- CDC committee recommends adding COVID-19 to childhood vaccine schedule: The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), which makes guidance on vaccination policies, issued a report this week recommending that COVID-19 vaccines be added to the standard childhood immunization regimen. Under the new guidelines, most children ages six months and older should receive two doses of a Moderna or Pfizer vaccine, followed by a bivalent/Omicron-specific booster shot. Immunocompromised children are eligible for additional doses.
- KFF’s latest COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor focuses on winter surge: The Kaiser Family Foundation recently released the January 2023 update of its Vaccine Monitor project, which tracks U.S. sentiment around COVID-19 vaccines (and other pandemic topics) over time. In the latest round of surveys, KFF researchers found that about 38% of U.S. adults reported that “their households experienced either COVID-19, the flu, or RSV over the past month or so.” About 46% of adults reported that the news of these viruses made them more likely to take safety precautions. The report also includes data on bivalent booster shot uptake, behavior among immunocompromised people, and more.
- New variants have yet to emerge from China, study suggests: A new paper from researchers at the Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control, published in The Lancet this week, found that COVID-19 cases in China during November and December 2022 were primarily driven by the Omicron subvariants BA.5.2 and BF.7. Both of these lineages entered China from other countries, rather than evolving during the country’s surge following the end of its “zero COVID” policies. The new paper is good news for global health experts who’ve been worried about new variants emerging from China, though outside reviewers have cautioned that it’s only one small snapshot of cases in the country, according to reporting by POLITICO EU.
- Wastewater surveillance has a global health equity problem: Another study that caught my attention this week was a paper from the COVIDPoops19 team at the University of California Merced, summarizing findings from their global wastewater dashboard. The team reviewed wastewater surveillance projects at over 200 universities, 1,400 sites, and 55 countries, and found that monitoring primarily occurred in high-income countries. The researchers also examined open access to data, finding that high-income countries were better at sharing information with researchers and with the public. For wastewater-based epidemiology to reach its full potential, “show us the data,” the team writes in their paper’s abstract.
- Microbiome research shows promise for understanding ME/CFS: In one more piece of research news: two recent studies suggest that the gut microbiome could play a role in causing myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), a debilitating chronic disease that often occurs after viral infection. In research projects funded by the National Institutes of Health, scientists found specific changes to gut bacteria that were associated with ME/CFS patients. These changes could potentially be used as biomarkers to diagnose ME/CFS and as starting points for treatment. The new research also has potential implications for Long COVID, as many Long COVID patients meet the diagnostic criteria for ME/CFS.
Tag: China
-
Sources and updates, February 12
-
China’s not the only country with unreliable COVID-19 data
China is currently facing a massive COVID-19 surge, after ending many of its stringent “zero COVID” policies in December. Some estimates suggest that the country is experiencing over a million new cases each day, and widespread travel over the Lunar New Year later this month will likely prolong the surge.
Among U.S. media outlets covering the situation, a common topic is China’s lack of reliable COVID-19 data. For example: “The country no longer tallies asymptomatic infections or reliably reports COVID deaths—employing not the distortion of statistics but their omission,” writes Dhruv Khullar in The New Yorker.
Articles like Khullar’s accurately describe how difficult it is to understand the scale of COVID-19’s impact on a country without accurate data. But they fail to explain that this is far from a uniquely Chinese problem. In fact, many of the same claims that writers and health experts have made about China could also apply to the U.S., albeit on a different scale.
Some examples:
- Without widespread PCR testing, officially-reported case counts are likely significant underestimates of true infections.
- Public health agencies are no longer doing widespread contact tracing or attempting to track asymptomatic cases.
- Official death statistics are also likely underestimates, due to errors and omissions on death certificates.
- Unchecked spread of the virus could contribute to the development of new variants that evade prior infections and/or vaccinations, but such variants will be hard to quickly identify due to low testing rates.
