- Cost details about new treatment from Project Next Gen: The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has recently started to share more details about Project Next Gen, a federal initiative to support new vaccines and treatments as the coronavirus continues evolving. This week, HHS announced details about its agreement with Regeneron, a company working on a new monoclonal antibody with federal funding. If a new treatment arises from this research, Regeneron cannot sell it for a higher price in the U.S. than elsewhere in the world, HHS said. This is a relatively small step for treatment access, but still could set a precedent for other products that come out of Project Next Gen.
- Viral persistence in Long COVID: A new paper from some top Long COVID researchers (including Amy Proal, Michael VanElzakker, and others) reviews evidence about viral reservoirs, or pockets of coronavirus continuing to replicate in people’s bodies. Past studies have found these viral reservoirs throughout the body; Proal and her colleagues explain how they may contribute to different Long COVID symptoms. The review paper also recommends priorities for further research on this topic and potential treatment options. “Many aspects of SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in Long COVID require further study,” Proal wrote in a Twitter thread summarizing the paper. “For example, we need to better understand factors that differentiate SARS-CoV-2 persistence in Long COVID from persistence in asymptomatic individuals.”
- Genetic factors for COVID-19 risk: In another notable paper from this week, researchers from a global consortium published results about how genetic factors may contribute to COVID-19 risk. The team reviewed genomic data from about 220,000 people who had COVID-19 and three million who had not tested positive. They found 51 areas of the genome that were statistically correlated to a higher risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 or more severe symptoms. These findings could lead to “identification of the mechanisms involved in the susceptibility and the severe course of the disease,” one of the study’s lead authors said in a press release.
- Updated Medicaid unwinding data from KFF: The Kaiser Family Foundation has updated its Medicaid Enrollment and Unwinding Tracker, which shares data about people losing their Medicaid coverage thanks to the end of the federal health emergency. As of September 8, at least 5.9 million people across 48 states and Washington, D.C. have lost their coverage, KFF reports. Disenrollment varies widely by state, from 9% in Michigan to 72% in Texas. And the majority of people who lost their Medicaid coverage have done so due to procedural reasons, meaning an error of lost paperwork (rather than an actual change in eligibility, in many cases).
Author: Betsy Ladyzhets
-
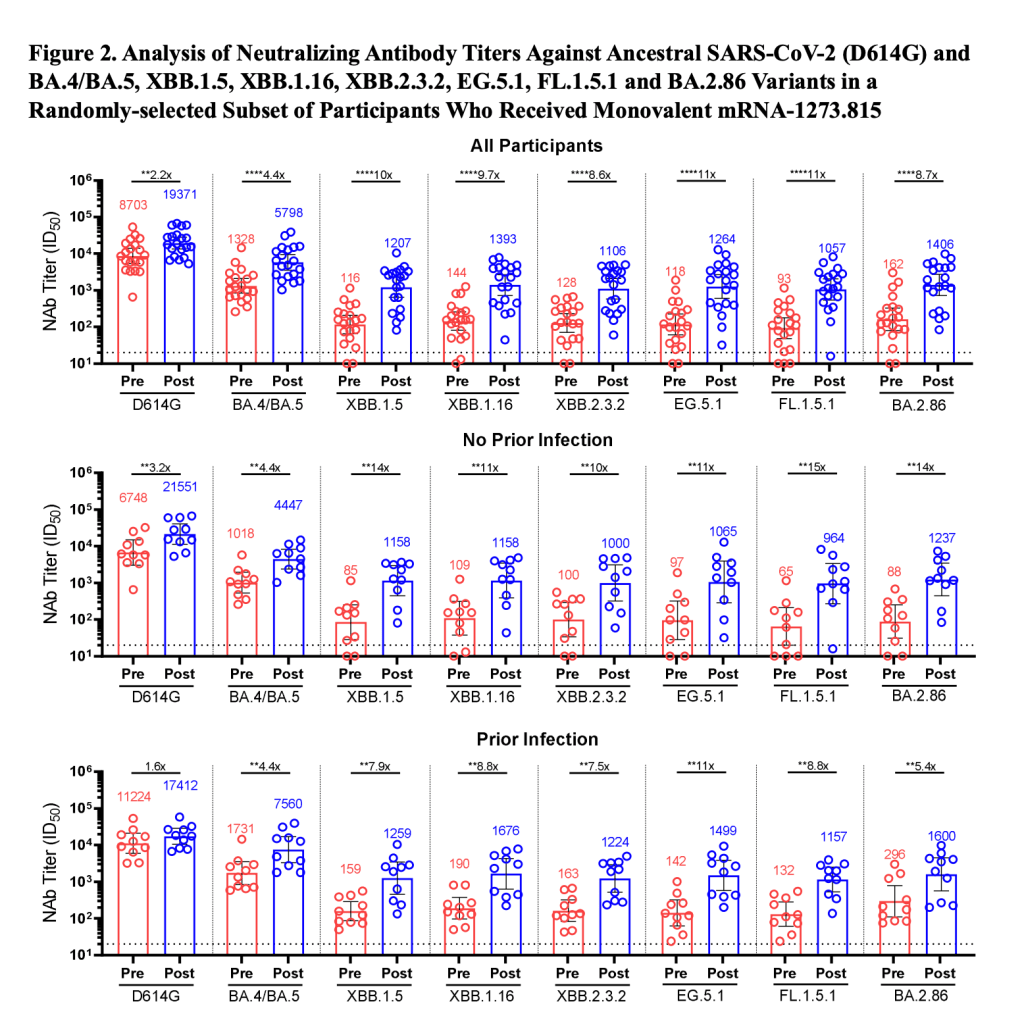
New data on BA.2.86 suggest the fall booster may work well
Since BA.2.86 emerged a couple of weeks ago, scientists around the world have been racing to evaluate this variant. Several teams posted data in the last week, and the news is promising: while BA.2.86 does have an advantage over past variants, the lab findings suggest that vaccines (including the upcoming boosters) and past infections provide protection against it.
