In the past week (April 9 through 15), the U.S. reported about 220,000 new COVID-19 cases, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 31,000 new cases each day
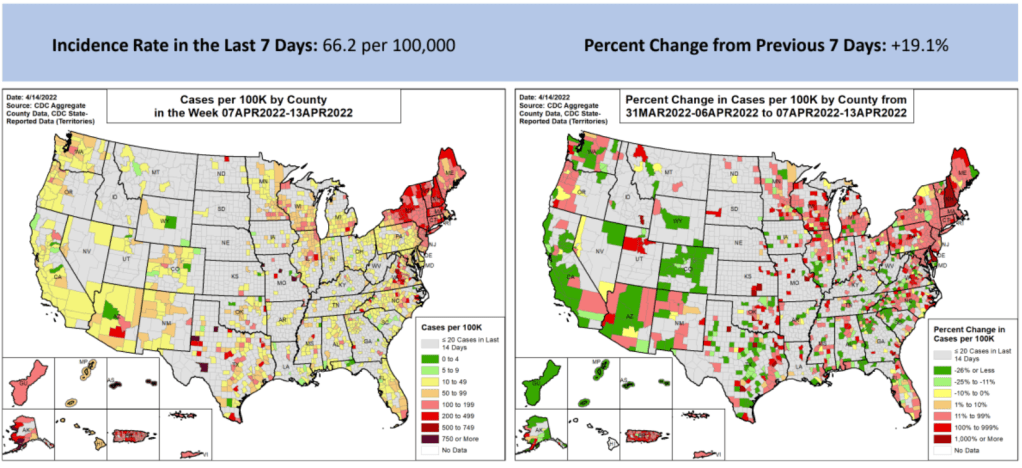
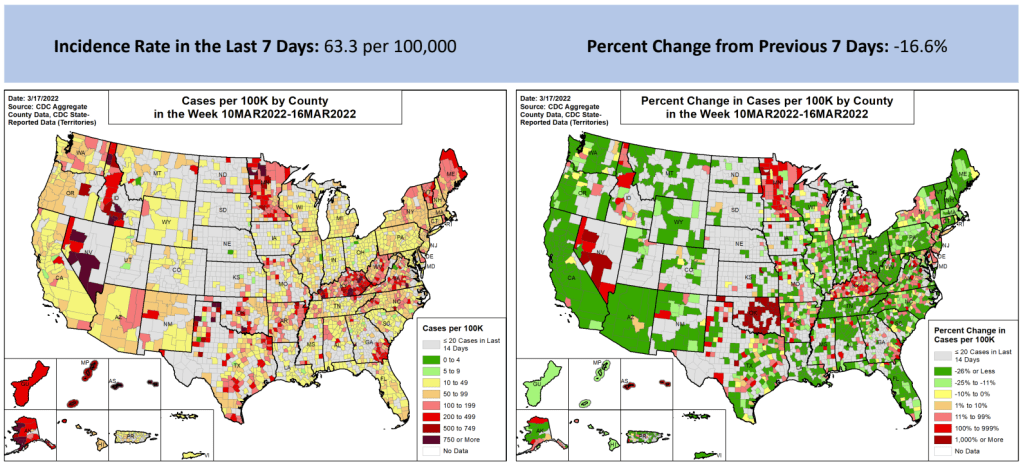
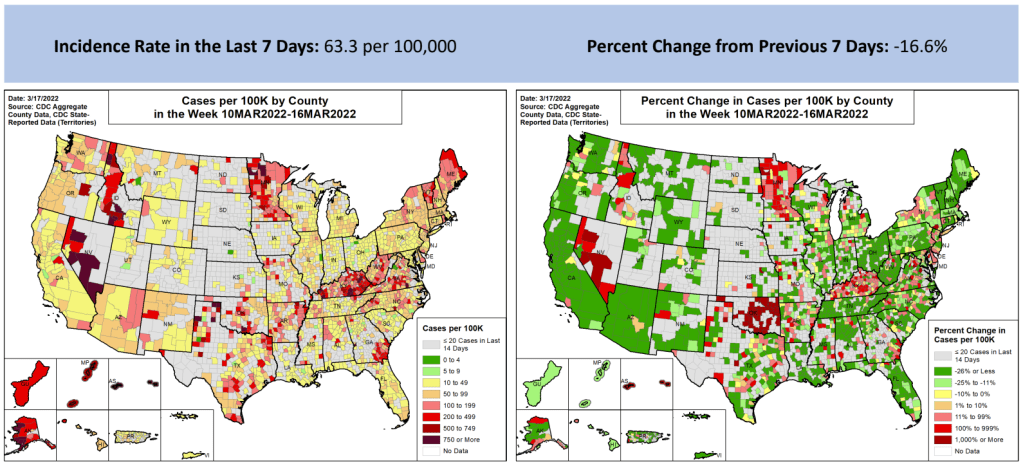
- 67 total new cases for every 100,000 Americans
- 19% more new cases than last week (April 2-8)
In the past week, the U.S. also reported about 10,000 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals. This amounts to:
- An average of 1,400 new admissions each day
