks of heart attack, stroke and other clotting conditions, especially in the first few months after COVID-19 infection,” she said, along with warnings about potential links to conditions like diabetes, Alzheimer’s and cancer.
And we need other methods of studying Long COVID outcomes that don’t rely on a deeply flawed death investigation system. These could include studies of excess mortality following COVID-19 cases, Long COVID patient registries that monitor people long-term, and collaborations with patient groups to track suicides.
For any reporters and editors who may be interested, MuckRock’s story is free for other outlets to republish.
More Long COVID reporting
-

The “one million deaths” milestone fails to capture the pandemic’s true toll
This week, many headlines declared that the U.S. has reached one million COVID-19 deaths. While a major milestone, this number is actually far below the full impact of the pandemic; looking at excess deaths and demographic breakdowns allows us to get closer.
NBC News was the first outlet to make this declaration, announcing that its internal COVID-19 tracker had hit the one million mark. Other trackers, including the CDC itself, have yet to formally reach this number, but major publications still jumped on the news cycle in anticipation of this milestone. (Various trackers tend to have close-but-differing COVID-19 counts due to differences in their methodologies; Sara Simon wrote about this on the COVID Tracking Project blog back when the official death toll was 200,000.)
But the recent articles about “one million deaths” fail to mention that the U.S. actually reached this milestone a long time ago. This is because the official count only includes the deaths formally logged as COVID-19, in which the disease was listed on a death certificate or diagnosed before a patient passed. Such a count fails to include deaths that were tied to COVID-19, but never proven with a positive test result, or deaths that were indirectly linked to the pandemic for a myriad of reasons.
To get closer to the pandemic’s true toll, demographers use a metric called excess deaths: the number of deaths that occurred in a given region and time period above what would be expected for that region and time period. Experts calculate that “expected death” number with statistical models based on patterns from previous years.
In total, the U.S. has reported 1,118,540 excess deaths between early 2020 and last month. 221,026 of those deaths have not been formally tied to COVID-19. According to a new World Health Organization report, the U.S. was already close to one million COVID-related deaths by December 2021.
To give a more specific example: in the U.S., in the week ending January 22, 2022, CDC analysts estimated that 61,303 deaths would have occurred if there were no COVID-19 pandemic. But actually, a total of 85,179 deaths occurred in the country that week. The difference between the observed and expected values, 23,876, is the excess deaths for this week.
I selected the week ending January 22 as an example here because it has one of the highest excess death tolls of any week in the last two years. This week marked the peak of the Omicron surge, a variant that many U.S. leaders called “mild” and dismissed without instituting further safety measures.
During this week, the CDC reports 21,130 official COVID-19 deaths. That suggests most of the excess deaths in this week, the deaths which occurred over pre-pandemic expectations, were directly caused by the virus.
But what about the 2,746 deaths that weren’t? How many of these deaths were also caused by COVID-19, but in patients who were never able to access a PCR test? How many occurred in counties like Cape Girardeu, Missouri, where coroner Wavis Jordan claimed his office “doesn’t do COVID deaths” and refuses to put the disease on a death certificate without specific proof?
And how many deaths resulted from people being unable to access the healthcare they needed because hospitals were full of COVID-19 patients, or people dying in car accidents during an era of less road safety, or people dying of opioid overdoses brought on by increased stress and financial instability?
Answering these questions takes a lot of in-depth reporting, which I know well because the Documenting COVID-19 team has been doing our best to answer them through our (award-winning!) Uncounted investigation.
As we’ve found, every state—and in some cases, every county—has a unique system for investigating and reporting deaths, especially those linked to the pandemic. In some places, coroners or medical examiners are elected officials who face political pressure to report COVID-19 deaths in a particular way. In others, they face chronic underfunding and a lack of training, leaving them to work long hours in an attempt to produce accurate numbers.
You can see the resource difference when comparing officially-reported COVID-19 deaths to excess deaths by state or county. Some states, like those in New England, have COVID-19 death numbers that closely match or even exceed their excess death numbers; medical examiners in these states have centralized death reporting systems and a lot of resources for this process, reporting by my colleague Dillon Bergin showed.
