This week, I had a new story published with FiveThirtyEight and the Documenting COVID-19 project about the data and implementation challenges of wastewater surveillance.
COVID-19 levels in waste—or, from our poop—have become an increasingly popular data source in the last couple of months (in this newsletter and for many other reporters and commentators), as PCR testing sites close and at-home tests become the norm. Wastewater can provide us with early warnings of rising transmission, and it includes COVID-19 infections from people who can’t or don’t want to get a PCR test.
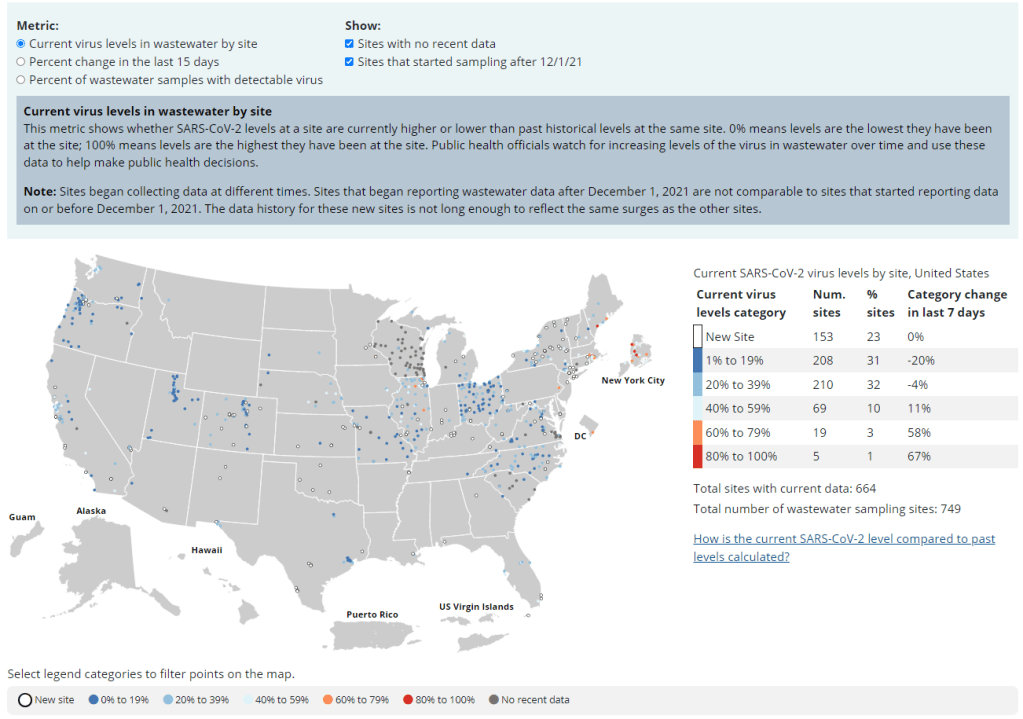
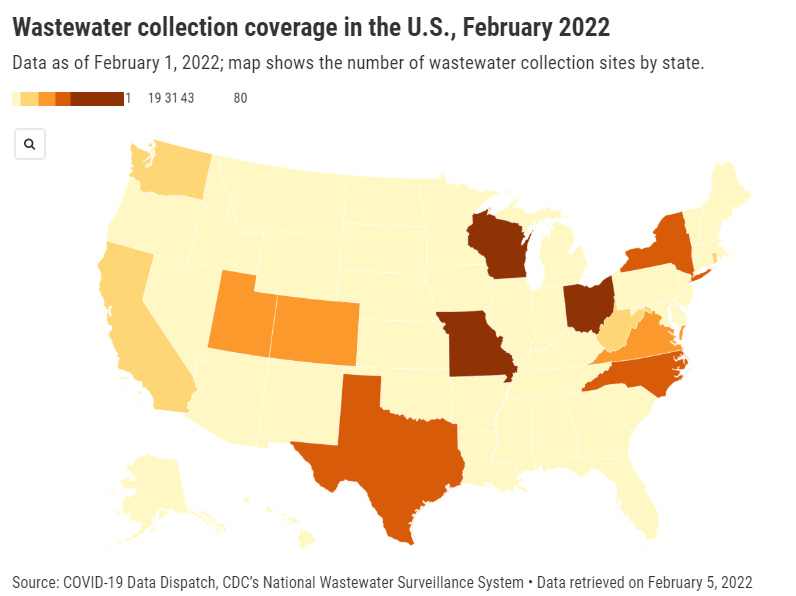
But wastewater surveillance is very uneven across the country, as I’ve noted before. A lot of local health agencies, research groups, and utility companies are now trying to expand their COVID-19 monitoring in wastewater, but they face a lot of barriers. My reporting suggests that we are many months (and a lot of federal investment) out from having a national wastewater surveillance system that can actually replace case data as a reliable source for COVID-19 trends and a driver for public health action.