The new studies come from research groups in the U.S., China, Japan, Switzerland, and South Africa. These scientists studied BA.2.86 by growing the variant in petri dishes and evaluating it against antibodies from blood samples. Overall, they found that BA.2.86 can infect people who were recently infected with XBB.1.5 and its relatives, but this variant isn’t as successful at getting into human cells as XBB.1.5.
Another notable study came from researchers at Moderna, who evaluated how the company’s upcoming booster shot performs against BA.2.86. This team found that the booster—which is designed from XBB.1.5—helps the immune system prepare for XBB variants as well as BA.2.86. While lab studies like this one don’t translate perfectly to real-world effectiveness, the data do suggest that Moderna’s booster should protect well against BA.2.86 infection for a few weeks after vaccination, and against severe disease for longer.
You might have seen the figure below shared around on social media in the last few days. This chart, from the Moderna team, shows how the new booster improves immunity toward several variants. For example, patients who received the booster had 8.7 times more neutralizing antibodies against BA.2.86 and 10 times more neutralizing antibodies against XBB.1.5 than those who had not received it.

This figure, from a preprint by Moderna scientists, shows how the company’s upcoming fall booster performs against different variants. Pfizer has also tested their new booster against BA.2.86 and found similar results, according to a report from Reuters. This company’s results have yet to be shared in a scientific paper, though.
The studies I’ve discussed here are all preprints, meaning the results have yet to be peer-reviewed (outside of the informal review process that happens on social media for this type of urgent research). It’s also worth noting that lab studies look at immune system signals, rather than actually tracking who’s getting this new variant and their disease outcomes.
Even if BA.2.86 is not “the next Omicron,” as some scientists suggested based on its mutations, it could still contribute to a new uptick in cases this fall. And all cases carry the risk of severe illness, Long COVID, and other poor outcomes. The new boosters are likely to help reduce risk (which is good news), but other measures are still needed.
References about the new studies:
- The BA.2.86 variant and the new booster (Ground Truths by Eric Topol)
- BA.2.86 update (Your Local Epidemiologist by Katelyn Jetelina)
- More COVID-19 studies suggest BA.2.86 may be less immune-evasive than feared (University of Minnesota CIDRAP)
- Covid is on the rise again, but it’s different now (Vox)
-
Answering reader questions: Incubation period, vaccines coming this fall, nasal sprays
I received a couple of reader questions in recent weeks that I’d like to answer here, in the hopes that my responses will be more broadly helpful. As a reminder, if you ever have a COVID-19 question that you’d like to ask, you can email me at betsy@coviddatadispatch.com, or send it anonymously through this Google form.
COVID-19’s incubation period
One reader asked:
I’d love to learn more about COVID’s incubation period. I have read that it’s 2 to 14 days … but the median time seems to be on the low end (and could be as low as 24 hours?) How likely is it that it’s more like 14 days? I’d love to better understand this so that I know how to better handle exposures… Should I avoid someone who has had an exposure for two full weeks?
This is a tricky question for two reasons. First, the incubation period—or the time between exposure to COVID-19 and starting to show symptoms of infection—does indeed vary a lot. One review of studies on this topic, posted as a preprint in May, found a range from two to seven days, though it can be even longer. The CDC recommends precautions for up to ten days after exposure.
Second, the incubation period has changed as the coronavirus has mutated. The virus is constantly evolving to keep infecting us even as people build up immunity; shortening the incubation period is one of its strategies. Omicron has a notably shorter period than past variants; Katherine Wu at The Atlantic wrote an article about this in December 2021 that I think is still informative.
The preprint I cited above found that Omicron had an average incubation period of 3.6 days, shorter than other variants. I think it’s reasonable to assume that this period has continued to get shorter as Omicron has evolved into the many lineages we’re dealing with now. But the pace of research on this topic has slowed somewhat (with less contact-tracing data available for scientists to work with), so it’s hard to say for certain.
So, with these complexities in mind, how should one handle exposures? My personal strategy for this (noting that I’m not a doctor or qualified to give medical advice, just sharing my own experience) is to rely on a combination of timing, testing, and symptom monitoring. For the first couple of days after exposure, you wouldn’t be likely to have a positive test result even if you are infected, as it takes time for enough virus to build up in the body for tests to catch it. So, for those days, I’d just avoid people as much as possible.