This Twitter thread, from the writer and podcast host Artie Vierkant, shows the similarities pretty clearly:
Don’t get me wrong—the current surge in China is an immense tragedy. But we can’t talk about it in a vacuum, or ignore the very similar problems plaguing the U.S. and many other countries. Poor COVID-19 data is, unfortunately, a global issue right now.
More international data
-
Sources and updates, January 8
- NIH launches at-home testing telehealth program: This week, the National Institutes of Health announced the first location for “Home Test to Treat,” a new program that will make it easier for people in vulnerable communities to receive Paxlovid after testing positive on at-home, rapid tests. The Biden administration first announced this program in September, but it’s formally launching now with Berks County, Pennsylvania as the first participating community. As Paxlovid shifts to a drug that must be privately purchased instead of provided for free by the federal government, more programs like this one will be needed to fill access gaps.
- Study estimates global Long COVID prevalence: A large team of researchers, led by population health scientists at the University of Washington, conducted an extensive review of Long COVID symptoms. The analysis used 54 prior studies and two medical record databases, incorporating data from 1.2 million people in total. Overall, about 6% of patients reported at least one class of Long COVID symptoms three months after their initial infections, with the vast majority of cases occurring in people who had mild acute cases. The study was published in JAMA in October, but gained attention this week thanks to an article that its leading authors wrote in The Conversation.
- China’s COVID-19 data are unreliable: It’s been about a month since China loosened its COVID-19 protocols in the wake of protests and contagious Omicron subvariants, and the country is now facing a massive surge—with as many as one million new cases a day according to some modeling estimates. Yet COVID-19 deaths reported in the country have been very low, fewer than five a day. This discrepancy suggests that China’s authorities are not correctly counting their COVID-19 deaths, while the country’s dismantled testing infrastructure has also led to less reliable case numbers. Officials from the World Health Organization have formally called on the country to “be more forthcoming with information” about its COVID-19 surge, reports Helen Branswell at STAT News.
- CDC testing airplane wastewater on flights from China: In response to surveillance concerns, the CDC is working to test wastewater on flights arriving from China in select U.S. airports. This method is, of course, more efficient than testing every single traveler from the country in the interest of identifying any new variants that might arise. (Though it’s worth noting that some experts are skeptical about the potential of new variants arising in China.) Scientists from Concentric, a company that works with the CDC on traveler surveillance, previously talked about plane wastewater testing during our interview in November.
- Race/ethnicity differences among child vaccination rates: Finally, a notable study in this week’s CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: researchers at the CDC and collaborators examined vaccination rates among children ages five to 17 using data from the National Immunization Survey. They found vaccination coverage (with at least one dose) was highest among Asian children (at about 75%), followed by Hispanic or Latino children (49%), white children (45%), and Black children (43%). The researchers also noted differences among vaccination rates by other socioeconomic factors, and by parents’ mask-wearing habits.