- 3.1 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 1% more new admissions than last week
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 2,900 new COVID-19 deaths (0.9 for every 100,000 people)
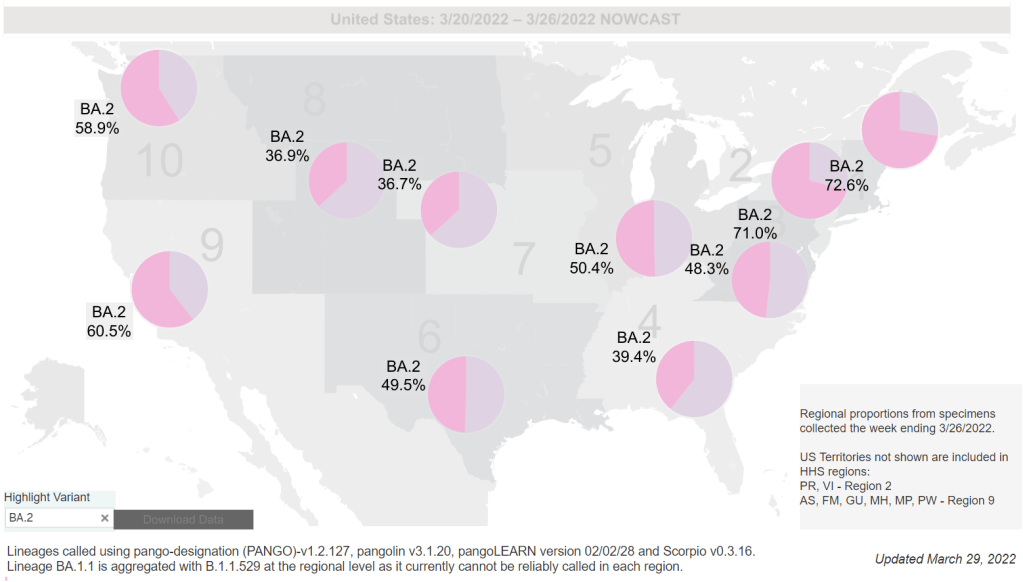
- 100% of new cases are Omicron-caused; 86% BA.2-caused (as of April 9)
- An average of 100,000 vaccinations per day (per Bloomberg)
New COVID-19 cases in the U.S. have gone up for the second week in a row, and the increase was sharper this week. While the daily average of new cases (about 31,000) remains low