After three to four days, PCR tests would start to be effective, and after five to six days, rapid tests would be. So at that point, I’d start testing: using a mix of PCR and rapid tests over the course of several days, up to two weeks after exposure. Studies have shown that the more tests you do, the more likely you are to catch an infection (and this applies to both PCRs and rapids). Daily is the best strategy, but less frequent regimens can still be useful if your access to tests is limited. At the same time, I’d keep track of any new symptoms, as that can be a sign of infection even if all tests are negative.
I’d personally be comfortable hanging out with someone who has had an exposure but consistent negative test results and no symptoms. But others who are less risk-tolerant than I am might avoid any contact for two weeks. The type of contact matters, too: a short, outdoor meeting or one with masks on is safer than a prolonged indoor, no-mask meeting.
Vaccine effectiveness
Another reader asked:
Is there any information on the effectiveness of the latest vaccines, including vaccines that combine Covid and RSV, and are there similarities between these viruses (related?)
As we head into respiratory virus season in the U.S., there will be, for the first time, vaccines available for all three major diseases: COVID-19, the flu, and RSV. I’ll talk about effectiveness for each one separately, because they are all separate vaccines for separate viruses. There’s no combined COVID-RSV vaccine on the market.
COVID-19: We know the fall boosters will target XBB.1.5, a variant that has dominated COVID-19 spread in the U.S. recently. There isn’t much data available on these vaccines yet, because the companies developing them (Pfizer, Moderna, Novavax) have yet to present about their boosters to the FDA and CDC, as is the typical process. The CDC’s vaccine advisory committee is meeting this coming Tuesday to talk fall vaccines, though, so it’s likely we will see some data from that meeting.
Also worth noting: some early laboratory studies suggest that vaccines based on XBB.1.5 will provide good protection against BA.2.86, despite concerns about differences between these variants. (More on this later in today’s issue.)
Flu: Every year, scientists and health officials work together to update flu vaccines based on the influenza strains that are circulating around the world. Effectiveness can vary from year to year, depending on how well the shots match circulating strains.
This week, we got a promising update about the 2023 flu vaccines: CDC scientists and colleagues studied how well these shots worked in the Southern Hemisphere, which has its flu season before the Northern Hemisphere. The vaccine reduced patients’ risk of flu-related hospitalization by 52%, based on data from several South American countries that participate in flu surveillance. This is pretty good by flu vaccine standards; see more context about the study in this article from TIME.
RSV: There are two new RSV vaccines that will be available this fall, both authorized by the FDA and CDC in recent months. These vaccines—one produced by Pfizer, one by GSK—both did well in clinical trials, reducing participants’ risks of severe RSV symptoms by about 90% (for the first year after infection, with effectiveness declining over time).
Both vaccines were authorized specifically for older adults, and Pfizer’s was also authorized for pregnant people as a protective measure for their newborns. We’ll get more data about these vaccines as the respiratory virus season progresses, but for now, experts are recommending that eligible adults do get the shots. This article from Yale Medicine goes into more details.
Nasal sprays as COVID-19 protection
Another reader asked:
I’m thinking of researching what foods and supplement are anti-viral anti-COVID. I’m wondering if anyone has done any research on that?
I haven’t seen too much research on about foods and supplements, since dietary options are usually not considered medical products for study. Generally, having a healthy diet can be considered helpful for reducing risk from many health conditions, but it’s not something to rely on as a precaution in the same way as you might rely on masking or cleaning air.
Another thing you might try, though, would be nasal sprays to boost the immune system. I have yet to try these myself, but have seen them recommended on COVID-19 Safety Twitter and by cautious friends. The basic idea of these nasal sprays is to kill viruses in one’s upper respiratory tract, essentially blocking any coronavirus that might be present from spreading further. People take these sprays as a preventative measure before potential exposures.