Other states, like Alaska, Oregon, and West Virginia, have officially logged fewer than three in four excess deaths as COVID-19 deaths. Such a number may signal that a state is failing to properly identify all of its COVID-19 fatalities.
For more granular data on this topic, I recommend reading the work of Andrew Stokes and his team at Boston University. Andrew is the Documenting COVID-19 project’s main academic collaborator on Uncounted; his team just shared their latest county-level excess death estimates in a preprint. (County-level data are also available in the Uncounted project’s GitHub repository.)
Excess deaths can also show how the pandemic continues to hit disadvantaged Americans harder. In 2020, COVID-19 death rates (i.e. deaths per 100,000 people) for Black, Indigenous, and Hispanic Americans were higher than the rates for White Americans; in 2021, some of these disparities actually got worse despite the broad availability of vaccines and other mitigation measures. Non-white groups also saw all-cause mortality (not just COVID-19 deaths) increase more from 2019 in both 2020 and 2021, compared to white Americans.
Please note, the chart below shows crude death rates, which don’t account for differences in age breakdowns between race and ethnicity groups. For example, crude death rates for white Americans tend to be higher because white people generally live longer than people of color in the U.S., and more seniors have died of COVID-19. You can see the difference that ade-adjustment makes in the CDC charts here.
Why is it important to acknowledge and investigate these excess deaths, going beyond the reported COVID-19 numbers? At an individual level, family members who lost loved ones to COVID-19 find that diagnosis important; they can access FEMA aid for funerals, and can receive acknowledgment of how this one death fits into the broader pandemic.
And at the county, state, and national levels, looking at excess deaths allows us to see a full picture of how COVID-19 has affected us. Experts say that inaccurate COVID-19 death numbers can create a negative feedback loop: if your community has a too-low toll, you may not realize the disease’s impact, and so you may be less likely to wear a mask or practice other safety precautions—contributing to more deaths going forward.
As a data journalist, sharing these statistics and charts is my way of acknowledging the one million deaths milestone, and all of the uncounted deaths that are not included in it. But this pales in comparison to actual stories shared by family members and friends of those who have died in the last two years.