compared to the Omicron surge, this trend is still concerning—especially when factoring in all the at-home rapid tests that are going unreported right now.
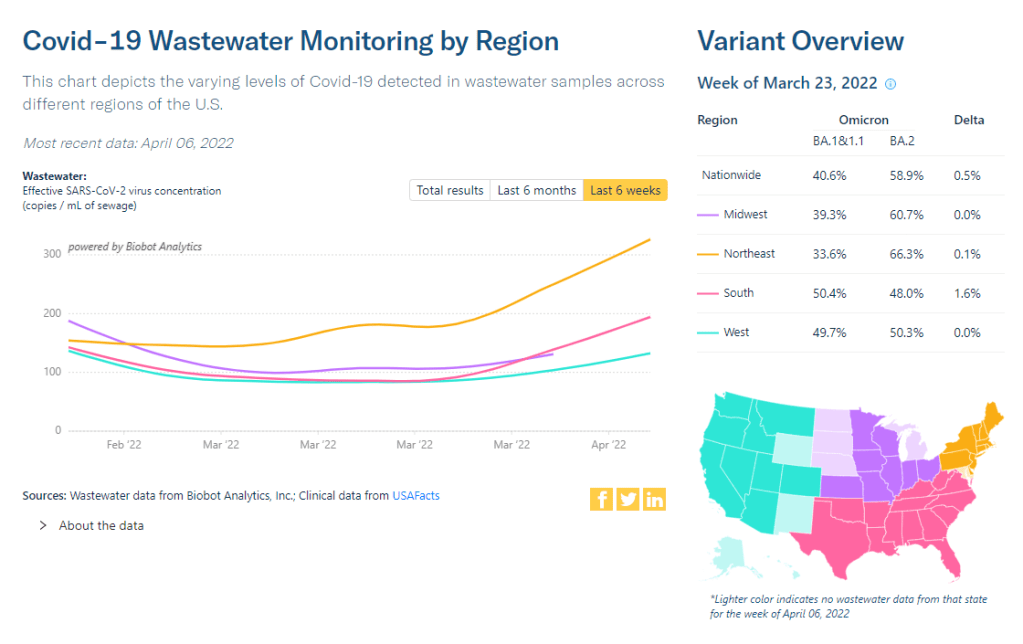
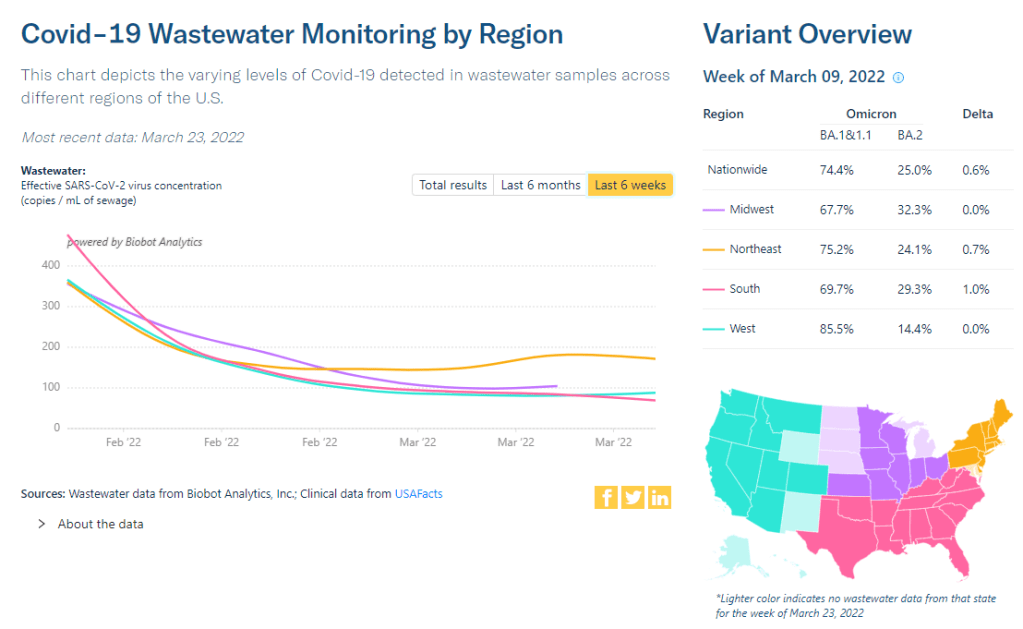
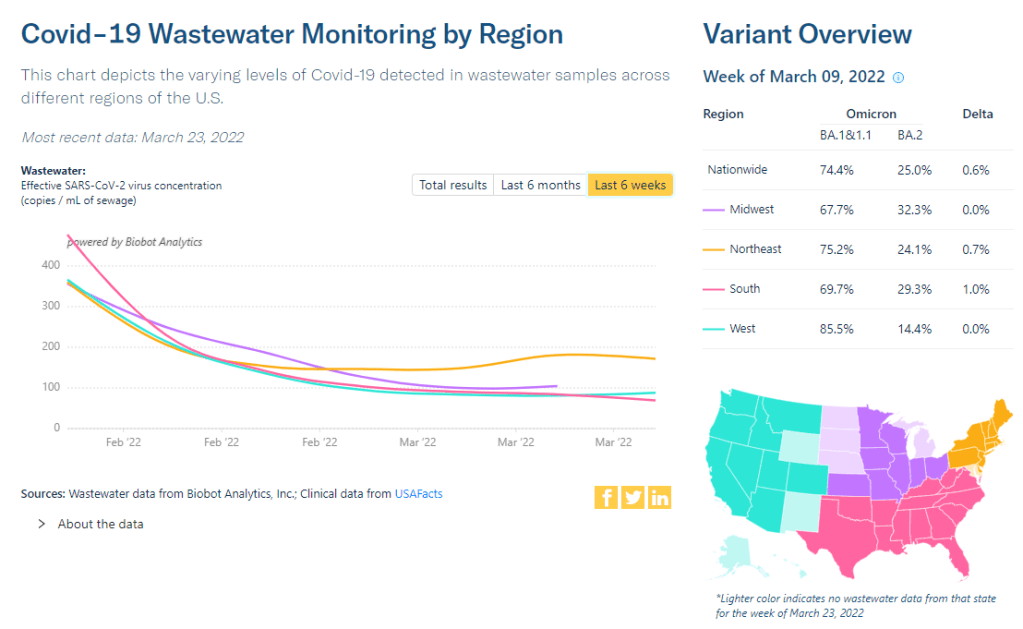
Wastewater trends suggest that cases will continue rising in the coming weeks. Biobot’s dashboard suggests a national increase (most pronounced in the Northeast region), while about 60% of sites in the CDC’s network have reported increasing coronavirus levels in the last two weeks.