A couple of references on nasal sprays:
- Does nitric oxide nasal spray (Enovid/VirX/FabiSpray) help prevent or treat COVID-19? (Those Nerdy Girls)
- As COVID market narrows, SaNOtize moves to carve a new one: over-the-counter prevention (Fierce Biotech)
- Clinical efficacy of nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) for the treatment of mild COVID-19 infection (Scientific paper in The Journal of Infection)
-
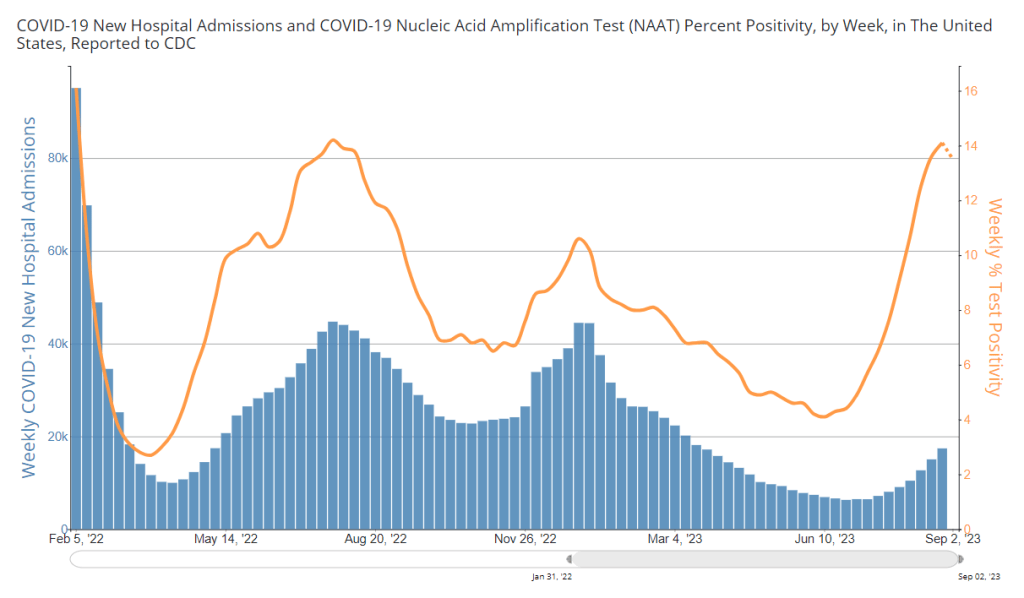
National numbers, September 10
COVID-19 test positivity and viral levels in wastewater may be turning around, but hospitalizations are still going up. Chart from the CDC, data as of September 7. During the most recent week of data available (August 20-26), the U.S. reported about 17,400 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 2,500 new admissions each day
- 5.3 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 16% more new admissions than the prior week (August 13-19)
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 13.5% of tests in the CDC’s surveillance network came back positive
- A 0.3% higher concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater than last week (as of September 6, per Biobot’s dashboard)
- 23% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.6; 22% by EG.5; 15% by FL.1.5.1 (as of September 2)
After two months of consistent increases in major COVID-19 metrics, we have once again reached, “Has the surge peaked?” territory. Preliminary data from wastewater and testing are suggesting potential plateaus, while more people are still getting hospitalized with COVID-19.
National trends from Biobot Analytics’ wastewater surveillance network show very similar coronavirus levels in sewage this week and last week: 641 virus copies per milliliter of sewage on September 6, compared to 639 on August 30. These data are preliminary, though, and could change as more sewersheds report.
Biobot’s regional data suggest different trends in different parts of the country: the South and West coast might be turning around, the Northeast is still reporting an increase (but the speed of increase there is slowing), and the Midwest is reporting a sharp increase following a recent decrease.
Data from the CDC network and WastewaterSCAN similarly show mixed results depending on your location. Among CDC sites with recent data, about half reported increased coronavirus in their wastewater in the last two weeks, while the other half reported decreases. WastewaterSCAN’s network reports continued increases in Midwestern states, including sewersheds in Michigan, Ohio, and Kansas.
Test positivity data from the CDC’s respiratory surveillance network also indicate that the summer surge might have peaked, or at least might be slowing. For the first time in several weeks, test positivity decreased slightly in the most recent CDC update, from 14.1% in the week ending August 26 to 13.5% in the week ending September 2.
Walgreens’ COVID-19 positivity tracker (which shares data from tests conducted by the pharmacy network) reported a slight decrease as well, from 43.6% in the week ending August 26 to 40.6% in the week ending September 2. Like the wastewater surveillance data, this information is preliminary but could be a good sign.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 hospitalizations—a more delayed metric—are still increasing. About 2,500 people were newly hospitalized with COVID-19 each day in the week ending August 26. Hospitalizations have particularly gone up for older adults, according to data from insurance company Humana shared with STAT News.
Many students went back to school last week, as the fall semester gets underway. This could be another driver of COVID-19 spread, as travel and gatherings were in the summer. Better air quality, masks, and other measures could make schools safer for students, teachers, staff, and their families.
-
COVID source shout-out: People’s CDC in-person gathering guide
The People’s CDC, a public health advocacy organization that seeks to provide COVID-19 communication and guidance where the federal CDC has failed, recently shared an update to its guide for safer in-person gatherings.
The organization shared an updated, abbreviated version of the guide on its Substack this weekend, in advance of a more detailed update in the works for its web toolkit. This guide walks readers through ways that they can organize gatherings with lower COVID-19 risk, including actions to take before, during, and after an event. It’s written in accessible language and cites scientific sources.
I am a big fan of the People’s CDC (frequently citing their work in this newsletter and freelance articles), and this guide is one of my favorite resources they’ve developed. If you’re hosting an event, traveling, or taking part in any other kind of in-person gathering this weekend, I recommend checking out their guidance.
-
Sources and updates, September 3
- CDC respiratory virus updates: The CDC has a new webpage dedicated to “updates on the respiratory illness season.” So far, it just includes summaries of the agency’s two reports on new variant BA.2.86. Going forward, the page will be updated weekly with further information on COVID-19, flu, RSV, and other viruses spreading this fall and winter.
- Potential biomarker for Long COVID brain fog: A new paper, published this week in Nature by a coalition of researchers in the U.K., connects blood clot issues during acute COVID-19 to cognitive symptoms later on. The researchers found that some patients had low levels of two specific proteins connected to blood clots, based on blood samples taken early in their infections; the same patients were likely to experience brain fog and similar symptoms. If these results are replicated in other studies, the proteins could be used as biomarkers (i.e. medical indicators) of Long COVID symptoms, potentially a big step for research and treatments.