To read these stories, I often turn to memorial projects like Missing Them (from THE CITY), which captures names and stories of over 2,000 New Yorkers who died from COVID-19. Social media accounts like FacesOfCOVID also share these stories. And if any COVID-19 Data dispatch readers would like to share a story of someone they lost to this disease, please email me at betsy@coviddatadispatch.com; I would be honored to share your words in next week’s issue.
More federal data
-
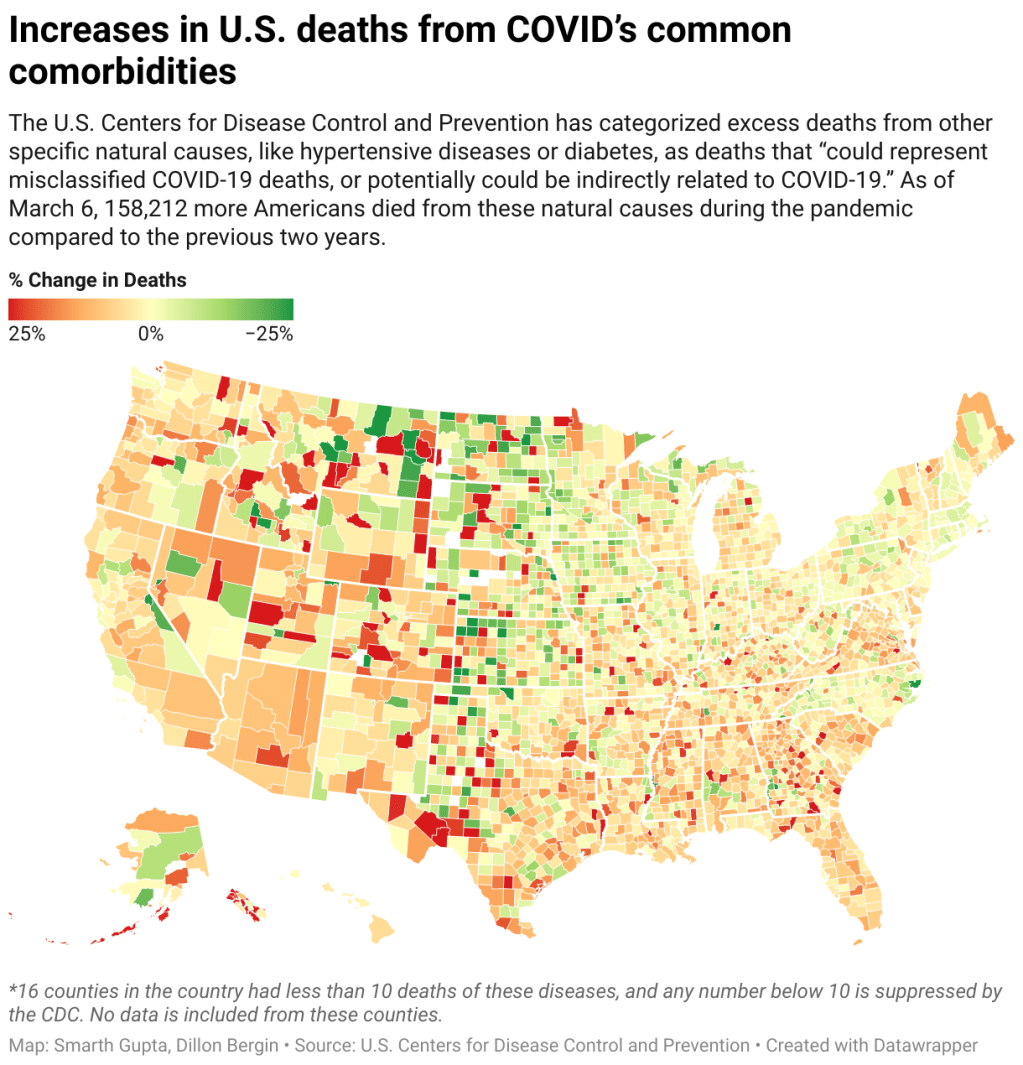
New CDC mortality data release from the Documenting COVID-19 project
Many readers may know that, since last fall, I’ve been working part-time at the Documenting COVID-19 project: a public records, data, and investigative project at Columbia University’s Brown Institute for Media Innovation and the public records site MuckRock.
One major focus at Documenting COVID-19 is our Uncounted investigation, an effort to understand how COVID-19 deaths—and other deaths indirectly caused by the pandemic—have gone under-reported in the last two years. The CDC has reported nearly one million official COVID-19 deaths; but that figure doesn’t include over 300,000 deaths of natural causes that occurred over what researchers expected in 2020 and 2021.
These natural causes logged on Americans’ death certificates—such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory conditions—may have been linked to COVID-19. In fact, about 158,000 deaths during the pandemic were specifically linked to natural causes that the CDC considers potentially COVID-related. But the official records make it hard to say for sure.
In a story with USA TODAY published late last year, Documenting COVID-19 found massive gaps and inconsistencies in the U.S.’s death system, which likely contributed to these undercounts. These include: a lack of standardization for medical examiners and coroners’ offices, workers in these positions becoming overwhelmed during the pandemic, and failures in some cases to order COVID-19 tests for patients or push back when families insisted a death wasn’t COVID-related.
Documenting COVID-19 is working on further follow-up stories in this investigation. But we also want to empower other reporters—especially local reporters—and researchers to investigate pandemic deaths. To that end, our team recently released a GitHub data repository that provides county-level CDC mortality data from 2020 and 2021.
The data come from the CDC’s provisional mortality database; our team signed a data-use agreement with the agency so that we can use their API to gather data more quickly and efficiently than what’s possible with the CDC’s WONDER portal.