For this story, I surveyed 19 state and local health agencies, as well as scientists who work on wastewater sampling. Here are some major challenges that I heard from them (pulled from an old draft of the story):
- Wastewater surveillance is highly sensitive to changes in a community’s coronavirus transmission levels, particularly when those levels are low, as has been the case across the U.S. in recent weeks.
- Every wastewater collection site is different, with unique environmental and demographic factors – such as weather patterns or popularity with tourists – that must be accounted for.
- While the CDC has led some coordinated efforts through the National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS), wastewater sampling techniques overall aren’t standardized across the country, leading to major differences in data quality.
- Sparsely populated, rural communities are particularly challenging to monitor, as their small sizes lead to even more heightened sensitivity in wastewater.
- Wastewater data is hard to communicate, especially when public health officials themselves aren’t sure how to use it. The CDC’s NWSS dashboard is a prime example.
As bonus material in today’s COVID-19 Data Dispatch, I wanted to share one of the interviews I did for the story, which provides a good case study of the benefits and challenges of COVID-19 surveillance in wastewater.
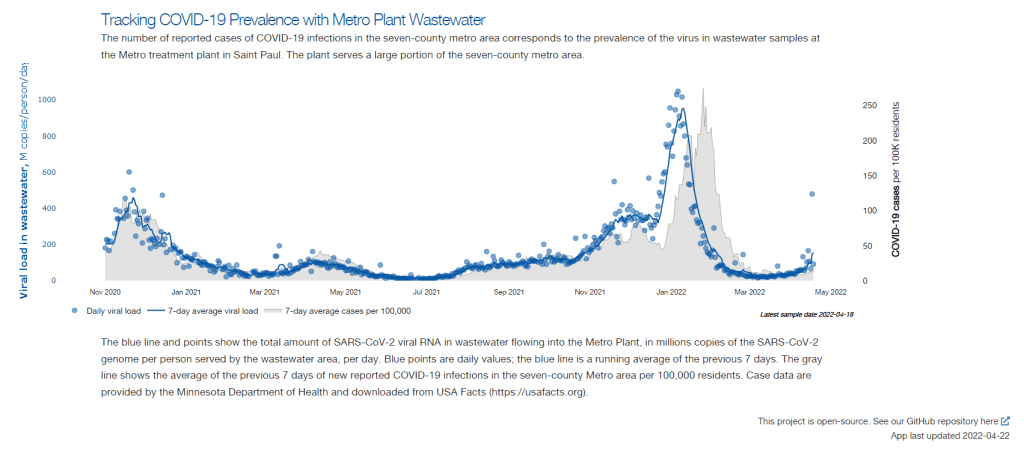
In this interview, I talked to Steve Balogh, a research scientist at the Metropolitan Council, a local agency in the Twin Cities, Minnesota metro area that manages the public water utility (along with public transportation and other services). Balogh and his colleagues started monitoring Twin Cities’ wastewater for COVID-19 in 2020, working with a research lab at the University of Minnesota.
Balogh gave me a detailed description of his team’s process for analyzing wastewater samples. Our conversation also touches on the learning curve that it takes to set up this surveillance, the differences between monitoring in urban and rural areas, and the dynamics at play when a wastewater plant suddenly becomes an important source for public health information. Later in the interview, Bonnie Kollodge, public relations manager at the Metropolitan Council, chimed in later to discuss the wastewater data’s media reception.