- Long COVID research presented at Keystone Symposia event: Speaking of Long COVID research: scientists gathered to discuss this condition at a conference last week in New Mexico. The conference was hosted by Keystone Symposia, an organization that convenes meetings on important life sciences topics. Highlights from the event included a presentation showing changes to muscle tissue during post-exertional malaise, along with presentations from the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, the National Institutes of Health, Resia Pretorius from Stellenbosch University in South Africa, Akiko Iwasaki from Yale University, and more. I look forward to seeing papers expanding on the talks that occurred at this meeting.
- COVID-19’s impact on Native Americans: Another notable paper from this week examined COVID-19’s disproportionate impacts on Native Americans in New Mexico. Researchers at the University of New Mexico Hospital analyzed patient outcomes in early pandemic waves, from spring 2020 through winter 2021. Compared to white and Hispanic patients, Native Americans were more likely to experience severe COVID-19 outcomes such as more time spent in the hospital and going on a ventilator. “Self-reported AI/AN race/ethnicity emerged as the highest risk factor for severe COVID-19,” the researchers reported, suggesting that this vulnerable group of people deserves additional safety resources.
- COVID-19 burden for cancer patients: One more study to highlight: researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital examined COVID-19 mortality among cancer patients during the first two years of the pandemic, using data from the CDC. People with cancer were more likely to die of COVID-19 during the winter Omicron wave in 2021-2022, compared to the surge during the prior winter (with 18% higher deaths). Meanwhile, deaths among the general population went down from the first to the second winters. Like the study above, this paper suggests that greater protections are needed for vulnerable people during times of high COVID-19 spread. (For example: we could keep masks in healthcare settings!)
-
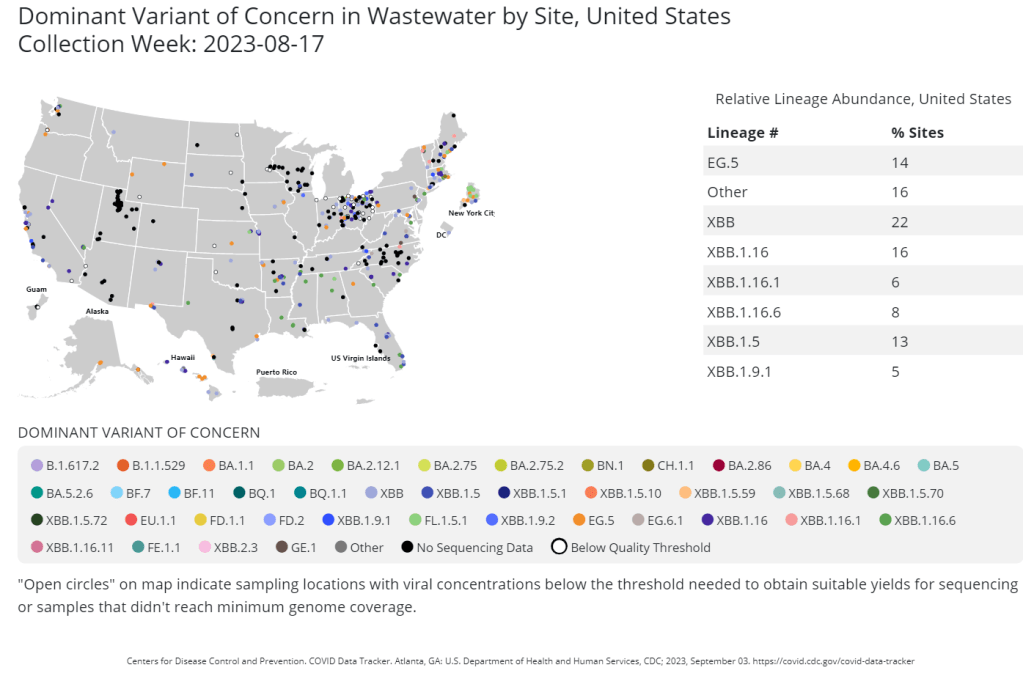
Wastewater surveillance is crucial for tracking new variants, BA.2.86 shows us
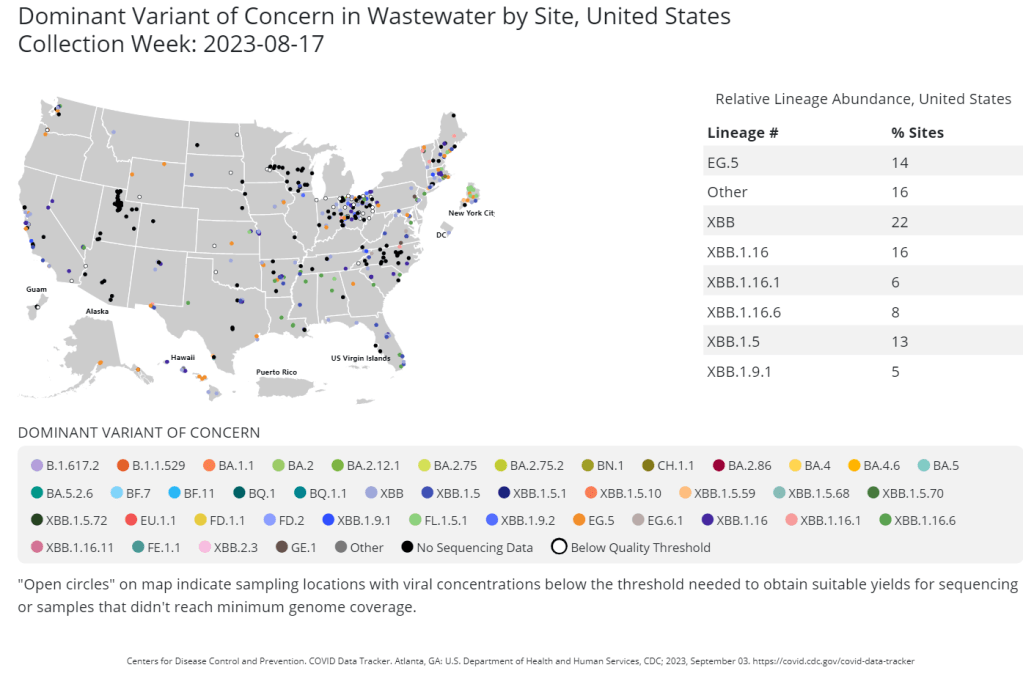
The CDC publishes data from about 400 wastewater testing sites that are sequencing their samples. Chart shows data from the week of August 17. This week, the health department in New York City, where I live, announced that they’d identified new variant BA.2.86 in the city’s wastewater. (For more details about BA.2.86, see last week’s Q&A post.)