!function(){“use strict”;window.addEventListener(“message”,(function(e){if(void 0!==e.data[“datawrapper-height”]){var t=document.querySelectorAll(“iframe”);for(var a in e.data[“datawrapper-height”])for(var r=0;r<t.length;r++){if(t[r].contentWindow===e.source)t[r].style.height=e.data["datawrapper-height"][a]+"px"}}}))}();Here’s a brief summary of what’s in the repository, taken from a write-up by my colleague Dillon Bergin:
- Leading external causes of death in the 113 CDC code list, by underlying cause of death;
- Natural causes of death associated with COVID-19, using the CDC’s categories for excess deaths associated with COVID-19, by underlying cause of death;
- All deaths by race and ethnicity, with age-adjusted rate, regardless of underlying cause of death;
- Information to help contextualize the CDC data, including excess mortality numbers modeled by demographers at Boston University, vaccination rates, and a Department of Justice survey released in December of all medical examiner and coroner offices in the country.
And here are some other links related to Uncounted and the CDC’s mortality data:
- A landing page on MuckRock including all stories in the Uncounted project;
- A Q&A with me and Dillon from last December, discussing the CDC’s data;
- A reporting recipe on using the CDC’s data for local investigations;
- A webinar with the Documenting COVID-19 team about these data.
If you’re a journalist who wants to use these data, the Documenting COVID-19 team is happy to help! If you have questions or want support, feel free to reach out to the team at covid@muckrock.com, or to me specifically at betsy@muckrock.com.
More federal data
-
Sources and updates, March 20
Data sources and data-related updates for this week:
- APM Research Lab relaunches Color of Coronavirus tracker: From April 2020 to March 2021, the American Public Media (APM) Research Lab compiled state-level data on COVID-19 deaths by race and ethnicity, in order to present a picture of which U.S. populations were most hard-hit by the pandemic. The project relaunched this week, now utilizing CDC mortality statistics instead of compiling data from states. One major finding from the updated data: “Indigenous Americans have the highest crude COVID-19 mortality rates nationwide—about 2.8 times as high as the rate for Asians, who have the lowest crude rates.”
- CDC might take back hospital data reporting responsibilities from HHS: As longtime readers may remember, back in summer 2020, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) developed a new data system for hospitals to report COVID-19 patient numbers and other related metrics. At the time, the HHS was taking over responsibility for these data from the CDC; this inspired some political posturing and concerns about data quality, though the eventual HHS dataset turned out to be very comprehensive and useful. (This original data switch was the subject of my very first CDD issue, and I followed the HHS data system closely throughout 2020.) Now, Bloomberg reports, the CDC wants to take back hospital data reporting from the HHS. More political posturing and data quality concerns are, it seems, inevitable—this time tied to the CDC’s challenges in modernizing its data systems.
- Hospitalizations among young children, by race/ethnicity during Omicron surge: Two MMWR studies that caught my attention this week: one examined hospitalization rates among young children, ages 0 to 4, between March 2020 and February 2022. This study found that COVID-19 hospitalization rates among children in this age range were five times higher at the peak of the Omicron surge compared to the Delta surge. The second report examined hospitalizations by race and ethnicity, finding that, during Omicron’s peak, hospitalization rates among Black adults were nearly four times higher than rates among white adults. Both reports clearly demonstrate who is still vulnerable to COVID-19 as the U.S. abandons safety measures.
- Pfizer and Moderna both seeking EUAs for additional booster shots: POLITICO reported this week that first Pfizer, then Moderna have requested Emergency Use Authorization for fourth doses of their COVID-19 vaccines. Pfizer’s request is specifically for people age 65 and over, while Moderna’s is for all adults. Notably, Pfizer’s request is based on data from Israel suggesting that immunity from an initial booster wanes after several months—just as Pfizer’s initial case for boosters in the fall was also based on Israeli data.
- Global COVID-related deaths may be three times higher than official records: Throughout the pandemic, researchers have used excess mortality (i.e. the deaths occurring in a given region and time period above what’s expected) to determine the true toll of COVID-19. A new study, published this week in The Lancet, took this approach for 191 countries and territories from January 2020 to December 2021. The researchers estimate that about 18 million people died worldwide due to the pandemic—including not just direct COVID-19 deaths but also others caused by COVID-related disruptions. That’s three times higher than the 6 million COVID-19 deaths that have been officially reported in this time period.