This interview has been lightly edited and condensed for clarity. Also, it’s worth noting that the interview was conducted in early April; since then, COVID-19 levels have started rising again in the Twin Cities metro area’s wastewater.
Betsy Ladyzhets: The first thing I wanted to ask about was, the backstory of sampling at the Metro Plant. I saw the dashboard goes back to November 2020, and I was wondering if that’s when you got started, and how that happened?
Steve Balogh: We actually started looking into it in April of 2020. And we contracted with Biobot at that time… But in May, their price went up, so we started looking for alternatives. Then, we started a partnership with people at the University of Minnesota Genomics Center, who know about measuring RNA in things.
At that point, we tried to figure out how to extract the RNA from our samples. They [University of Minnesota researchers] didn’t know anything about wastewater, but they knew everything about RNA. We know all about wastewater, but we don’t know anything about RNA. So it was a good match.
That summer, [the university researchers] started trying to do the extractions and it didn’t really work out so well… So we said, “Okay, we’re going to try this.” By September of 2020, we had built our own lab, and we were trying out our own extractions, based on what we were seeing in the literature, and all the preprints that were piling up. In October, basically we settled on [a sampling process] that worked. And by November 1, we were actually getting data.
BL: Yeah, that definitely aligns with what I’ve heard from some of the other scientists I’ve talked to who have worked on this, where it’s like, everybody was figuring [wastewater sampling methods] out on their own back in 2020.
SB: Yeah, it was on the fly. Papers were coming out daily, just about, with new ideas on how to do things. And we had, like, four different extraction methods that we wanted to look at, also looking at sludge, in addition to influent wastewater… Honestly, it was pretty much pure luck that we settled on [a method] that really, really worked.
We tried to get daily samples, and to put up numbers and see what [the data] looked like. And it actually did work—it actually tracked the reported caseload quite well. We figured, well, it must be working. We also did QA [quality assurance] in the lab, spiking the samples with known amounts of RNA, and trying to get that back. And all of that came back really well, too. So, we have a lot of confidence in our method.
BL: So that [QA] is like, you put in certain RNA, and then you check to make sure that it shows up in the sample?
SB: Exactly, yeah.
BL: What is your process for analyzing the samples and distinguishing those trends, like seeing how they match the case numbers?
SB: We do the extractions at our lab, with the samples from the Metro Plant. We take three milliliters of wastewater and we add 1.5 milliliters of something called Zymo DNA/RNA Shield, from a company in California called Zymo. That’s a buffer that stabilizes the RNA—it basically explodes whatever virus particles are in there, breaks them up, and then it stabilizes the RNA in the sample. So you can actually store those samples at room temperature for days, or maybe even weeks, because the RNA is stabilized.
Then, we put that treated sample through a two-step extraction process. The first step is, we put the whole thing into a Zymo III-P column, combined with 12 milliliters of pure ethanol, and run that through the column. This is a silica column, so the RNA in the sample binds to the silica. Then we wash it and elute that RNA in 200 microliters of water. And then we take that 200 microliters, and run it though the second stage, which is just a smaller silica column. The RNA that’s in that 200 microliters binds onto the smaller column, and then we wash it and elute that into 20 microliters.
Our total concentration is going from three milliliters of wastewater down to 20 microliters of pure water. That’s a concentration factor of 150. We figured that would work for pretty much most situations, and it’s turned out to be true.
Then, we store those samples at minus 80 degrees Celsius. Until we take them over weekly to the University of Minnesota, where they do droplet digital PCR, RT-PCR, to amplify and detect the RNA that’s in our samples. We started out just getting the total viral load back in November 2020. But then, in the early part of 2021 when Alpha showed up, we started doing variant analysis as well. We’re now also looking for specific mutations that distinguish the different variants of concern, like Alpha and Delta and Omicron.
BL: So, you take the samples every day, but then you bring them over [to the university] once a week, is that correct?
SB: That’s correct.
BL: When you’re getting that data, coming from the U of MN lab, what are you doing to interpret it? Or, in communicating the data on your dashboard, what are the considerations there?