I covered the news for local outlet Gothamist/WNYC, and the story got me thinking about how important wastewater surveillance has become for tracking variants. With less clinical testing, sewage is now a crucial source for understanding how the coronavirus is mutating and what impacts those mutations have. But there are continued barriers to obtaining and interpreting wastewater data.
Quoting from the story:
The declaration of the end of the public health emergency in May made COVID-19 tests less available in health care settings, and sewage monitoring has since emerged as an important way to identify new variants.
“As the wastewater testing has gotten better, the patient surveillance has decreased,” [said Marc Johnson, a virologist at the University of Missouri]. Several variants have been found in sewage before cases were confirmed, he said.
That list now includes BA.2.86, in New York City as well as Ohio and other countries. The CDC publishes variant data from about 400 wastewater testing sites, including the city’s.
But wastewater data from New York City is reported unevenly, with significant delays between when samples are collected and when data is published on dashboards run by the CDC and New York state.
Wastewater surveillance has some distinct advantages, when it comes to variant monitoring:
- It covers thousands of people—the entire population of a sewershed—with one sample. In big cities like NYC, one sample can include data from more than one million residents.
- Through sewage samples, scientists can look for multiple variants at once, rather than compiling data over many PCR test results. They can also track population-level trends over time.
- Unlike traditional case data, wastewater data don’t rely on how many people are getting tested or where. This lack of testing bias is important, as people typically use rapid tests—which are not reported to health systems—over PCR these days (rapid tests are easier to access, PCR sites have closed following the end of the federal public health emergency, etc.).
But there are also some problems, as the NYC detection this week demonstrated:
- Public health officials are still getting used to using and sharing wastewater data, as this is a relatively novel source with novel pipelines for transmitting data. While the CDC and other organizations are working to compile these data in a standardized way, it’s still a work in progress.
- Discrepancies and delays can sometimes occur as a result. For example, in New York, the governor’s office put out a press release on Tuesday morning claiming that BA.2.86 hadn’t been detected in the state yet—then, just hours later, the city health department announced they’d found it. State health officials weren’t aware of the detection before the city made its public announcement, I learned for my news story.
- Health officials are also still learning how to interpret and act on wastewater data. The NYC health department failed to answer my questions about in which sewershed or from which sampling date they found BA.2.86; it’s unclear if they’re using the detection to take any specific actions, besides simply warning the public that this variant is present.
- As wastewater surveillance captures such broad samples, it’s difficult to tie new variant detections to clinical data, such as whether an infected person went to the hospital due to their symptoms. Officials can’t contact trace from these detections, making it hard to answer questions like whether BA.2.86 causes more severe symptoms.
For more reading on this topic, I recommend my feature for Gothamist/WNYC and MuckRock last fall about NYC’s wastewater surveillance program, as well as other past posts at the COVID-19 Data Dispatch.