Newly hospitalized COVID-19 patients, an indicator that’s typically behind cases but more reliable, is also showing a small increase as of this week. This will be an important metric to watch in the next few weeks: will BA.2 strain hospitals the same way that Omicron BA.1 did in December and January?
BA.2, it’s important to note, is now causing the vast majority of new COVID-19 cases in the U.S. The CDC’s latest estimates suggested that this sublineage made up 86% of cases in the week ending April 9. And some parts of the country may be seeing further mutation of BA.2—more on that later in the issue.
The Northeast continues to be a leader in this surge, as shown by both the wastewater trends and case data. According to the April 14 Community Profile Report, states with the highest case rates in the last week include: Vermont, Washington D.C., Rhode Island, New York, Massachusetts, Alaska, New Jersey, Maine, Connecticut, and New Hampshire.
All of these states are seeing high transmission, according to the CDC’s old guidance. But the new guidance places most counties in these states in low or medium “community levels;” largely because hospitalizations—which, again, are a lagging indicator—haven’t started rising yet.
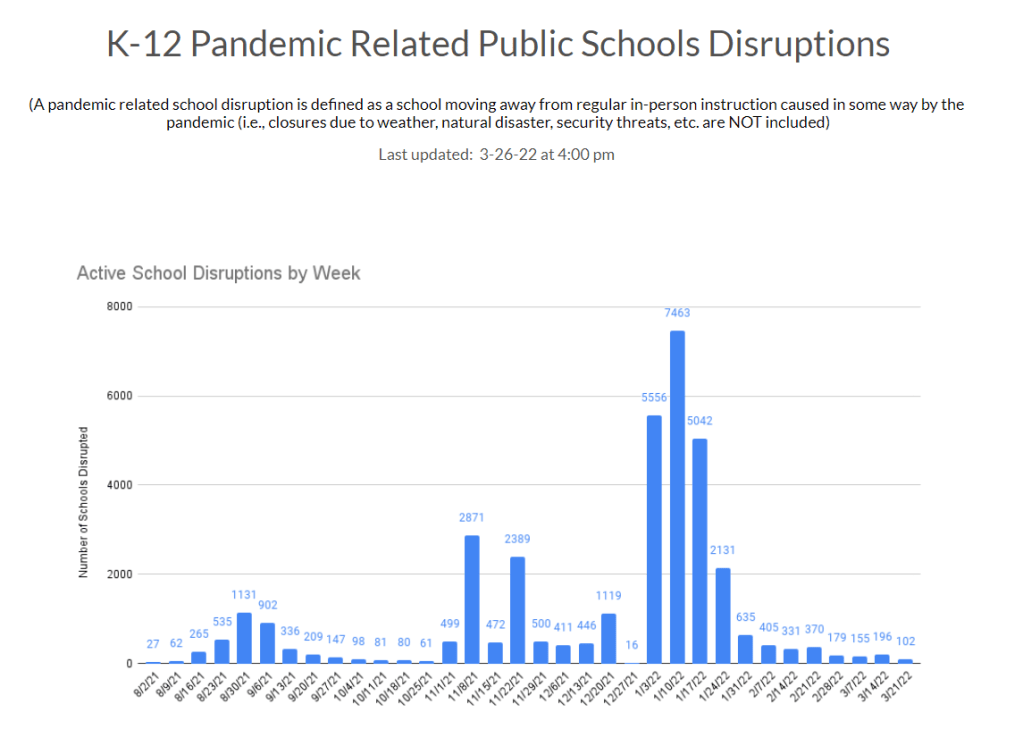
This week, Philadelphia became the first major U.S. city to once again require masks in public indoor spaces, in response to rising cases and hospitalizations. I hope to see other cities and localities follow Philadelphia’s lead, but I know current attitudes make this unlikely.