SB: We work up the numbers and calculate a total load of the virus, or the particular variants, that’s coming into the plant. And then we basically put that up on the dashboard. There’s not a whole lot of interpretation or manipulation of the data—we’re simply importing the load, basically, of what we see coming into the plant. The load is the concentration that we’ve measured in the sample, times the total volume of wastewater coming into the plant.
We think that’s a sufficient normalization procedure for a large wastewater treatment plant. I know some groups are using other normalization techniques, but we think load is sufficient to tell us what’s happening out in our sewer shed.
BL: Yeah, that makes sense. I know this gets more complicated when you have smaller sites, but your sewer shed is serving a big population—
SB: Almost two million people. Yeah, it’s a big sewershed. If you had 50% of your population leaving during the day to go to work in the next community, that would be something that you might have to consider using other normalization techniques. But that just isn’t the case [in the Twin Cities]. We see a pretty steady signal here.
BL: Makes sense. Have you considered expanding to other sites? Or are is the plan to just stick with sampling at the main sewer ship location?
SB: We already have, actually. We operate nine different wastewater treatment plants in the seven-county metro area. And we’ve already expanded to three of those other sites, so we now have four total plants that we’re taking samples at and having them analyzed at the Genomic Center. It only started within the last month, so we don’t have quite the database to really start showing it on our dashboard yet. But when we do [have more data], our plan is to put that up [on the dashboard] as well.
BL: Do you have a sense of how much time it might take before you feel the data is useful enough to put on the dashboard?
SB: Part of the problem has been, all of these samples that we’re getting from these other plants, we’re just taking the entire sample over to the Genomics Center, and they’re doing the extractions. They’re using my extraction procedure, but they’re doing it in their lab. So, there was some learning curve for them to figure that out. And also to hire staff and come up to speed in terms of facility, and procedure, and people… Now, it’s been a few weeks, and I think they’re just about there [in getting a handle on the RNA extraction methods]. So, I think our data will start to shape up pretty quickly.
Another thing that may be keeping us, at this point, from showing the data is, nothing’s happening. We’re at this bottom [with low coronavirus levels in the wastewater] where everything just looks noisy, because nothing’s changing. But as soon as we start to go up, and if we get higher—the current position is just going to look like a flat line. But right now, people could look at it and say, “Well, that’s just junk.”
So, in that sense, we just don’t want to confuse matters and say, “Here’s a bunch of junk for you to look at. We want to put it into some context. And the context really is, when things start taking off, then you see, “Oh, it used to be very low. And now it’s very high.”
(Editor’s note: Since this interview was conducted in early April, COVID-19 levels have started rising in the Twin Cities metro area.)
BL: That makes a lot of sense. Also, I hear you on the challenges of learning these methods. I was a biology major in school, and I worked in a lab, briefly, that did RNA extraction. And I remember how tricky it is, so I can envision the learning curve.
SB: Well, these are experts at the Genomics Center, they know what they’re doing. But I think even they have been surprised at how how robust the viral RNA is in wastewater. A lot of people at the beginning of this pandemic said, “You’ll never see it in wastewater. It’s RNA, RNA is very sensitive, it’ll break down.” But that just isn’t the case—the RNA is quite robust in wastewater, and the signal lasts for a long time. It has to last for many hours, for it to travel from the far end of our sewershed to get to us [at the treatment plant]. And then, even in the refrigerator, when you refrigerate just the raw sample, it’ll stay in a reasonable concentration without dropping too much for days.
BL: What has the reception to this work been from the public, the state health department, or from local media or other people who are using and watching the data?
SB: It’s been incredible. You can ask Bonnie more about it.
Bonnie Kollodge: It’s ginormous. I mean, it just has spread everywhere. I don’t even know the social spread, but I think somebody was tracking our impressions in print and online media… I think there were, like, 11 million impressions between January and the end of March. And we get lots of requests for Steve’s time, lots of requests for a daily accounting [of the data].
When we began this work, it really was out of public service—seeing that there’s a pandemic going on, and what can we do to help? That’s when they started developing this idea, then working with the Depratment of Health, which is really our state lead on this [COVID-19 response]. They came to rely heavily on our information, to compare it against what their test results were showing. Then, as people started to do home testing, that was a whole other factor. It was really wastewater that was taking the lead on showing what was happening with the virus and the variants…
Every week, we put an update online, and reporters go right to it, to determine how they’re gonna position [their COVID-19 updates]. Steve also provides, in addition to the data, a little narrative about what’s happening that helps reporters—some who are very conversant in data, but others who are not—it helps them it understand what we’re seeing.