More about wastewater surveillance
-
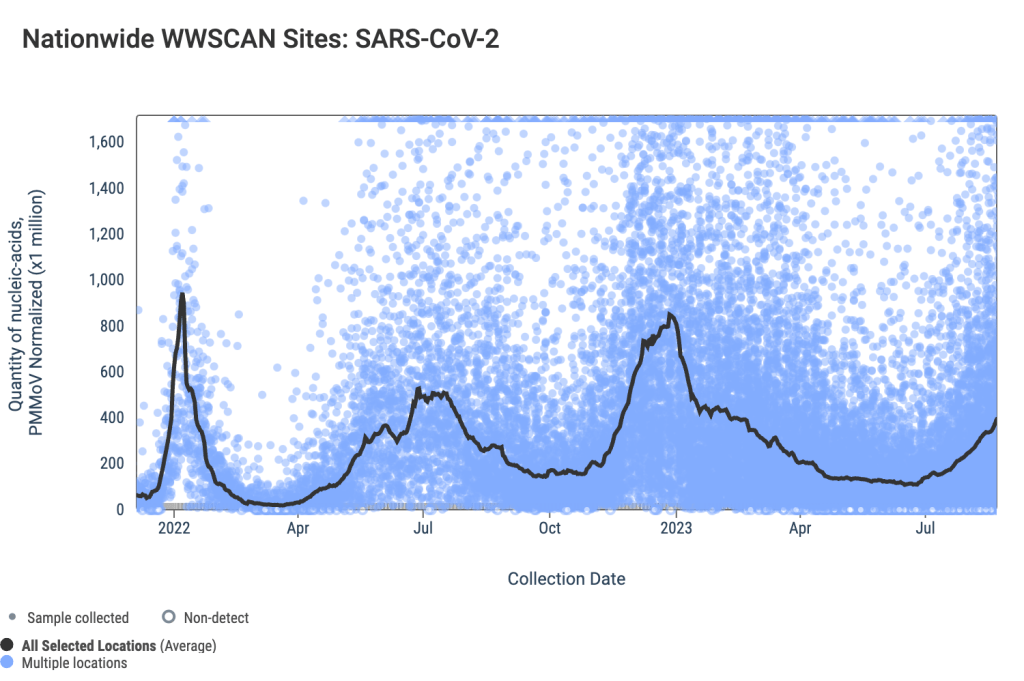
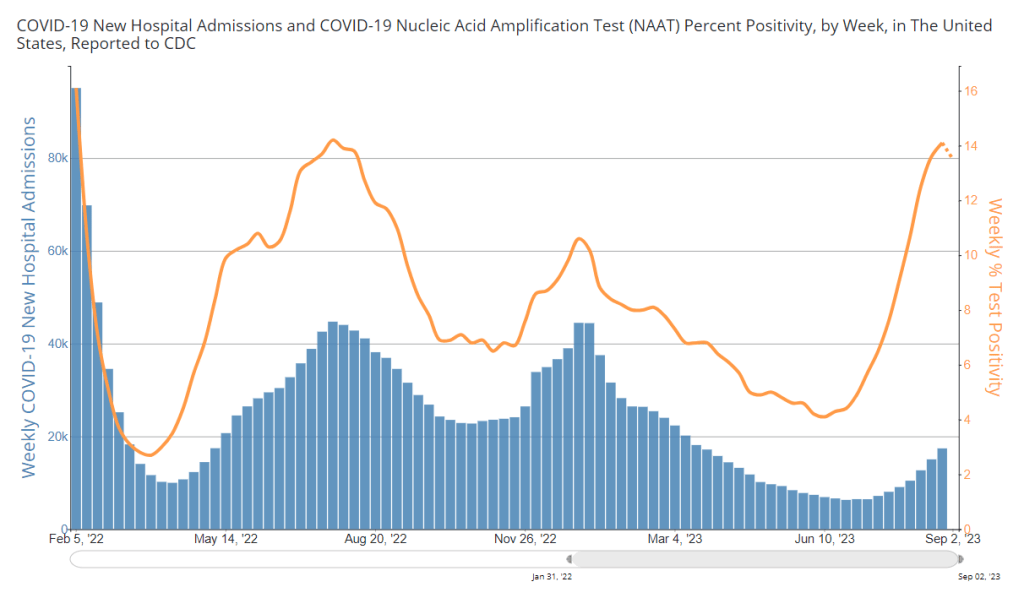
National numbers, September 3
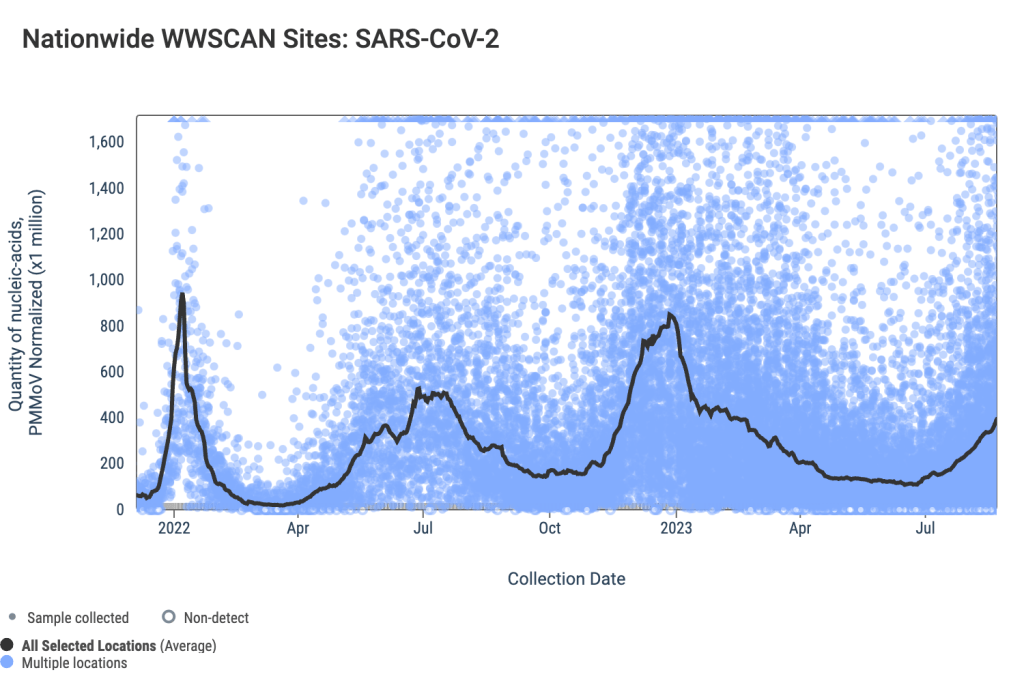
COVID-19 data from WastewaterSCAN suggest that coronavirus spread is still trending up nationwide. During the most recent week of data available (August 13-19), the U.S. reported about 15,100 new COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals, according to the CDC. This amounts to:
- An average of 2,200 new admissions each day
- 4.6 total admissions for every 100,000 Americans
- 19% more new admissions than the prior week (August 6-12)
Additionally, the U.S. reported:
- 14.9% of tests in the CDC’s surveillance network came back positive
- A 3% higher concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater than last week (as of August 30, per Biobot’s dashboard)
- 23% of new cases are caused by Omicron XBB.1.6; 22% by EG.5; 15% by FL.1.5.1 (as of September 2)
The late-summer COVID-19 surge is still in full swing, with all major metrics showing further increases in disease spread this week. BA.2.86 isn’t spreading widely yet but is worth continued surveillance.