-
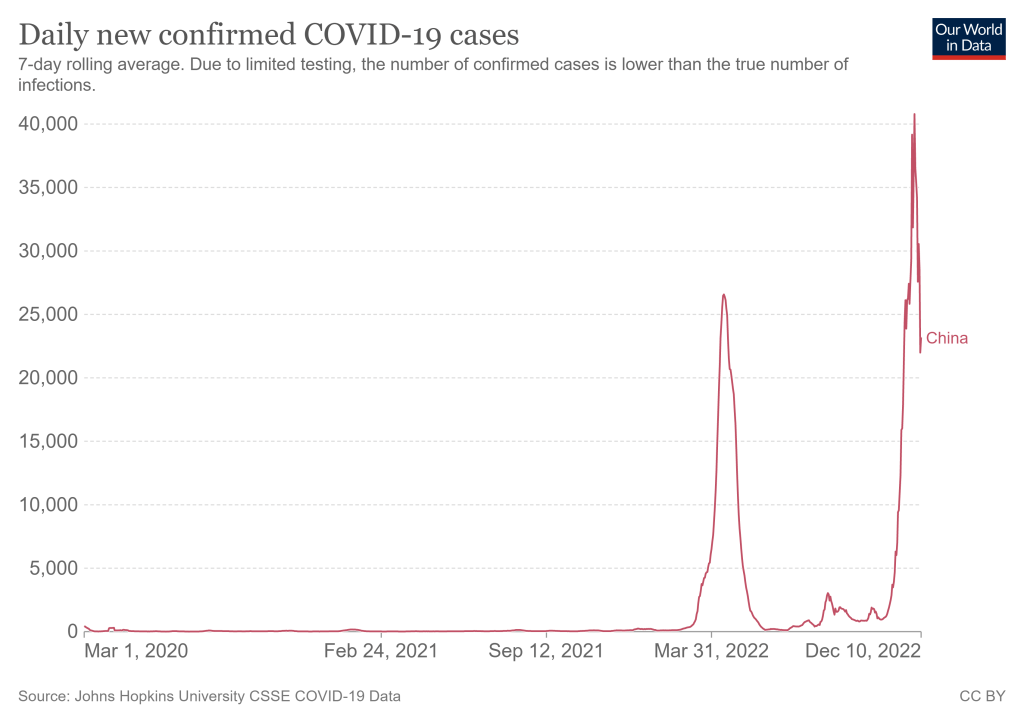
Data implications of China ending its zero-COVID policies

As China rolls back on COVID-19 safety measures, its rising case load is likely to shoot up further. Chart from Our World in Data. China has rolled back some of its most rigorous COVID-19 safety policies, essentially moving away from its “zero COVID” strategy, following recent protests. I am no expert on China’s political or health policies here, but I did want to share some reflections on what this rollback could mean for global COVID-19 data, citing from Katherine Wu’s recent story in The Atlantic.
First of all, it’s important to note that we don’t have much information about coronavirus variants circulating in China. According to the global database GISAID, China has submitted a total of just 667 Omicron sequences—compared to nearly two million from the U.S. The country’s most recent sample was submitted on November 29, almost two weeks ago. Some reports, like this one in the Global Times, suggest that Omicron BF.7 is the dominant variant in Beijing, but the pattern could be different in other parts of the country.
Without more data, it’s hard to say for sure. And this is concerning because, if a new variant evolves in China as the virus spreads more widely there in the coming weeks, it could take more time for the rest of the world to learn about it than if a new variant emerged in other countries. Quick responses and international collaboration have been crucial in responses to new variants over the last two years; the global scientific community needs to be prepared to study and adapt to any new variant that might come out of China.
At the same time, China’s case data are going to become less reliable as the country reduces its clinical testing. Daily case numbers have already appeared to drop, per Our World in Data, but this could be a product of less testing for asymptomatic people (and/or data delays) rather than a surge actually turning around. I also noted that Our World in Data does not have any testing numbers for China more recent than April 2022.
China is already more limited at sharing COVID-19 data than other countries. But if case numbers become less reliable, it will get harder for international health experts to keep tabs on how bad China’s surge is getting. And it could get very bad: one modeling analysis, published in Nature in May, found that an unchecked Omicron wave in the country could lead to demand for intensive care units at 15.6 times the country’s current capacity—and 1.55 million deaths.
Based on its current healthcare system, China is not prepared for a massive national surge of severe COVID-19 cases. It’s probably even less prepared for the massive surge of Long COVID cases that could follow. This has implications for global health, economics, and more.
From the last paragraph of Wu’s great article:
Even without a spike in severe disease, a wide-ranging outbreak is likely to put immense strain on China—which may weigh heavily on its economy and residents for years to come. After the SARS outbreak that began in 2002, rates of burnout and post-traumatic stress among health-care workers in affected countries swelled. Chinese citizens have not experienced an epidemic of this scale in recent memory, Chen told me. “A lot of people think it is over, that they can go back to their normal lives.” But once SARS-CoV-2 embeds itself in the country, it won’t be apt to leave. There will not be any going back to normal, not after this.
More international data