BL: I can see how that would be helpful, especially if you’re releasing a week’s worth of data points at once. You sort-of have a mini trend to talk about.
BK: Yeah, and we send it to the governor’s office, and to the Health Department. They appreciate the transparency… They know what’s happening [with the virus], and can adapt.
BL: Right. And Bonnie, you mentioned something I wanted to ask more about, which is how the increased use of at-home tests and lower availability of PCR tests has increased the demand for wastewater data in the last few months, in particular. Now that you maybe have less reliable case data to compare against, has the thinking and interpreting the wastewater data shifted at all?
SB: I think we’ve actually had that statement from reporters. They’ve said, “We can’t trust the testing data anymore. And it’s going to be wastewater from here on out.”
BK: Just this week, there was a reporter who asked to get early results tomorrow. And he said, “This [wastewater data] is what I’m watching.” … The public has glommed on to this resource as a demonstration of what’s happening. And, like Steve said, it’s not a small sample. There are almost two million people served by this by this particular plant.
BL: From what I understand, part of what can be really helpful [with wastewater data] is when you have that longevity of data, as you all do. You have a year and a half of trends. And so when you see a new spike, it’s easier to compare to past numbers than for other parts of the country that are just starting their wastewater surveillance right now.
SB: Yeah. I think the other thing that has been really useful for our [state] department of health is, they’ve really appreciated the variant data that we have. That was really the first thing that got their attention… And we were giving them [variant] data ahead of time. The clinical tests were taking days or weeks to come back, and we could give them variant data the same week. So, that was the first thing that got our department of health here interested. But when they saw that we can track trends, they recognized that this has value at lower levels when testing goes away, basically.
BL: How would you want to see support from the federal government in expanding this wastewater work? Like you mentioned, getting it in more treatment plants, and any other resources that you feel would be helpful.
SB: Well, I think that’s underway, as we understand it, with the National Wastewater Surveillance System, NWSS. I think they’re funded through 2025, and I think the goal there is to basically sign up as many treatment plants as they can in the country.
(Editor’s note: This is accurate, per a CDC media briefing in February.)
Hopefully, that’s the beginning of something that is going to go beyond the pandemic, and give us a measure of community health in the future. Because wastewater is a community urine test, basically. It’s everybody contributing, and it can be useful for other pathogens and viruses in the future. So, yeah, [expanding that network] would be great. Let’s do it.
BL: Do you envision adding other viruses to the testing that you’re doing? Flu or RSV are ones that I’ve heard some folks are considering.
SB: Yeah, that would be something to do going forward for us. Though, it’s not clear how long we continue this work, just because these other projects are expanding, like the national project. And even our department of health here [in Minnesota] is talking about bringing this type of analysis into their own laboratory. Certainly going forward, long-term, that would be a goal for any work done here in Minnesota—to add those things to the menu of what we’re analyzing.
BL: Right. So you might be taking the samples to the Minnesota health department instead of the university, or something like that?
SB: Someday. Yeah, we just don’t know at this point.
BK: This is an evolving scinece. And this is not what we typically do—I mean, we do wastewater collection and treatment. So this [COVID-19 reporting] is a little outside of our regular parameters. But, like Steve and his superiors have been saying, this is an evolving science, so let’s see where this takes us, in terms of infectious disease.
It’s funny, when I go out and talk to people and say, “I work for the Met Council, and I help in communications with the wastewater analysis,” everybody knows what I’m talking about. It’s just so much out there. But I think that these things [testing for other diseases] are all being explored, and this has really opened up new possibilities.
SB: From the beginning, it’s just been a scramble. You don’t know what’s going to be coming. What I’m doing, a lot, is trying to get ourselves in a position so that, when the next variant of concern pops up, we have an assay that can measure it. There’s still a lot of unknowns about what’s going on, and everything’s new every day, just about.