Last week, I wrote that wastewater data from Biobot Analytics showed a potential plateau—but cautioned those data were tentative. Unfortunately, further updates this week suggest that COVID-19 transmission is still increasing, albeit not as dramatically as it was in July.
Data from WastewaterSCAN show a similar pattern: a sharp increase in COVID-19 spread from late June through July, followed by a slight leveling off, and then followed by further increase. This could be caused by a newer variant entering the picture, driven by behaviors, or (most likely) some combination of the two.
Regional data from both Biobot and WastewaterSCAN indicate that COVID-19 transmission might be approaching plateaus in the South and Midwest, but is going up sharply in the Northeast and West coast. The Midwest, after showing decreases in Biobot’s data over recent weeks, is now trending up again.
The CDC’s test positivity and hospitalization numbers continue to rise as well. New hospital admissions for COVID-19 reached 2,000 per day during the week ending August 19, and are likely still higher now. Test positivity is up to 15%, the highest this metric has been since last winter’s holiday surge.
In the CDC’s latest variant estimates (posted on Saturday), EG.5 and XBB.1.6 continue to dominate in a crowded landscape of Omicron XBB relatives. The agency hasn’t yet found enough BA.2.86 for this new variant to be included in the update. However, this could indicate low testing rather than an actual low prevalence of BA.2.86.
The CDC often takes COVID-19 reporting breaks over holiday weekends, and this one is no exception: the agency will not update its dashboard on Monday, according to a note posted at the top of the page. Hospitalizations, test positivity, and other metrics will be updated later in the week.
Of course, the coronavirus doesn’t care about holidays—in fact, it usually spreads more widely when people travel and gather. Fully understanding this Labor Day weekend’s impact could take several weeks, at our current pace of data reporting.
-
COVID source callout: CDC infection control committee may roll back protections
A little-known CDC advisory committee is suddenly in the public spotlight, as it considers recommending fewer safety measures to reduce infection in hospitals and other healthcare settings. Despite major pushback at a recent meeting, it’s unclear whether this committee will actually live up to its infection control duties.
The Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, or HICPAC, is a group of experts that advises the CDC on infectious disease safety measures in healthcare settings. It develops guidance that is rigorously followed across U.S. facilities, and the guidance is due for an update this year—for the first time since COVID-19 hit.
In the last three years, healthcare and public health workers have learned a lot about the importance of masks and clean air for reducing respiratory disease risk. You might think that HICPAC would acknowledge this in its updated guidance, calling for hospitals to use high-quality masks and ventilation. Instead, however, HICPAC’s guidance disregards the last three years of airborne virus research, suggesting for example that N95s aren’t more protective than surgical masks and that masking is only needed when a disease is spreading very widely.
These guidelines could have massive implications for the healthcare system. Many high-risk people are already hesitant to go to the doctor, in a time when mask requirements in these settings have largely been lifted. COVID-19 is spreading widely in these settings, limited data suggest. The new guidelines, if adopted, would extend the current COVID-19 “normal” to many other diseases, from seasonal flu to new viruses that may emerge.
Naturally, a coalition of better-informed individuals and organizations (healthcare workers, scientists, patients, etc.) are pushing back against HICPAC. At a public meeting this past Tuesday, many attendees spoke against the guidance change, citing health research as well as their own experiences in the last three years. The committee failed to meaningfully acknowledge this criticism; in fact, it cut off the public comment period after just 40 minutes, leaving many attendees unable to share their feedback.
Transparency concerns about HICPAC—which doesn’t usually share public updates or livestream its meetings—add to concerns about the committee’s guidance decisions. But the pressure is on for HICPAC to respond to its critics, improve its new guidance, and live up to its title.
Further reading and how to get involved: