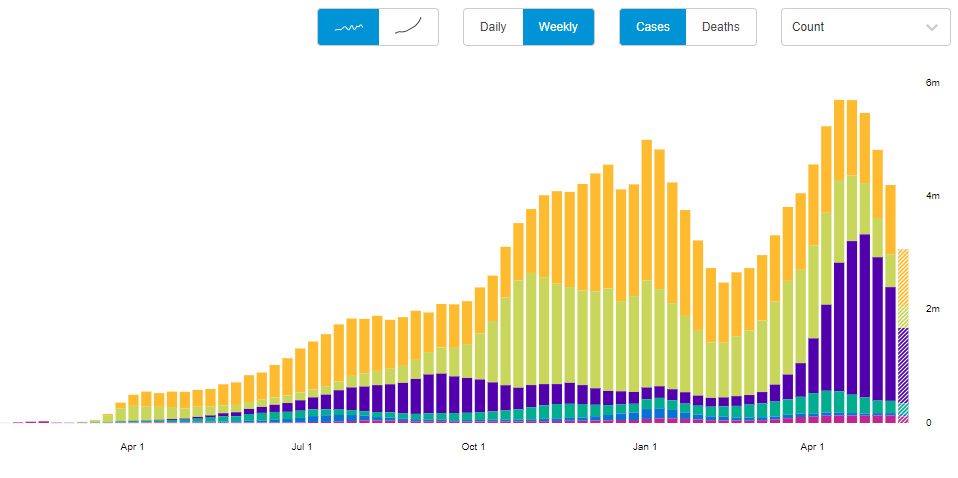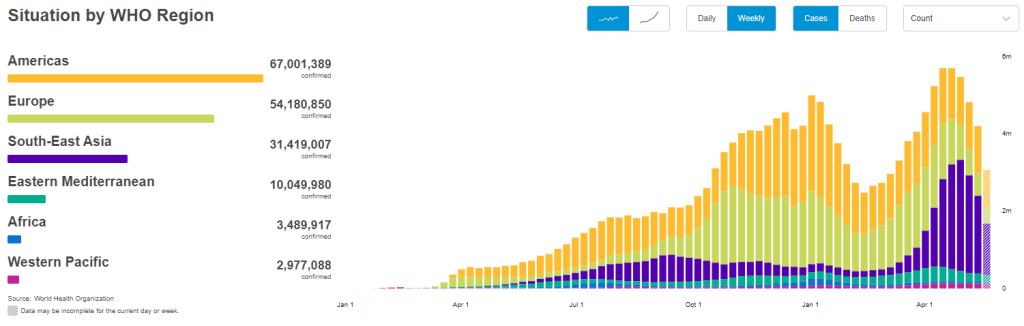
In the past week (May 22 through 28), the U.S. reported about 151,000 new cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 22,000 new cases each day
- 46 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 22% fewer new cases than last week (May 15-21)
Last week, America also saw:
- 21,900 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals (6.7 for every 100,000 people)
- 3,000 new COVID-19 deaths (0.9 for every 100,000 people)
- 70% of new cases in the country now B.1.1.7-caused (as of May 8)
- An average of 1.4 million vaccinations per day (per Bloomberg)
Cases, deaths, and hospitalizations all continue to drop nationwide. The U.S. reported about 3,000 COVID-19 deaths last week, in total—at the peak of the winter surge, we saw more than 3,000 deaths a day.
This trend is echoed in most states. In the May 27 Community Profile Report, the HHS classifies almost every state as “orange” (between 50 and 100 new cases per 100,000 residents over the past week) or “yellow” (between 10 and 50 cases per 100,000). Wyoming is the only state in the “red” classification, at 101 cases per 100,000 over the past week—while California is in the green, with only 9 cases per 100,000.
In New York City, where I live, every single ZIP code currently has a test positivity rate at 3% or lower—for the first time since last summer. This is yet another piece of good news showing how well the vaccines work. Half of the total U.S. population has had at least one dose and more than half of the adult population is fully vaccinated, as of yesterday.
The vaccines also continue to do their part against variants. The CDC variant data—updated this week—indicate that B.1.1.7 is still growing, but it’s leveling off as new cases slow. This variant has gone from causing about 60% of cases in early April, to 67% in mid-April, to 70% in early May; a much slower decline than what we saw in February and March.
Of more concern: P.1, the variant first identified in Brazil, is causing 7% of U.S. cases as of May 8—and the CDC’s Nowcast estimate puts it at almost 10% of cases by May 22. B.1.617, the variant first identified in India, is also sharply increasing; its case share doubled from April 24 to May 8. Both of these variants are more transmissible (B.1.617 dangerously so) and may have lowered vaccine efficacy.
But the harm these variants can cause in the heavily-vaccinated U.S. pales in comparison to the risk they pose in other nations. As evidenced by the World Health Organization chart above, the share of cases in Southeast Asia and other lower-income nations is increasing even as cases in the U.S. and Europe drop. The U.S. should focus on providing aid to the nations where vaccinations are lagging so that we can help inoculate people before more, harder-to-contain variants evolve.
In other words, there’s a reason I’m not giving space to the lab leak theory in this publication. If you’d like to read more about the issue, I recommend this article by Amy Maxmen.